Business Modelling: - tud.ttu.ee
Business Modelling: - tud.ttu.ee
Business Modelling: - tud.ttu.ee
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
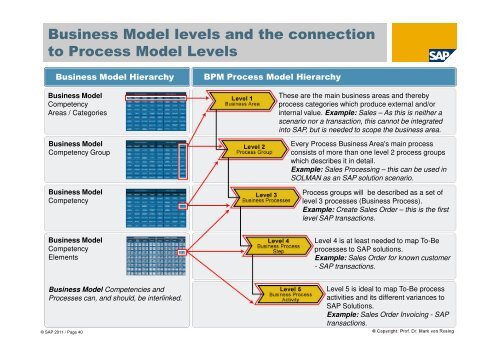
<strong>Business</strong> Model levels and the connectionto Process Model Levels<strong>Business</strong> Model Hierarchy<strong>Business</strong> ModelCompetencyAreas / Categories<strong>Business</strong> ModelCompetency Group<strong>Business</strong> ModelCompetencyBPM Process Model HierarchyThese are the main business areas and therebyprocess categories which produce external and/orinternal value. Example: Sales – As this is neither ascenario nor a transaction, this cannot be integratedinto SAP, but is n<strong>ee</strong>ded to scope the business area.Every Process <strong>Business</strong> Area's main processconsists of more than one level 2 process groupswhich describes it in detail.Example: Sales Processing – this can be used inSOLMAN as an SAP solution scenario.Process groups will be described as a set oflevel 3 processes (<strong>Business</strong> Process).Example: Create Sales Order – this is the firstlevel SAP transactions.<strong>Business</strong> ModelCompetencyElementsLevel 4 is at least n<strong>ee</strong>ded to map To-Beprocesses to SAP solutions.Example: Sales Order for known customer- SAP transactions.<strong>Business</strong> Model Competencies andProcesses can, and should, be interlinked.© SAP 2011 / Page 40Level 5 is ideal to map To-Be processactivities and its different variances toSAP Solutions.Example: Sales Order Invoicing - SAPtransactions.



![[ ] rad - tud.ttu.ee](https://img.yumpu.com/51069910/1/184x260/-rad-tudttuee.jpg?quality=85)