- Page 3 and 4:
POCKETNOTEBOOKPocketMEDICINEFourth
- Page 5 and 6:
Contributing AuthorsForewordPreface
- Page 7 and 8:
HIV/AIDS 6-17Tick-Borne Diseases 6-
- Page 9 and 10:
Rajat Gupta, MDInternal Medicine Re
- Page 11 and 12:
FOREWORDTo the 1st EditionIt is wit
- Page 13 and 14:
ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHYApproach (a syst
- Page 15 and 16:
CHEST PAINDisorderUnstableanginaMIP
- Page 17 and 18:
CORONARY ANGIOGRAPHY AND REVASCULAR
- Page 19 and 20:
Likelihood of ACSFeature High Inter
- Page 21 and 22:
STEMIReperfusion• Immediate reper
- Page 23 and 24:
• VT/VF: lido or amio 6-24 h, th
- Page 25 and 26:
PA Catheter WaveformsLocation RA RV
- Page 27 and 28:
Evaluation of the causes of heart f
- Page 29 and 30:
CARDIOMYOPATHIESDiseases with mecha
- Page 31 and 32:
RESTRICTIVE CARDIOMYOPATHY (RCMP)De
- Page 33 and 34:
AORTIC INSUFFICIENCY (AI)Etiology (
- Page 35 and 36:
Clinical manifestations (Lancet 200
- Page 37 and 38:
PERICARDIAL DISEASEGENERAL PRINCIPL
- Page 39 and 40:
CONSTRICTIVE PERICARDITISEtiology
- Page 41 and 42:
• Pharmacologic options (if HTN o
- Page 43 and 44:
ACUTE AORTIC SYNDROMESDefinitions (
- Page 45 and 46:
OnsetRateRhythmP wavemorphologyResp
- Page 47 and 48:
ATRIAL FIBRILLATIONClassification (
- Page 49 and 50:
SYNCOPEDefinition• Symptom of sud
- Page 51 and 52:
INTRACARDIAC DEVICESPacemaker CodeA
- Page 53 and 54:
Pre-operative testing and therapy
- Page 55 and 56:
DYSPNEAPathophysiologyEtiologiesAir
- Page 57 and 58:
Other• Behavior modification: ide
- Page 59 and 60:
CHRONIC OBSTRUCTIVE PULMONARY DISEA
- Page 61 and 62:
HEMOPTYSISDefinition and pathophysi
- Page 63 and 64:
INTERSTITIAL LUNG DISEASEWORKUP OF
- Page 65 and 66:
PLEURAL EFFUSIONPathophysiology•
- Page 67 and 68:
VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM (VTE)Definit
- Page 69 and 70:
Risk stratification for Pts with PE
- Page 71 and 72:
• SupportiveOxygen: maintain S aO
- Page 73 and 74:
MECHANICAL VENTILATIONIndications
- Page 75 and 76:
Tailoring the ventilator settings
- Page 77 and 78:
SEPSISDefinitionsSystemic2 or more
- Page 79 and 80:
ESOPHAGEAL AND GASTRIC DISORDERSDYS
- Page 81 and 82:
GASTROINTESTINAL BLEEDINGDefinition
- Page 83 and 84:
DIARRHEA, CONSTIPATION, AND ILEUSAC
- Page 85 and 86:
Dx: IgA antitissue transglutaminase
- Page 87 and 88:
DIVERTICULAR DISEASEDIVERTICULOSISD
- Page 89 and 90:
MANAGEMENT (Lancet 2007;369:1641 &
- Page 91 and 92:
PANCREATITISPathogenesis• Acinar
- Page 93 and 94:
ABNORMAL LIVER TESTSTests of hepato
- Page 95 and 96:
HEPATITISVIRALHepatitis A (ssRNA; a
- Page 97 and 98:
AUTOIMMUNE HEPATITIS (AIH)Classific
- Page 99 and 100:
CIRRHOSISDefinition (Lancet 2008;37
- Page 101 and 102:
PrognosisModified Child-Turcotte-Pu
- Page 103 and 104:
HEPATIC VASCULAR DISEASEPortal vein
- Page 105 and 106:
BILIARY TRACT DISEASECHOLELITHIASIS
- Page 107 and 108:
ACID-BASE DISTURBANCESGENERALDefini
- Page 109 and 110:
Workup for AG metabolic acidosis•
- Page 111 and 112:
Etiologies of Metabolic AlkalosisSa
- Page 113 and 114:
Hypovolemic hypotonic hyponatremia
- Page 115 and 116:
POLYURIADefinition and pathophysiol
- Page 117 and 118:
Treatment• If true potassium defi
- Page 119 and 120:
Treatment• Treat underlying disor
- Page 121 and 122:
DIALYSISGeneral• Substitutes for
- Page 123 and 124:
Treatment• ANCA or anti-GBM: ste
- Page 125 and 126:
HEMATURIAEtiologies of HematuriaExt
- Page 127 and 128:
ANEMIAT in RBC mass: Hct 41% or Hb
- Page 129 and 130:
MACROCYTIC ANEMIASincludes megalobl
- Page 131 and 132:
• Infection: splenic infarction S
- Page 133 and 134:
PLATELET DISORDERSTHROMBOCYTOPENIA
- Page 135 and 136:
• Treatment of type II (NEJM 2006
- Page 137 and 138:
HYPERCOAGULABLE STATESSuspect in Pt
- Page 139 and 140: TRANSFUSION THERAPYPacked red blood
- Page 141 and 142: MYELOPROLIFERATIVE NEOPLASMS (MPN)G
- Page 143 and 144: LEUKEMIAACUTE LEUKEMIADefinition•
- Page 145 and 146: Prognosis• CR achieved in 80% of
- Page 147 and 148: LYMPHOMADefinition• Malignant dis
- Page 149 and 150: Consider CNS prophylaxis w/ intrath
- Page 151 and 152: Treatment (NEJM 2004;351:1860; Lanc
- Page 153 and 154: • Sinusoidal obstruction syndrome
- Page 155 and 156: TNM Staging System for NSCLCN stage
- Page 157 and 158: Simplified Staging System for Breas
- Page 159 and 160: COLORECTAL CANCER (CRC)Epidemiology
- Page 161 and 162: PANCREATIC TUMORSPathology and gene
- Page 163 and 164: • Prostate, breast, and lung canc
- Page 165 and 166: PNEUMONIAMicrobiology of PneumoniaC
- Page 167 and 168: FUNGAL INFECTIONSCandida species•
- Page 169 and 170: URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS (UTI)Defin
- Page 171 and 172: Diagnostic studies• Superficial s
- Page 173 and 174: INFECTIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEMACU
- Page 175 and 176: VIRAL ENCEPHALITISDefinition• Vir
- Page 177 and 178: Diagnostic studies• Blood culture
- Page 179 and 180: TUBERCULOSISEpidemiology• U.S.: 1
- Page 181 and 182: HIV/AIDSDefinition• AIDS: HIV CD
- Page 183 and 184: Cutaneous• Seborrheic dermatitis;
- Page 185 and 186: TICK-BORNE DISEASESDistinguishing F
- Page 187 and 188: FEVER OF UNKNOWN ORIGIN (FUO)Defini
- Page 189: PITUITARY DISORDERSHYPOPITUITARY SY
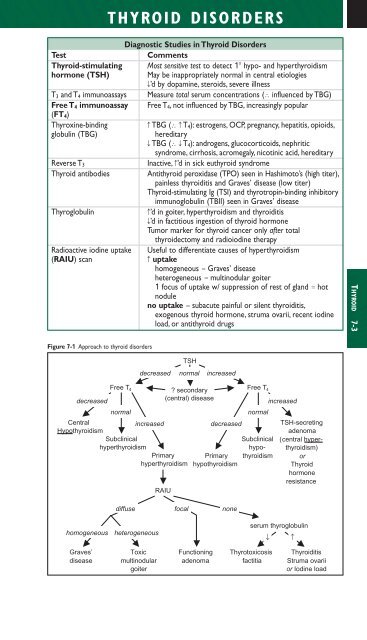
- Page 193 and 194: Clinical manifestations of hyperthy
- Page 195 and 196: ADRENAL DISORDERSCushing’s Syndro
- Page 197 and 198: Treatment• Adenoma or carcinoma S
- Page 199 and 200: CALCIUM DISORDERSLaboratory Finding
- Page 201 and 202: DIABETES MELLITUSDefinition (Diabet
- Page 203 and 204: Typical DKA “Flow sheet” SetupV
- Page 205 and 206: ARTHRITIS—OVERVIEWApproach to pat
- Page 207 and 208: RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS (RA)Definition
- Page 209 and 210: CRYSTAL DEPOSITION ARTHRITIDESGOUTD
- Page 211 and 212: SERONEGATIVE SPONDYLOARTHRITISGENER
- Page 213 and 214: INFECTIOUS ARTHRITIS & BURSITISDIAG
- Page 215 and 216: CONNECTIVE TISSUE DISEASES% Autoant
- Page 217 and 218: Clinical manifestations• Muscle w
- Page 219 and 220: SYSTEMIC LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS (SLE)M
- Page 221 and 222: VASCULITISLARGE-VESSEL VASCULITISTa
- Page 223 and 224: Maintenance: MTX or AZA for 2 yfor
- Page 225 and 226: CRYOGLOBULINEMIADefinition & Types
- Page 227 and 228: CHANGE IN MENTAL STATUSDefinitions
- Page 229 and 230: SEIZURESDefinitions (NEJM 2003;349:
- Page 231 and 232: ALCOHOL WITHDRAWALPathophysiology
- Page 233 and 234: Treatment of ischemic stroke (NEJM
- Page 235 and 236: MYASTHENIA GRAVISDefinition and epi
- Page 237 and 238: BACK AND SPINAL CORD DISEASEDdx of
- Page 239 and 240: ACLS ALGORITHMSFigure 10-1 ACLS VF/
- Page 241 and 242:
Figure 10-3 ACLS bradycardia algori
- Page 243 and 244:
DrugClassDoseper kgaverageSedationM
- Page 245 and 246:
FORMULAE AND QUICK REFERENCECARDIOL
- Page 247 and 248:
P KUOsmFigure 10-5 Acetaminophen to
- Page 249 and 250:
Warfarin-heparin overlap therapy•
- Page 251 and 252:
5-NT6-MPa/wAAAAADAbABEABGabnlABPAab
- Page 253 and 254:
FRCFSGSFSHFTIFUOFVCG6PDGBGBMGBSGCAG
- Page 255 and 256:
PIDPIFPIPPKDPMPMFPMHxPMIPMLPMNPMVPM
- Page 257 and 258:
AA-a gradient, 2-18, 10-8abdominal
- Page 259 and 260:
Ddactylitis, 8-7decerebrate posturi
- Page 261 and 262:
Liddle’s syndrome, 4-5, 4-10, 7-8
- Page 263 and 264:
shock, 1-13, 10-4cardiogenic, 1-13s
- Page 265 and 266:
NOTES
- Page 267 and 268:
RadiologyPHOTO INSERT P-11 Normal P
- Page 269 and 270:
PHOTO INSERT P-37 Right middle lobe
- Page 271 and 272:
13 Normal chest CT at level of pulm
- Page 273 and 274:
17 Normal abdomen CT at level of li
- Page 275 and 276:
EchocardiographyVentricular septumR
- Page 277 and 278:
Anterolateralfree wallLeft ventricl
- Page 279 and 280:
Coronary Angiography3LEFT CORONARY
- Page 281:
PHOTO INSERT P-153 CML. 4 CLL.All p