- Page 2 and 3:
Acute Aortic Disease
- Page 4 and 5:
15. Heart Failure: Basic Science an
- Page 6:
52. Clinical, Interventional, and I
- Page 9 and 10:
Informa Healthcare USA, Inc. 270 Ma
- Page 12 and 13:
Introduction Informa Healthcare has
- Page 14 and 15:
Foreword There is no disease more c
- Page 16 and 17:
Preface Over 100 years ago, the gre
- Page 18:
Preface xi Some distinguishing feat
- Page 21 and 22:
xiv Acknowledgments Above all, than
- Page 23 and 24:
xvi Contents 6. Genetic Basis of Th
- Page 26 and 27:
Contributors Nili Avidan Division o
- Page 28:
Contributors xxi Arun Raghupathy Di
- Page 31 and 32:
2 Nienaber and Ince Table 1 Risk Co
- Page 33 and 34:
4 Nienaber and Ince In addition to
- Page 35 and 36:
6 Nienaber and Ince CLASSIFICATION
- Page 37 and 38:
8 Nienaber and Ince Lansman’s Cla
- Page 39 and 40:
10 Nienaber and Ince Figure 4 Curve
- Page 41 and 42:
12 Nienaber and Ince Figure 6 Evolu
- Page 43 and 44:
14 Nienaber and Ince dissection, su
- Page 45 and 46:
16 Nienaber and Ince (A) (B) Probab
- Page 47 and 48:
18 Nienaber and Ince Table 5 Risk P
- Page 49 and 50:
20 Nienaber and Ince of the predila
- Page 51 and 52:
22 Nienaber and Ince 34. Pieters FA
- Page 53 and 54:
24 Nienaber and Ince 75. Mehta RH,
- Page 55 and 56:
26 Nienaber and Ince hematoma (IMH)
- Page 57 and 58:
28 Nienaber and Ince One good featu
- Page 59 and 60:
30 Isselbacher SYMPTOMS Pain Experi
- Page 61 and 62:
32 Isselbacher and wane in severity
- Page 63 and 64:
34 Isselbacher The mechanisms are u
- Page 65 and 66:
36 Isselbacher deficits are most co
- Page 67 and 68:
38 Isselbacher 3. Nallamothu BK, Me
- Page 69 and 70:
40 Danias spinal arteries) and the
- Page 71 and 72:
42 Danias Figure 2 Anteroposterior
- Page 73 and 74:
44 Danias However, due to the dista
- Page 75 and 76:
46 Danias TEE is highly sensitive f
- Page 77 and 78:
48 Danias faster, with higher resol
- Page 79 and 80:
50 Danias Figure 6 Transverse slice
- Page 81 and 82:
52 Danias hematoma, CT was reported
- Page 83 and 84: 54 Danias Figure 9 Transverse black
- Page 85 and 86: 56 Danias Figure 12 Single phase-co
- Page 87 and 88: 58 Danias restricted to the absolut
- Page 89 and 90: 60 Danias In conclusion, in the rig
- Page 91 and 92: 62 Danias DISCUSSION AND COMMENTARY
- Page 93 and 94: 64 Danias tomography, among others.
- Page 95 and 96: 66 Danias cardiac silhouette. The a
- Page 97 and 98: 68 Raghupathy and Eagle the inciden
- Page 99 and 100: 70 Raghupathy and Eagle Figure 1 Sp
- Page 101 and 102: 72 Raghupathy and Eagle SIGNS A tho
- Page 103 and 104: 74 Raghupathy and Eagle patients ma
- Page 105 and 106: 76 Raghupathy and Eagle Table 5 Dia
- Page 107 and 108: 78 Raghupathy and Eagle Table 6 A S
- Page 109 and 110: 80 Raghupathy and Eagle Figure 6 (A
- Page 111 and 112: 82 Raghupathy and Eagle Figure 9 (A
- Page 113 and 114: 84 Raghupathy and Eagle EDITOR’S
- Page 115 and 116: 86 Raghupathy and Eagle 30. Erbel R
- Page 117 and 118: 88 Raghupathy and Eagle is highly l
- Page 119 and 120: 90 Elefteriades and Rizzo required
- Page 121 and 122: 92 Elefteriades and Rizzo Table 1 S
- Page 123 and 124: 94 Elefteriades and Rizzo 70s, this
- Page 125 and 126: 96 Elefteriades and Rizzo Table 3 C
- Page 127 and 128: 98 Elefteriades and Rizzo DISCUSSIO
- Page 129 and 130: 100 Milewicz et al. KNOWN GENETIC S
- Page 131 and 132: 102 Milewicz et al. Table 2 Quick G
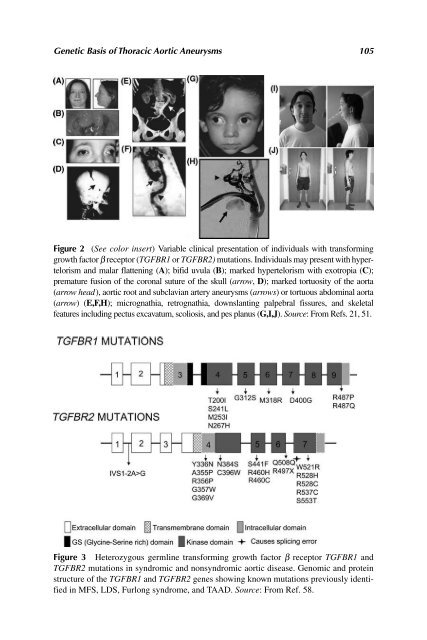
- Page 133: 104 Milewicz et al. ascending aorti
- Page 137 and 138: 108 Milewicz et al. dissection in t
- Page 139 and 140: 110 Milewicz et al. Figure 5 Haplot
- Page 141 and 142: 112 Milewicz et al. A genome wide s
- Page 143 and 144: 114 Milewicz et al. Structural anal
- Page 145 and 146: 116 Milewicz et al. assembly of a h
- Page 147 and 148: 118 Milewicz et al. in the nuclei o
- Page 149 and 150: 120 Milewicz et al. 22. Furlong J,
- Page 151 and 152: 122 Milewicz et al. DISCUSSION AND
- Page 153 and 154: 124 Milewicz et al. Figure A Distri
- Page 155 and 156: 126 Elefteriades and Koullias Figur
- Page 157 and 158: 128 Elefteriades and Koullias prope
- Page 160 and 161: 8 Matrix Metalloproteinases in Aort
- Page 162 and 163: Matrix Metalloproteinases in Aortic
- Page 164 and 165: Matrix Metalloproteinases in Aortic
- Page 166 and 167: Matrix Metalloproteinases in Aortic
- Page 168 and 169: Matrix Metalloproteinases in Aortic
- Page 170 and 171: Matrix Metalloproteinases in Aortic
- Page 172 and 173: Matrix Metalloproteinases in Aortic
- Page 174 and 175: Matrix Metalloproteinases in Aortic
- Page 176 and 177: INTRODUCTION 9 Inflammation and Rem
- Page 178 and 179: Inflammation and Remodeling in the
- Page 180 and 181: Inflammation and Remodeling in the
- Page 182 and 183: Inflammation and Remodeling in the
- Page 184 and 185:
Inflammation and Remodeling in the
- Page 186 and 187:
Inflammation and Remodeling in the
- Page 188 and 189:
Inflammation and Remodeling in the
- Page 190 and 191:
10 Weight Lifting and Aortic Dissec
- Page 192 and 193:
Weight Lifting and Aortic Dissectio
- Page 194 and 195:
Weight Lifting and Aortic Dissectio
- Page 196 and 197:
Weight Lifting and Aortic Dissectio
- Page 198 and 199:
11 Timing of Acute Aortic Events: H
- Page 200 and 201:
Timing of Acute Aortic Events 171 F
- Page 202 and 203:
SECTION IV: TREATMENT OF ACUTE AORT
- Page 204 and 205:
Natural History of Thoracic Aortic
- Page 206 and 207:
Natural History of Thoracic Aortic
- Page 208 and 209:
Natural History of Thoracic Aortic
- Page 210 and 211:
Natural History of Thoracic Aortic
- Page 212 and 213:
Natural History of Thoracic Aortic
- Page 214 and 215:
Natural History of Thoracic Aortic
- Page 216 and 217:
Natural History of Thoracic Aortic
- Page 218 and 219:
Natural History of Thoracic Aortic
- Page 220 and 221:
Natural History of Thoracic Aortic
- Page 222 and 223:
Natural History of Thoracic Aortic
- Page 224 and 225:
Natural History of Thoracic Aortic
- Page 226 and 227:
Natural History of Thoracic Aortic
- Page 228 and 229:
Natural History of Thoracic Aortic
- Page 230 and 231:
Natural History of Thoracic Aortic
- Page 232:
Natural History of Thoracic Aortic
- Page 235 and 236:
206 Shahriari and Farkas properties
- Page 237 and 238:
208 Shahriari and Farkas Figure 2 E
- Page 239 and 240:
210 Shahriari and Farkas Less than
- Page 241 and 242:
212 Shahriari and Farkas helpful if
- Page 243 and 244:
214 Shahriari and Farkas Figure 6 A
- Page 245 and 246:
216 Shahriari and Farkas (68). Many
- Page 247 and 248:
218 Shahriari and Farkas Figure 9 H
- Page 249 and 250:
220 Shahriari and Farkas fistula is
- Page 251 and 252:
222 Shahriari and Farkas MEGS is de
- Page 253 and 254:
224 Shahriari and Farkas 26. Svenss
- Page 255 and 256:
226 Shahriari and Farkas 63. Fehren
- Page 258 and 259:
14 Acute Aortic Dissection: Anti-im
- Page 260 and 261:
Acute Aortic Dissection 231 lamella
- Page 262 and 263:
Acute Aortic Dissection 233 P t is
- Page 264 and 265:
Acute Aortic Dissection 235 From th
- Page 266 and 267:
Acute Aortic Dissection 237 Figure
- Page 268 and 269:
Acute Aortic Dissection 239 concern
- Page 270 and 271:
Acute Aortic Dissection 241 Table 2
- Page 272 and 273:
Acute Aortic Dissection 243 dissect
- Page 274 and 275:
Acute Aortic Dissection 245 22. Bax
- Page 276 and 277:
Acute Aortic Dissection 247 62. Lin
- Page 278:
Acute Aortic Dissection 249 DISSCUS
- Page 281 and 282:
252 Elefteriades and Griepp ACUTE A
- Page 283 and 284:
254 Elefteriades and Griepp Figure
- Page 285 and 286:
256 Elefteriades and Griepp sometim
- Page 287 and 288:
258 Elefteriades and Griepp Figure
- Page 289 and 290:
260 Elefteriades and Griepp Figure
- Page 291 and 292:
262 Elefteriades and Griepp to a se
- Page 293 and 294:
264 Elefteriades and Griepp Natural
- Page 295 and 296:
266 Elefteriades and Griepp CONCLUS
- Page 297 and 298:
268 Elefteriades and Griepp DISCUSS
- Page 299 and 300:
270 Brinster et al. thoracic aneury
- Page 301 and 302:
272 Brinster et al. Figure 1 Retrop
- Page 303 and 304:
274 Brinster et al. artery. Z3 land
- Page 305 and 306:
276 Brinster et al. or ischemia of
- Page 307 and 308:
278 Brinster et al. registry arm (2
- Page 309 and 310:
280 Brinster et al. Table 3 Early P
- Page 311 and 312:
282 Brinster et al. According to th
- Page 313 and 314:
284 Brinster et al. ranged from 1 t
- Page 315 and 316:
Table 4 Meta-Analysis of Tevar for
- Page 317 and 318:
288 Brinster et al. conventional op
- Page 319 and 320:
290 Brinster et al. using no (or lo
- Page 321 and 322:
292 Brinster et al. Table 5 Risk Fa
- Page 323 and 324:
294 Brinster et al. wire manipulati
- Page 325 and 326:
296 Brinster et al. Thoracoabdomina
- Page 327 and 328:
298 Brinster et al. 25. Hagan PG, N
- Page 329 and 330:
300 Brinster et al. 60. Elefteriade
- Page 331 and 332:
302 Brinster et al. 98. Liu ZG, Sun
- Page 333 and 334:
304 Brinster et al. 131. Szeto WY,
- Page 335 and 336:
306 Brinster et al. 100% 90% 80% 70
- Page 337 and 338:
308 Brinster et al. ● “Long-ter
- Page 339 and 340:
310 Hackmann et al. treatment. New
- Page 341 and 342:
312 Hackmann et al. tissue than in
- Page 343 and 344:
314 Hackmann et al. Table 1 Pharmac
- Page 345 and 346:
316 Hackmann et al. Some anti-hyper
- Page 347 and 348:
318 Hackmann et al. inhibits NF-κB
- Page 349 and 350:
320 Hackmann et al. Patients with C
- Page 351 and 352:
322 Hackmann et al. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
- Page 353 and 354:
324 Hackmann et al. 34. Thompson RW
- Page 355 and 356:
326 Hackmann et al. 70. LeMaire SA,
- Page 357 and 358:
328 Hackmann et al. 105. Marra DE,
- Page 359 and 360:
330 Hackmann et al. DISCUSSION AND
- Page 361 and 362:
332 Elefteriades Diseases of the th
- Page 363 and 364:
334 Elefteriades Table 1 Individual
- Page 365 and 366:
336 Elefteriades Table 1 Individual
- Page 367 and 368:
338 Elefteriades Failure to Diagnos
- Page 369 and 370:
340 Elefteriades of physicians on t
- Page 371 and 372:
342 Elefteriades Figure 3 Computed
- Page 373 and 374:
344 Elefteriades reviewed over the
- Page 375 and 376:
346 Elefteriades DISCUSSION AND COM
- Page 377 and 378:
348 Elefteriades Figure 1 (See colo
- Page 379 and 380:
350 Elefteriades that are the subje
- Page 382 and 383:
SECTION VII: SYNTHESIS 20 The Key L
- Page 384 and 385:
The Key Lessons of This Book—In a
- Page 386 and 387:
The Key Lessons of This Book—In a
- Page 388:
The Key Lessons of This Book—In a
- Page 391 and 392:
362 Index Aging, aortic aneurysms a
- Page 393 and 394:
364 Index Cytokines, aortic aneurys
- Page 395 and 396:
366 Index Pathoanatomy classificati
- Page 397 and 398:
368 Index [Thoracic aortic aneurysm
- Page 399 and 400:
Figure 1.C Note from schematic depi
- Page 401 and 402:
Figure 8.1 Dramatic clinical exampl
- Page 403 and 404:
Figure 11.2 Proposed schema for the
- Page 405:
Figure 19.1 Future prospects in car