- Page 4 and 5:
B. B. 6yX08I4e8. B. JI. KpU8IleHIC0
- Page 6 and 7:
First published 1971 Second printin
- Page 8 and 9:
6 Chapter 5. Geometrical Optics •
- Page 10 and 11:
8 PROBLEMS engineer arrived at the
- Page 12 and 13:
10 PROBLEMS c rIII a Fig. 3 01 IIII
- Page 14 and 15:
12 PROBLEMS ....------1----.... str
- Page 16 and 17:
14 PROBLEMS velocity at a constant
- Page 18 and 19:
16 PROBLEMS the highest point of th
- Page 20 and 21:
18 PROBLEM~ friction if the weight
- Page 22 and 23:
20 PROBLEMS Fig. 28 H 11/ r ~--I---
- Page 24 and 25:
22 PROBLEMS Fig. 25 Fig. 26 B m; is
- Page 26 and 27:
24 PROBLEMS ~ 1 2 • ~ Fig. 29 tha
- Page 28 and 29:
2(; PROBLEMS m m Fig. 32 Fig. 33 90
- Page 30 and 31:
28 PROBLEMS o ;...-. ..... 8 D Fig.
- Page 32 and 33:
a Fig. 41 Fig. 42 for the rotating
- Page 34 and 35:
32 PROBLEMS Fig. 48 122. In Guerick
- Page 36 and 37:
34 PROBLEMS (I) What work is done b
- Page 38 and 39:
36 PROBLEMS ~ city of the weights a
- Page 40 and 41:
38 PROBLEMS wedge. The block can sl
- Page 42 and 43:
40 PROBLEMS s II ne. 61 Fl,. 62 182
- Page 44 and 45:
42 PROBLEMS A A N o B " Fig. 65 Fig
- Page 46 and 47:
44 PROBLEMS 178. A ball bearing sup
- Page 48 and 49:
46 PROBLEMS Fig. 73 Fig. 74 189. At
- Page 50 and 51:
a 0' Fig. 80 Fig- 8/ ces '1 and " f
- Page 52 and 53:
50 PROBLEMS Fig. 84 Fig. 85 205. A
- Page 54 and 55:
52 PROBLEMS surface. Find the angul
- Page 56 and 57:
54 PROBLEMS '-... ' ..........-....
- Page 58 and 59:
56 PROBLEMS ~==-==~~~~---------- --
- Page 60 and 61:
58 PROBLEMS "/I I 11 L..-__----...,
- Page 62 and 63:
60 PROBLEMS the chamber closes herm
- Page 64 and 65:
62 PROBLEMS made of the same materi
- Page 66 and 67:
--- --r-- - Fig. 114 ~--l---I"" Fig
- Page 68 and 69:
66 PROBLEMS ~ ~ I A ~ • B Fig. 11
- Page 70 and 71:
CHAPTER 2 HEAT. MOLECULAR PHYSICS 2
- Page 72 and 73:
70 PROBLEMS What quantity of heat w
- Page 74 and 75:
72 PROBLEMS 315. A barometer gives
- Page 76 and 77:
74 PROBLEMS pressure Po = 760 mm Hg
- Page 78 and 79:
76 PROBLEMS of the air in the room
- Page 80 and 81:
78 PROBLEMS -- II -- - --- -- - - -
- Page 82 and 83:
80 PROBLEMS angle will be different
- Page 84 and 85:
82 PROBLEMS ~ Fig. 141 force F will
- Page 86 and 87:
84 PROBLEMS tube when the nut is tu
- Page 88 and 89:
86 PROBLEMS p - --- Fig. 146 Fig. 1
- Page 90 and 91:
88 PROBLEMS 400. If only one charge
- Page 92 and 93:
90 PROBLEMS 417. A metal leaf is at
- Page 94 and 95:
92 PROBLEMS Fig. 153 Fig. 154 431.
- Page 96 and 97:
94 PROBLEMS Prove that if these cap
- Page 98 and 99:
96 PROBLEMS of the vessel is placed
- Page 100 and 101:
A Fig. /66 Fig. /67 463. Two conduc
- Page 102 and 103:
100 PROBLEMS It At the moment of ti
- Page 104 and 105:
102 . PROBLEMS . Fig. 174 Fig. /75
- Page 106 and 107:
104 PROBLEMS length of L = 5.6 km t
- Page 108 and 109: 106 PROBLEMS an energy of QU/2 is l
- Page 110 and 111: 108 ....------------- PROBLEJ\\S Fi
- Page 112 and 113: 110 PROBLEMS Fig. 187 Fig. 188 Cons
- Page 114 and 115: 112 PROBLEMS 3-4. Magnetic Field of
- Page 116 and 117: 114 PROBLEMS 553. Will the density
- Page 118 and 119: 116 PROBLEMS tic field in the direc
- Page 120 and 121: 118 PROBLEMS Fig. 206 Fig. 207 ving
- Page 122 and 123: 120 PROBLEMS is , and its length l
- Page 124 and 125: 122 PROBLEMS -~ t Fig. 218 597. An
- Page 126 and 127: 124 PROBLEMS 608. Determine the eff
- Page 128 and 129: 126 PROBLEMS rent I. flowing throug
- Page 130 and 131: PROBLEMS 625. Find the period of os
- Page 132 and 133: 130 PROBLEMS Fig. 227 tions of a we
- Page 134 and 135: 132 PROBLEMS 1; ~ ----- v Fig. 230
- Page 136 and 137: 134 PROBLEMS 00 DC- Fig. 232 Fig. 2
- Page 138 and 139: 136 PROBLEMS the third one that was
- Page 140 and 141: 138 PROBLEMS 680. Find graphically
- Page 142 and 143: 140 PROBLEMS W 689. Two flat mirror
- Page 144 and 145: 142 PROBLEMS 702. A ray incident on
- Page 146 and 147: 144 PROBLEMS .9' Fig. 247 length of
- Page 148 and 149: 146 PROBLEMS a point source arrange
- Page 150 and 151: 148 PROBLEMS displaced with respect
- Page 152 and 153: 150 PROBLEMS 757. Two men, a far-si
- Page 154 and 155: 152 PROBLEMS H 767. Two point sourc
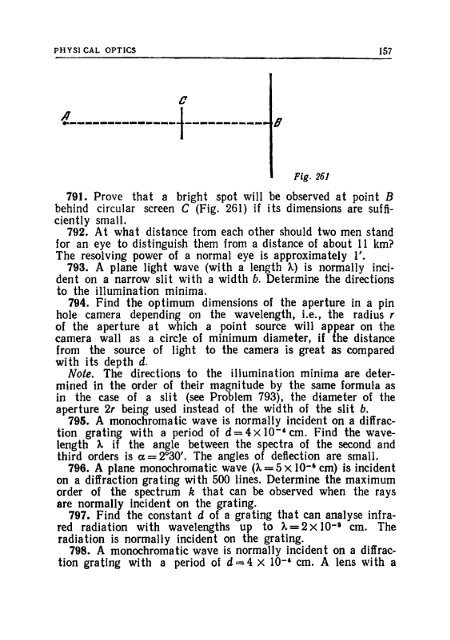
- Page 156 and 157: 154 PROBLEMS 773. A convergent lens
- Page 160 and 161: 158 P~OBLEMS focal length of f = 40
- Page 162 and 163: ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS CHAPTER 1 MEC
- Page 164 and 165: 162 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS I 2 9 5 G
- Page 166 and 167: 164 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS depend on
- Page 168 and 169: 166 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS Hence and
- Page 170 and 171: 168 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS \ \\\\\\\
- Page 172 and 173: o s Fig. 278 .D A B B' Fig. 277 25.
- Page 174 and 175: 172 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS '0; U2 OI
- Page 176 and 177: 174 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS 35. The a
- Page 178 and 179: 176 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS ice dry s
- Page 180 and 181: 178 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS The addit
- Page 182 and 183: 180 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS --+- 0 9
- Page 184 and 185: 182 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS 65. Initi
- Page 186 and 187: 184 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS Let us as
- Page 188 and 189: 186 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS where s i
- Page 190 and 191: 188 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS 1-5. Stat
- Page 192 and 193: 190 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS Hence, F=
- Page 194 and 195: o • • • ~. Fig. 306 Fig. 907
- Page 196 and 197: 194 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS A C~~7;7l
- Page 198 and 199: 196 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS N F;r 9 m
- Page 200 and 201: 198 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS .0 Fig. 3
- Page 202 and 203: 200 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS rnicircle
- Page 204 and 205: 202 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS The wagon
- Page 206 and 207: 204 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS 132. Acco
- Page 208 and 209:
206 ANSWERS AND SOLUTiONS 140. On t
- Page 210 and 211:
208 ANSWERS AND SOLUTION The kineti
- Page 212 and 213:
210 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS I :h I o
- Page 214 and 215:
212 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS Fig. 326
- Page 216 and 217:
214 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS Fig. 329
- Page 218 and 219:
216 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS Fig.3d1 F
- Page 220 and 221:
218 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS a Fig. 33
- Page 222 and 223:
220 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS " ...-- ,
- Page 224 and 225:
222 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS Therefore
- Page 226 and 227:
224 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS 171. The
- Page 228 and 229:
226 ANS\VERS AND SOLUTIONS A 2u (6)
- Page 230 and 231:
228 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS Fig. 346
- Page 232 and 233:
230 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS T=(M +m)
- Page 234 and 235:
232 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS 9-"-,,~,
- Page 236 and 237:
234 . ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS Newton'
- Page 238 and 239:
236 o ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS a A H F
- Page 240 and 241:
238 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS Fig. 963
- Page 242 and 243:
240 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS The close
- Page 244 and 245:
242 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS time t: W
- Page 246 and 247:
244 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS Since the
- Page 248 and 249:
246 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS F F q equ
- Page 250 and 251:
248 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS 1-9. The
- Page 252 and 253:
250 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS ",' ,~ I
- Page 254 and 255:
(1 A6000-"""'------------..li.....-
- Page 256 and 257:
254 ANSWE~S AND SOLUTIONS entire th
- Page 258 and 259:
256 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS If the wa
- Page 260 and 261:
258 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS N Accordi
- Page 262 and 263:
260 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS acting on
- Page 264 and 265:
262 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS Thus, the
- Page 266 and 267:
264 ANSWERS AND SOLUTiONS The chang
- Page 268 and 269:
266 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS time to b
- Page 270 and 271:
CHAPTER 2 HEAT. MOLECULAR PHYSICS 2
- Page 272 and 273:
270 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS ! This sy
- Page 274 and 275:
272 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS 306. The
- Page 276 and 277:
274 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS P A ~ ---
- Page 278 and 279:
276 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS 320. Sinc
- Page 280 and 281:
278 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS 330. When
- Page 282 and 283:
280 ANS,WERS AND SOLUTIONS p 1.....
- Page 284 and 285:
282 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS Fig. 401
- Page 286 and 287:
284 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS Fig. 403
- Page 288 and 289:
286 ANSWERS AND SOLUT IONS JI!!!I!I
- Page 290 and 291:
288 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS 386. The
- Page 292 and 293:
290 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS 378. It i
- Page 294 and 295:
292 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS the kettl
- Page 296 and 297:
CHAPTER 3 ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM
- Page 298 and 299:
296 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS Upon solv
- Page 300 and 301:
298 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS 407. The
- Page 302 and 303:
300 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS .0 E + +
- Page 304 and 305:
302 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS In the se
- Page 306 and 307:
304 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS Fig. 416
- Page 308 and 309:
306 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS - - + + +
- Page 310 and 311:
308 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS + - +0-~a
- Page 312 and 313:
310 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS +/l U -1/
- Page 314 and 315:
312 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS A JJ a Fi
- Page 316 and 317:
314 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS sufficien
- Page 318 and 319:
316 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS a layer w
- Page 320 and 321:
318 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS the circu
- Page 322 and 323:
320 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS 468. The
- Page 324 and 325:
322 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS through w
- Page 326 and 327:
324 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS w Fig. 43
- Page 328 and 329:
326 ANSWERS AND SOLUTiONS to the e.
- Page 330 and 331:
328 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS Fig. 444
- Page 332 and 333:
330 t Fig. 445 ~ + - fj R -r ~ wher
- Page 334 and 335:
332 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS 9 !/min F
- Page 336 and 337:
334 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS Fig. 448
- Page 338 and 339:
336 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS "'---1/=1
- Page 340 and 341:
338 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS I t Fig.
- Page 342 and 343:
340 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS /16'4 D 2
- Page 344 and 345:
342 ANS'WERS AND SOLUTIONS .Irorn t
- Page 346 and 347:
344 . ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS Fig. 45
- Page 348 and 349:
346 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS II /"----
- Page 350 and 351:
348 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS cording t
- Page 352 and 353:
350 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS ; t B If
- Page 354 and 355:
352 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS the ring
- Page 356 and 357:
354 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS I proport
- Page 358 and 359:
356 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS u A u o F
- Page 360 and 361:
358 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS an e.rn.I
- Page 362 and 363:
360 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS retard th
- Page 364 and 365:
362 p ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS 612. Th
- Page 366 and 367:
364 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS and 11+J2
- Page 368 and 369:
366 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS 623. Each
- Page 370 and 371:
368 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS Let us so
- Page 372 and 373:
370 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS Rememberi
- Page 374 and 375:
372 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS Hence, 0)
- Page 376 and 377:
374 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS H (a) H t
- Page 378 and 379:
376 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS (curve ab
- Page 380 and 381:
A ~-..----4-----r--------r-- Fig. 4
- Page 382 and 383:
CHAPTER 5 GEOMETRICAL OPTICS 5-1. P
- Page 384 and 385:
382 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS· Paper -
- Page 386 and 387:
384 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS DAB =~-=-
- Page 388 and 389:
386 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS 684. (a)
- Page 390 and 391:
388 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS Fig. 500
- Page 392 and 393:
390 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS Then. acc
- Page 394 and 395:
392 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS a Fig. 50
- Page 396 and 397:
394 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS B -------
- Page 398 and 399:
396 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS ~-"":;:'-
- Page 400 and 401:
398 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS Fig. 514
- Page 402 and 403:
8' Fig. 519 s* IIIIIIII N P H' Fig.
- Page 404 and 405:
402 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS ..... ...
- Page 406 and 407:
404 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS ~---d---~
- Page 408 and 409:
406 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS E a S s'
- Page 410 and 411:
408 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS Fig. 536
- Page 412 and 413:
410 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS The dista
- Page 414 and 415:
412 ANS\\'ERS AND SOLUTIONS the sys
- Page 416 and 417:
414 J- ------....,.c 8- ----~--- AN
- Page 418 and 419:
416 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS Therefore
- Page 420 and 421:
418 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS N Fig. 54
- Page 422 and 423:
420 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS from the
- Page 424 and 425:
422 S, IT ........... In --.. U' .,
- Page 426 and 427:
424 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS dering tr
- Page 428 and 429:
426 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS Fig 556 T
- Page 430 and 431:
428 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS 779. When
- Page 432 and 433:
430 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS Fig. 559
- Page 434 and 435:
432 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS Fig. 561
- Page 436 and 437:
434 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS cent slit
- Page 438 and 439:
436 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS 805. For
- Page 440 and 441:
438 ANSWERS AND SOLUTIONS (blue-vio