Thesis
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
38 Literature Survey<br />
(words, objects, … lacking context Greenwald and Leavitt, and partially<br />
store the information obtained into memory (Foxall, Brown and Goldsmith, 1998).<br />
Focal attention can be voluntary, a selective type of attention when the consumer<br />
experiences a need to which the stimulus relates and which thus have relevancy to<br />
current intentions (Foxall, Brown and Goldsmith, 1998, Kardes, 1999). Attention<br />
can also be drawn from the environment in which the message take shape through<br />
different styles of messaging (Kotler, 2012), potentially more disruptive in nature,<br />
which can as such serve as salient, sometimes involuntary, stimuli (Kardes, 1999).<br />
The concepts of comprehension and elaboration will be discussed further on.<br />
The level of consumer involvement in the product strongly affects information<br />
processing (Krugman, 1965): in the case of high involvement, consumers<br />
have a high level of attention and evaluation to arguments proposed through the<br />
message, contrarily to low involvement where little information is being processed<br />
(Foxall, Brown and Goldsmith, 1998).<br />
The next section describes how the consumer gives meaning to the message<br />
which is in turn stored in memory.<br />
3.3.2 Comprehension and memory<br />
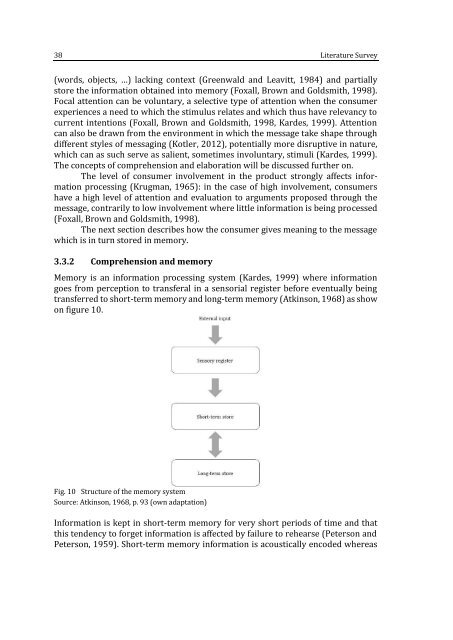
Memory is an information processing system (Kardes, 1999) where information<br />
goes from perception to transferal in a sensorial register before eventually being<br />
transferred to short-term memory and long-term memory (Atkinson, 1968) as show<br />
on figure 10.<br />
Fig. 10 Structure of the memory system<br />
Source: Atkinson, 1968, p. 93 (own adaptation)<br />
Information is kept in short-term memory for very short periods of time and that<br />
this tendency to forget information is affected by failure to rehearse (Peterson and<br />
Peterson, 1959). Short-term memory information is acoustically encoded whereas