Download - The India Economy Review
Download - The India Economy Review
Download - The India Economy Review
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
P LANNING P ARADIGM<br />
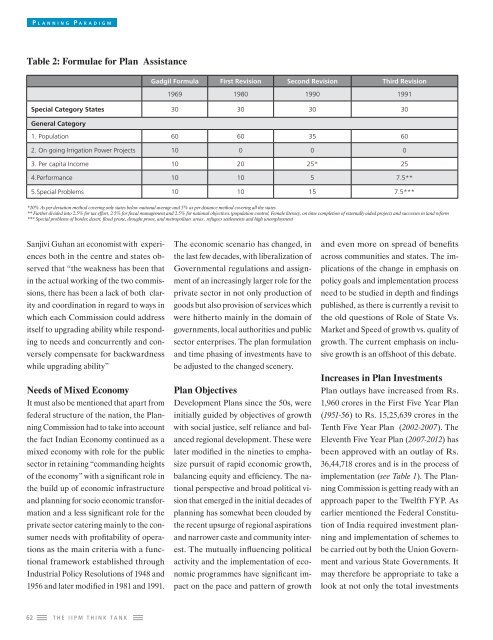
Table 2: Formulae for Plan Assistance<br />
Sanjivi Guhan an economist with experi-<br />
ences both in the centre and states ob-<br />
served that “the weakness has been that<br />
in the actual working of the two commissions,<br />
there has been a lack of both clarity<br />
and coordination in regard to ways in<br />
which each Commission could address<br />
itself to upgrading ability while responding<br />
to needs and concurrently and conversely<br />
compensate for backwardness<br />
while upgrading ability”<br />
Needs of Mixed <strong>Economy</strong><br />
It must also be mentioned that apart from<br />
federal structure of the nation, the Planning<br />
Commission had to take into account<br />
the fact <strong>India</strong>n <strong>Economy</strong> continued as a<br />
mixed economy with role for the public<br />
sector in retaining “commanding heights<br />
of the economy” with a signifi cant role in<br />
the build up of economic infrastructure<br />
and planning for socio economic transformation<br />
and a less signifi cant role for the<br />
private sector catering mainly to the consumer<br />
needs with profi tability of operations<br />
as the main criteria with a functional<br />
framework established through<br />
Industrial Policy Resolutions of 1948 and<br />
1956 and later modifi ed in 1981 and 1991.<br />
62 THE IIPM THINK TANK<br />
Gadgil Formula First Revision Second Revision Third Revision<br />
1969 1980 1990 1991<br />
Special Category States 30 30 30 30<br />
General Category<br />
1. Population 60 60 35 60<br />
2. On going Irrigation Power Projects 10 0 0 0<br />
3. Per capita Income 10 20 25* 25<br />
4.Performance 10 10 5 7.5**<br />
5.Special Problems 10 10 15 7.5***<br />
*20% As per deviation method covering only states below national average and 5% as per distance method covering all the states.<br />
** Further divided into 2.5% for tax effort, 2.5% for fi scal management and 2.5% for national objectives.(population control, Female literacy, on time completion of externally aided projects and successes in land reform<br />
*** Special problems of border, desert, fl ood prone, drought prone, and metropolitan areas , refugees settlements and high unemployment<br />
<strong>The</strong> economic scenario has changed, in<br />
the last few decades, with liberalization of<br />
Governmental regulations and assignment<br />
of an increasingly larger role for the<br />
private sector in not only production of<br />
goods but also provision of services which<br />
were hitherto mainly in the domain of<br />
governments, local authorities and public<br />
sector enterprises. <strong>The</strong> plan formulation<br />
and time phasing of investments have to<br />
be adjusted to the changed scenery.<br />
Plan Objectives<br />
Development Plans since the 50s, were<br />
initially guided by objectives of growth<br />
with social justice, self reliance and balanced<br />
regional development. <strong>The</strong>se were<br />
later modifi ed in the nineties to emphasize<br />
pursuit of rapid economic growth,<br />
balancing equity and effi ciency. <strong>The</strong> national<br />
perspective and broad political vision<br />
that emerged in the initial decades of<br />
planning has somewhat been clouded by<br />
the recent upsurge of regional aspirations<br />
and narrower caste and community interest.<br />
<strong>The</strong> mutually infl uencing political<br />
activity and the implementation of economic<br />
programmes have signifi cant impact<br />
on the pace and pattern of growth<br />
and even more on spread of benefi ts<br />
across communities and states. <strong>The</strong> implications<br />
of the change in emphasis on<br />
policy goals and implementation process<br />
need to be studied in depth and fi ndings<br />
published, as there is currently a revisit to<br />
the old questions of Role of State Vs.<br />
Market and Speed of growth vs. quality of<br />
growth. <strong>The</strong> current emphasis on inclusive<br />
growth is an offshoot of this debate.<br />
Increases in Plan Investments<br />
Plan outlays have increased from Rs.<br />
1,960 crores in the First Five Year Plan<br />
(1951-56) to Rs. 15,25,639 crores in the<br />
Tenth Five Year Plan (2002-2007). <strong>The</strong><br />
Eleventh Five Year Plan (2007-2012) has<br />
been approved with an outlay of Rs.<br />
36,44,718 crores and is in the process of<br />
implementation (see Table 1). <strong>The</strong> Planning<br />
Commission is getting ready with an<br />
approach paper to the Twelfth FYP. As<br />
earlier mentioned the Federal Constitution<br />
of <strong>India</strong> required investment planning<br />
and implementation of schemes to<br />
be carried out by both the Union Government<br />
and various State Governments. It<br />
may therefore be appropriate to take a<br />
look at not only the total investments