Clusters and competitiveness - PRO INNO Europe
Clusters and competitiveness - PRO INNO Europe
Clusters and competitiveness - PRO INNO Europe
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Other highly complete local production systems were the automotive industry, motorcycles<br />
<strong>and</strong> railway materials in the metropolitan area of Barcelona, which were also made up of<br />
nearly the entire value chain <strong>and</strong> had important associations, trade fairs, training centres<br />
<strong>and</strong> technology centres.<br />
With regard to their origins, some LPSs grew up close to the natural resources they needed<br />
for their work (wine <strong>and</strong> cava in Penedès, mineral water in La Selva, cotton spinning <strong>and</strong><br />
weaving in Central Catalonia, wood in Osona <strong>and</strong> La Selva, cork in the Costa Brava, paper<br />
<strong>and</strong> cardboard in the river basins of Anoia, Bitlles <strong>and</strong> Llobregat, etc.). Many others emerged<br />
close to Barcelona to take advantage of the proximity of suppliers, clients <strong>and</strong>/or the port.<br />
Others originated from investments made by large firms seeking to be near the port of<br />
Tarragona (raw chemicals in Camp de Tarragona). Others started to emerge after the<br />
investment made by SEAT (automotive industry, h<strong>and</strong>ling <strong>and</strong> elevating machinery, moulds<br />
<strong>and</strong> dies, etc.) while some grew up around successive spin-offs based on an initial company<br />
(household furniture in Montsià <strong>and</strong> Vallès Oriental, bodywork in La Selva, etc.).<br />
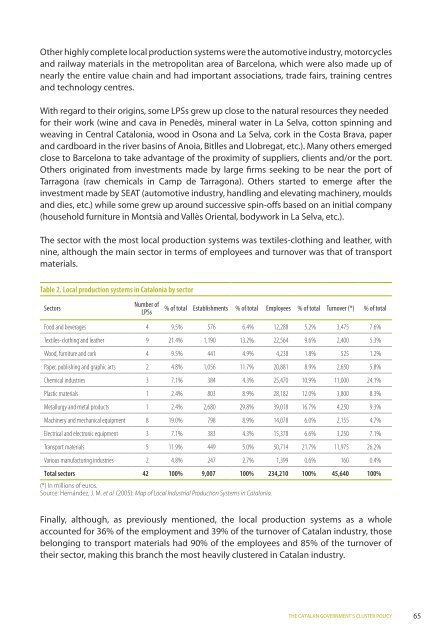
The sector with the most local production systems was textiles-clothing <strong>and</strong> leather, with<br />
nine, although the main sector in terms of employees <strong>and</strong> turnover was that of transport<br />
materials.<br />
Table 2. Local production systems in Catalonia by sector<br />
Sectors<br />
Number of<br />
LPSs<br />
% of total Establishments % of total Employees % of total Turnover (*) % of total<br />
Food <strong>and</strong> beverages 4 9.5% 576 6.4% 12,288 5.2% 3,475 7.6%<br />
Textiles-clothing <strong>and</strong> leather 9 21.4% 1,190 13.2% 22,564 9.6% 2,400 5.3%<br />
Wood, furniture <strong>and</strong> cork 4 9.5% 441 4.9% 4,238 1.8% 525 1.2%<br />
Paper, publishing <strong>and</strong> graphic arts 2 4.8% 1,056 11.7% 20,881 8.9% 2,650 5.8%<br />
Chemical industries 3 7.1% 384 4.3% 25,470 10.9% 11,000 24.1%<br />
Plastic materials 1 2.4% 803 8.9% 28,182 12.0% 3,800 8.3%<br />
Metallurgy <strong>and</strong> metal products 1 2.4% 2,680 29.8% 39,018 16.7% 4,250 9.3%<br />
Machinery <strong>and</strong> mechanical equipment 8 19.0% 798 8.9% 14,078 6.0% 2,155 4.7%<br />
Electrical <strong>and</strong> electronic equipment 3 7.1% 383 4.3% 15,378 6.6% 3,250 7.1%<br />
Transport materials 5 11.9% 449 5.0% 50,714 21.7% 11,975 26.2%<br />
Various manufacturing industries 2 4.8% 247 2.7% 1,399 0.6% 160 0.4%<br />
Total sectors 42 100% 9,007 100% 234,210 100% 45,640 100%<br />
(*) In millions of euros.<br />
Source: Hernández, J. M. et al. (2005): Map of Local Industrial Production Systems in Catalonia.<br />
Finally, although, as previously mentioned, the local production systems as a whole<br />
accounted for 36% of the employment <strong>and</strong> 39% of the turnover of Catalan industry, those<br />
belonging to transport materials had 90% of the employees <strong>and</strong> 85% of the turnover of<br />
their sector, making this branch the most heavily clustered in Catalan industry.<br />
THE CATALAN GOVERNMENT’S CLUSTER POLICY<br />
65