You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Rev 2.02<br />
Parallel circuit solutions<br />
Solving for parallel circuits for ac circuits is similar to the way we solved resistance parallel circuits. Remember the<br />
Equation:<br />
The solution involved finding the conductance (G) of each leg by dividing the resistances into 1 and summing them.<br />
This gave the total circuit conductance in Siemens. The Mho was the term previously used for Seimen.<br />
To find the resistance we divided the conductance into 1 and ended up with the parallel circuit resistance.<br />
We do the same thing to find the impedance of parallel ac circuits. The names of the circuit references change-<br />
Impedance becomes admittance, “Y”, (1/impedance). Resistance becomes conductance, “G”, (1/resistance)<br />
and susceptance , “B” (1/reactance) We start by finding the “conductance of the resistive and reactive<br />
components and just add them as we did in the resistance solution (remember we will be summing resistive (real)<br />
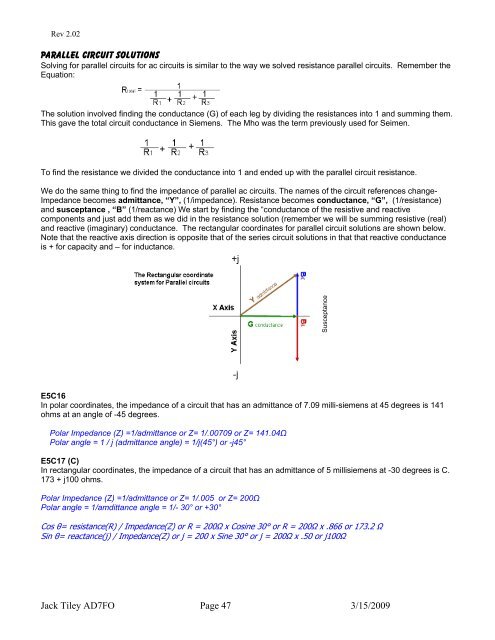
and reactive (imaginary) conductance. The rectangular coordinates for parallel circuit solutions are shown below.<br />
Note that the reactive axis direction is opposite that of the series circuit solutions in that that reactive conductance<br />
is + for capacity and – for inductance.<br />
E5C16<br />
In polar coordinates, the impedance of a circuit that has an admittance of 7.09 milli-siemens at 45 degrees is 141<br />
ohms at an angle of -45 degrees.<br />
Polar Impedance (Z) =1/admittance or Z= 1/.00709 or Z= 141.04Ω<br />
Polar angle = 1 / j (admittance angle) = 1/j(45°) or -j45°<br />
E5C17 (C)<br />
In rectangular coordinates, the impedance of a circuit that has an admittance of 5 millisiemens at -30 degrees is C.<br />
173 + j100 ohms.<br />
Polar Impedance (Z) =1/admittance or Z= 1/.005 or Z= 200Ω<br />
Polar angle = 1/amdittance angle = 1/- 30° or +30°<br />
Cos θ= resistance(R) / Impedance(Z) or R = 200Ω x Cosine 30° or R = 200Ω x .866 or 173.2 Ω<br />
Sin θ= reactance(j) / Impedance(Z) or j = 200 x Sine 30° or j = 200Ω x .50 or j100Ω<br />
Jack Tiley <strong>AD7FO</strong> Page 47 3/15/2009<br />
Susceptance