pg _ pga series - Stoewer-Getriebe.de
pg _ pga series - Stoewer-Getriebe.de
pg _ pga series - Stoewer-Getriebe.de
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
3. Il valore di Fr trovato è il valore<br />
di carico radiale massimo<br />
accettabile nella posizione<br />
E per una durata di vita<br />
<strong>de</strong>i cuscinetti h di:<br />
Albero di uscita<br />
Albero di entrata<br />
h = Durata di vita <strong>de</strong>i cuscinetti [h]<br />
n1 = Velocità di rotazione <strong>de</strong>ll’albero<br />
entrata [min -1 ]<br />
n2 = Velocità di rotazione <strong>de</strong>ll’albero<br />
uscita [min -1 ]<br />
Nel caso la durata di vita <strong>de</strong>i<br />
cuscinetti, calcolata con le sud<strong>de</strong>tte<br />
formule, non corrisponda<br />
a quella richiesta occorrerà <strong>de</strong>terminare<br />
il coefficiente di correzione<br />
<strong>de</strong>l carico radiale per<br />
ottenere la durata richiesta seguendo<br />
il seguente procedimento:<br />
4. Determinare il numero di cicli<br />
che l’albero compierà durante<br />
la durata di vita richiesta:<br />
nxh=n1-2 [min -1 ] x h [h].<br />
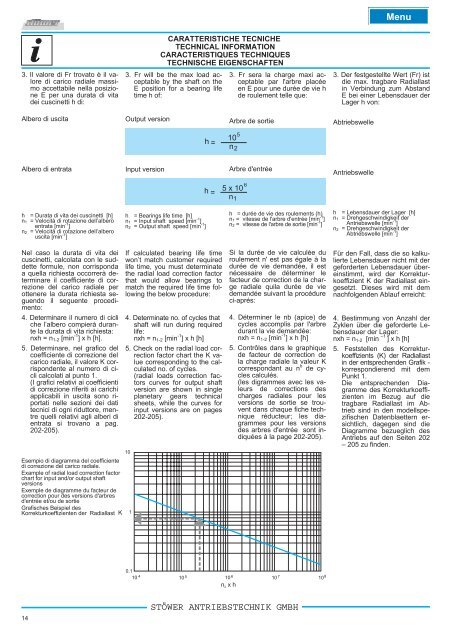
5. Determinare, nel grafico <strong>de</strong>l<br />
coefficiente di correzione <strong>de</strong>l<br />
carico radiale, il valore K corrispon<strong>de</strong>nte<br />
al numero di cicli<br />
calcolati al punto 1.<br />
(I grafici relativi ai coefficienti<br />
di correzione riferiti ai carichi<br />
applicabili in uscita sono riportati<br />
nelle sezioni <strong>de</strong>i dati<br />
tecnici di ogni riduttore, mentre<br />
quelli relativi agli alberi di<br />
entrata si trovano a pag.<br />
202-205).<br />
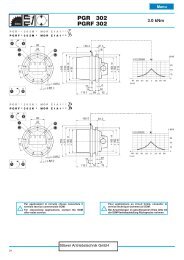
Esempio di diagramma <strong>de</strong>l coefficiente<br />
di correzione <strong>de</strong>l carico radiale.<br />
Example of radial load correction factor<br />
chart for input and/or output shaft<br />
versions<br />
Exemple <strong>de</strong> diagramme du facteur <strong>de</strong><br />
correction pour <strong>de</strong>s versions d'arbres<br />
d'entrée et/ou <strong>de</strong> sortie<br />
Grafisches Beispiel <strong>de</strong>s<br />
Korrekturkoeffizienten <strong>de</strong>r Radiallast K<br />
14<br />
3. Fr will be the max load acceptable<br />
by the shaft on the<br />
E position for a bearing life<br />
time h of:<br />
Output version<br />
Input version<br />
h = Bearings life time [h]<br />
n1 = Input shaft speed [min -1 ]<br />
n2 = Output shaft speed [min -1 ]<br />
h =<br />
h =<br />
If calculated bearing life time<br />
won’t match customer required<br />
life time, you must <strong>de</strong>terminate<br />
the radial load correction factor<br />
that would allow bearings to<br />
match the required life time following<br />
the below procedure:<br />
4. Determinate no. of cycles that<br />
shaft will run during required<br />
life:<br />
nxh=n1-2 [min -1 ]xh[h]<br />
5. Check on the radial load correction<br />
factor chart the K value<br />
corresponding to the calculated<br />
no. of cycles.<br />
(radial loads correction factors<br />
curves for output shaft<br />
version are shown in single<br />
planetary gears technical<br />
sheets, while the curves for<br />
input versions are on pages<br />
202-205).<br />
10<br />
1<br />
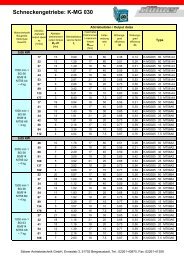
CARATTERISTICHE TECNICHE<br />
TECHNICAL INFORMATION<br />
CARACTERISTIQUES TECHNIQUES<br />
TECHNISCHE EIGENSCHAFTEN<br />
3. Fr sera la charge maxi acceptable<br />
par l'arbre placée<br />
en E pour une durée <strong>de</strong> vie h<br />
<strong>de</strong> roulement telle que:<br />
Arbre <strong>de</strong> sortie<br />
5<br />
10<br />
n2<br />
Arbre d'entrée<br />
5x10<br />
n1<br />
0.1<br />
10 10 10<br />
n2x h<br />
10 10<br />
4 5 6 7 8<br />
6<br />
h = durée <strong>de</strong> vie <strong>de</strong>s roulements (h)<br />
n1 = vitesse <strong>de</strong> l'arbre d'entrée [min -1 ]<br />
n2 = vitesse <strong>de</strong> l'arbre <strong>de</strong> sortie [min -1 ]<br />
Si la durée <strong>de</strong> vie calculée du<br />
roulement n' est pas égale à la<br />
durée <strong>de</strong> vie <strong>de</strong>mandée, il est<br />
nécessaire <strong>de</strong> déterminer le<br />
facteur <strong>de</strong> correction <strong>de</strong> la charge<br />
radiale quila durée <strong>de</strong> vie<br />
<strong>de</strong>mandée suivant la procédure<br />
ci-aprés:<br />
4. Déterminer le nb (apice) <strong>de</strong><br />
cycles accomplis par l'arbre<br />
durant la vie <strong>de</strong>mandée:<br />
nxh=n1-2 [min -1 ]xh[h]<br />
5. Contrôles dans le graphique<br />
<strong>de</strong> facteur <strong>de</strong> correction <strong>de</strong><br />
la charge radiale la valeur K<br />
correspondant au n b <strong>de</strong> cycles<br />
calculés.<br />
(les digrammes avec les valeurs<br />
<strong>de</strong> corrections <strong>de</strong>s<br />
charges radiales pour les<br />
versions <strong>de</strong> sortie se trouvent<br />
dans chaque fiche technique<br />
réducteur; les diagrammes<br />
pour les versions<br />
<strong>de</strong>s arbres d'entrée sont indiquées<br />
à la page 202-205).<br />
STÖWER ANTRIEBSTECHNIK GMBH<br />
3. Der festgestellte Wert (Fr) ist<br />
die max. tragbare Radiallast<br />
in Verbindung zum Abstand<br />
E bei einer Lebensdauer <strong>de</strong>r<br />
Lager h von:<br />
Abtriebswelle<br />
Antriebswelle<br />
Menu<br />
h = Lebensdauer <strong>de</strong>r Lager [h]<br />
n1 = Drehgeschwindigkeit <strong>de</strong>r<br />
Antriebswelle [min -1 ]<br />
n2 = Drehgeschwindigkeit <strong>de</strong>r<br />
Abtriebswelle [min -1 ]<br />
Für <strong>de</strong>n Fall, dass die so kalkulierte<br />
Lebensdauer nicht mit <strong>de</strong>r<br />
gefor<strong>de</strong>rten Lebensdauer übereinstimmt,<br />
wird <strong>de</strong>r Korrekturkoeffizient<br />
K <strong>de</strong>r Radiallast eingesetzt.<br />
Dieses wird mit <strong>de</strong>m<br />
nachfolgen<strong>de</strong>n Ablauf erreicht:<br />
4. Bestimmung von Anzahl <strong>de</strong>r<br />
Zyklen über die gefor<strong>de</strong>rte Lebensdauer<br />
<strong>de</strong>r Lager:<br />
nxh=n1-2 [min –1 ]xh[h]<br />
5. Feststellen <strong>de</strong>s Korrekturkoeffizients<br />
(K) <strong>de</strong>r Radiallast<br />
in <strong>de</strong>r entsprechen<strong>de</strong>n Grafik -<br />
korrespondierend mit <strong>de</strong>m<br />
Punkt 1.<br />
Die entsprechen<strong>de</strong>n Diagramme<br />
<strong>de</strong>s Korrekturkoeffizienten<br />
im Bezug auf die<br />
tragbare Radiallast im Abtrieb<br />
sind in <strong>de</strong>n mo<strong>de</strong>llspezifischen<br />
Datenblaettern ersichtlich,<br />
dagegen sind die<br />
Diagramme bezueglich <strong>de</strong>s<br />
Antriebs auf <strong>de</strong>n Seiten 202<br />
– 205 zu fin<strong>de</strong>n.