Vol. 35 – 2009 - Ecologia Mediterranea - Université d'Avignon et des ...
Vol. 35 – 2009 - Ecologia Mediterranea - Université d'Avignon et des ...
Vol. 35 – 2009 - Ecologia Mediterranea - Université d'Avignon et des ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
MUSTAPHA DADDI BOUHOUN, LOUHICHI BRINIS, MOHAMED LAKHDAR SAKER, MARC COTE, JACQUES RABIER<br />
44<br />
Date palms rooting study<br />
In absence of a mechanical probe for sampling<br />
and a study of tree root depth (R.d.) like<br />
that of field cultures (Hansson 1987), we used<br />
a m<strong>et</strong>hod of measurement based on a progressive<br />
survey of Degl<strong>et</strong> Noor date palm rooting<br />
since 85% of the root are distributed in<br />
the zone of 2 m deep and 2 m on both lateral<br />
si<strong>des</strong> (Munier 1973; Zaid 2002). We used a<br />
manual drill of 150 cm depth and a scale.<br />
This m<strong>et</strong>hod consisted in measuring rooting<br />
up to 120 cm of depth, at 80 cm far from the<br />
trunk, with a gradual survey up to 150 cm of<br />
depth to confirm an absence of roots beyond<br />
120 cm. For each farm, we carried out three<br />
random measurements of rooting on adult<br />
date palms in full production to calculate average<br />
maximum depth of rooting. Root depths<br />
were classified in four groups; 0-40 cm, 40-<br />
80 cm, 80-120 cm and higher than 120 cm of<br />
depth.<br />
Statistical analysis<br />
Groups of depth range for roots and water<br />
tables were chosen for practical reasons.<br />
Several grouping of observations for the 167<br />
farms were formed according the tested hypotheses.<br />
The hypotheses were that low water<br />
table or crusts depth alone or in combination<br />
limit root growth. Means and standard deviations<br />
for subgroups of palm areas are shown<br />
in Table 1. Preliminary results of regression<br />
analyse obtained for the whole group or by<br />
group of palm areas which gave a higher<br />
number of outliers and lower d<strong>et</strong>ermination<br />
coefficients are not shown. Means, standard<br />
deviations, regression analyse and d<strong>et</strong>ermination<br />
coefficient (R 2 ) were performed with<br />
Excel 2004 software.<br />
Results<br />
The synth<strong>et</strong>ic results (Table 1) showed that<br />
the hydro-edaphic environment in the Ouargla<br />
basin was degraded. The groundwater<br />
levels had serious effects on rooting of date<br />
palms and physico-chemical soils degradation<br />
by waterlogging, gypseous crusts formation<br />
and soils’ salinization.<br />
Hydro-edaphic study<br />
In this study, 53.9% of the palm plantations<br />
showed a shallow water table, lowers than<br />
1.2 m of depth, varying from 29 to 119.4 cm<br />
(Figure 2). According to the USSL classification<br />
(1954), modified by Durand (1958), salinity<br />
degree of groundwater varied b<strong>et</strong>ween<br />
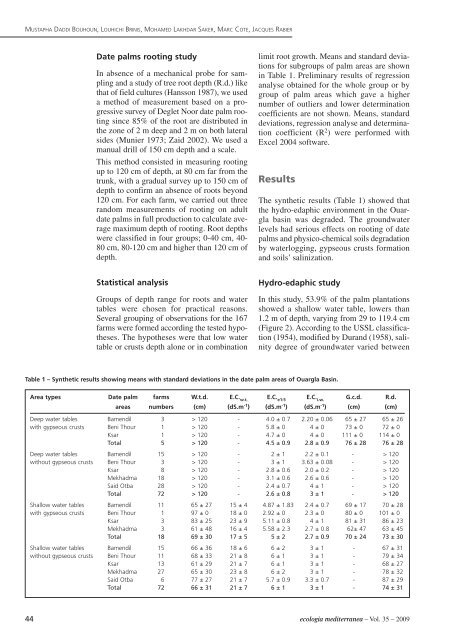
Table 1 <strong>–</strong> Synth<strong>et</strong>ic results showing means with standard deviations in the date palm areas of Ouargla Basin.<br />
Area types Date palm farms W.t.d. E.C. w.t. E.C. e1:5 E.C. i.w. G.c.d. R.d.<br />
areas numbers (cm) (dS.m-1 ) (dS.m-1 ) (dS.m-1 ) (cm) (cm)<br />
Deep water tables Bamendil 3 > 120 - 4.0 ± 0.7 2.20 ± 0.06 65 ± 27 65 ± 26<br />
with gypseous crusts Beni Thour 1 > 120 - 5.8 ± 0 4 ± 0 73 ± 0 72 ± 0<br />
Ksar 1 > 120 - 4.7 ± 0 4 ± 0 111 ± 0 114 ± 0<br />
Total 5 > 120 - 4.5 ± 0.9 2.8 ± 0.9 76 ± 28 76 ± 28<br />
Deep water tables Bamendil 15 > 120 - 2 ± 1 2.2 ± 0.1 - > 120<br />
without gypseous crusts Beni Thour 3 > 120 - 3 ± 1 3.63 ± 0.08 - > 120<br />
Ksar 8 > 120 - 2.8 ± 0.6 2.0 ± 0.2 - > 120<br />
Mekhadma 18 > 120 - 3.1 ± 0.6 2.6 ± 0.6 - > 120<br />
Said Otba 28 > 120 - 2.4 ± 0.7 4 ± 1 - > 120<br />
Total 72 > 120 - 2.6 ± 0.8 3 ± 1 - > 120<br />
Shallow water tables Bamendil 11 65 ± 27 15 ± 4 4.87 ± 1.83 2.4 ± 0.7 69 ± 17 70 ± 28<br />
with gypseous crusts Beni Thour 1 97 ± 0 18 ± 0 2.92 ± 0 2.3 ± 0 80 ± 0 101 ± 0<br />
Ksar 3 83 ± 25 23 ± 9 5.11 ± 0.8 4 ± 1 81 ± 31 86 ± 23<br />
Mekhadma 3 61 ± 48 16 ± 4 5.58 ± 2.3 2.7 ± 0.8 62± 47 63 ± 45<br />
Total 18 69 ± 30 17 ± 5 5 ± 2 2.7 ± 0.9 70 ± 24 73 ± 30<br />
Shallow water tables Bamendil 15 66 ± 36 18 ± 6 6 ± 2 3 ± 1 - 67 ± 31<br />
without gypseous crusts Beni Thour 11 68 ± 33 21 ± 8 6 ± 1 3 ± 1 - 79 ± 34<br />
Ksar 13 61 ± 29 21 ± 7 6 ± 1 3 ± 1 - 68 ± 27<br />
Mekhadma 27 65 ± 30 23 ± 8 6 ± 2 3 ± 1 - 78 ± 32<br />
Said Otba 6 77 ± 27 21 ± 7 5.7 ± 0.9 3.3 ± 0.7 - 87 ± 29<br />
Total 72 66 ± 31 21 ± 7 6 ± 1 3 ± 1 - 74 ± 31<br />
ecologia mediterranea <strong>–</strong> <strong>Vol</strong>. <strong>35</strong> <strong>–</strong> <strong>2009</strong>