correction exercices Précis de Physique-Chimie chapitre 5 à 9
correction exercices Précis de Physique-Chimie chapitre 5 à 9
correction exercices Précis de Physique-Chimie chapitre 5 à 9
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
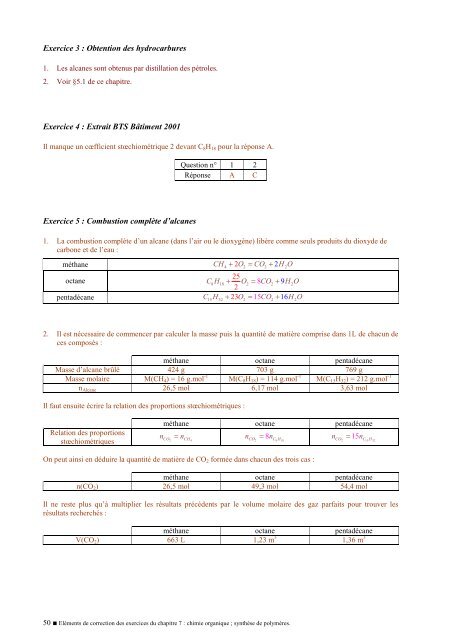
Exercice 3 : Obtention <strong>de</strong>s hydrocarbures<br />
1. Les alcanes sont obtenus par distillation <strong>de</strong>s pétroles.<br />
2. Voir §5.1 <strong>de</strong> ce <strong>chapitre</strong>.<br />
Exercice 4 : Extrait BTS Bâtiment 2001<br />
Il manque un cœfficient stœchiométrique 2 <strong>de</strong>vant C 8 H 18 pour la réponse A.<br />
Question n° 1 2<br />
Réponse A C<br />
Exercice 5 : Combustion complète d’alcanes<br />
1. La combustion complète d’un alcane (dans l’air ou le dioxygène) libère comme seuls produits du dioxy<strong>de</strong> <strong>de</strong><br />
carbone et <strong>de</strong> l’eau :<br />
méthane CH4 + 2O2 = CO2 + 2H 2O<br />
octane<br />
25<br />
C8 H18 + O2 = 8CO2 + 9H2O<br />
2<br />
pentadécane C15 H32 + 23O2 = 15CO2 + 16H 2O<br />
2. Il est nécessaire <strong>de</strong> commencer par calculer la masse puis la quantité <strong>de</strong> matière comprise dans 1L <strong>de</strong> chacun <strong>de</strong><br />
ces composés :<br />
méthane octane pentadécane<br />
Masse d’alcane brûlé 424 g 703 g 769 g<br />
Masse molaire M(CH 4 ) = 16 g.mol -1 M(C 8 H 18 ) = 114 g.mol -1 M(C 15 H 32 ) = 212 g.mol -1<br />
n Alcane 26,5 mol 6,17 mol 3,63 mol<br />
Il faut ensuite écrire la relation <strong>de</strong>s proportions stœchiométriques :<br />
méthane octane pentadécane<br />
Relation <strong>de</strong>s proportions<br />
nCO<br />
= n<br />
2 CH<br />
n<br />
4<br />
CO<br />
8n<br />
2 C8H<br />
n 15<br />
18<br />
CO<br />
= nC H<br />
stœchiométriques<br />
On peut ainsi en déduire la quantité <strong>de</strong> matière <strong>de</strong> CO 2 formée dans chacun <strong>de</strong>s trois cas :<br />
=<br />
2 15 32<br />
méthane octane pentadécane<br />
n(CO 2 ) 26,5 mol 49,3 mol 54,4 mol<br />
Il ne reste plus qu’à multiplier les résultats précé<strong>de</strong>nts par le volume molaire <strong>de</strong>s gaz parfaits pour trouver les<br />
résultats recherchés :<br />
méthane octane pentadécane<br />
V(CO 2 ) 663 L 1,23 m 3 1,36 m 3<br />
50 ■ Eléments <strong>de</strong> <strong>correction</strong> <strong>de</strong>s <strong>exercices</strong> du <strong>chapitre</strong> 7 : chimie organique ; synthèse <strong>de</strong> polymères.