Introduction à la théorie des poutres - mms2 - MINES ParisTech
Introduction à la théorie des poutres - mms2 - MINES ParisTech
Introduction à la théorie des poutres - mms2 - MINES ParisTech
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Théorie de Navier-Bernoulli, approche par le théorème de l’énergie<br />
potentielle<br />
Nous introduisons l’énergie potentielle qui sera exploitée dans le cours sur <strong>la</strong> théorie <strong>des</strong><br />
bifurcations et pour celui sur <strong>la</strong> théorie de stabilité.<br />
Il possible de déduire les lois de comportement <strong>des</strong> re<strong>la</strong>tions issues de <strong>la</strong> théorie générale <strong>des</strong><br />
milieux continus en appliquant le théorème de l’énergie potentielle avec l’hypothèse cinématique<br />
de Navier-Bernoulli.<br />
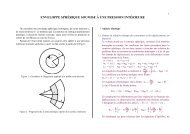
u = u 1 (x 1 , x 3 ) x 1 + u 3 (x 1 , x 3 ) x 3 ∀(x 1 , x 2 , x 3 ) ∈ Ω (40)<br />
u 1 = U(x 1 ) + θ(x 1 )x 3 u 3 = V (x 1 ) V ,1 + θ = 0 (41)<br />
⎛<br />
( ) ε.. = ⎝ U ⎞<br />
,1 − V ,11 x 3 0 0<br />
0 0 0⎠ (42)<br />
0 0 0<br />
W (ε ∼<br />
) = E 2 ε2 11<br />
∫ ∫<br />
F(U, V ) = W (ε ∼<br />
) dS dx 1 (43)<br />
C S<br />
− F 0 U(0) − F L U(L) − P 0 V (0) − P L V (L) − M 0 θ(0) − M L θ(L) (44)<br />
∫<br />
− (p V + t U) dx 1 (45)<br />
C<br />
MMS 2012, Théorie de Navier-Bernoulli <strong>Introduction</strong> à <strong>la</strong> théorie <strong>des</strong> <strong>poutres</strong> 26/28