Medicinus - Dexa Medica
Medicinus - Dexa Medica
Medicinus - Dexa Medica
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
14<br />
research original article<br />
glucose were purchased from Merck.<br />
Animals Experiment<br />
Wistar strain rats (Rattus norvegicus) (male, 8 weeks<br />
old, 200-220 g) were housed in individual cages in<br />
a room with controlled temperature and light (12h<br />
light:12-h dark cycle; lighting between 08:00 and<br />
20:00 h) and had free access to a standard diet and<br />
water. The animal study was conducted according<br />
to the regulation proposed by AAALAC (Association<br />
for Assessment and Accreditation of Laboratory Animal<br />
Care). The rats were aclimated for a week before<br />
treatment.<br />
Experimental Design<br />
Rats were allocated into 3 groups. The first group<br />
(n=7) was control group that was maintained on a<br />
standard diet. The second (n=7) and the third group<br />
(n=7) were maintained on a high-glucose diet for<br />
two weeks to make them insulin resistant with fructose<br />
15% and glucose 10%. The third group was later<br />
on treated with DLBS3233 at 9 mg/kg body weight<br />
for another two weeks. At the end of treatment period,<br />
blood samples were collected from tail veins of<br />
rats to measure the random glucose level. The rats<br />
of each group were then fasted overnight, fed and<br />
2 h later their blood samples were taken to measure<br />
the postprandial glucose. Furthermore, animals<br />
were fasted overnight again and blood sample was<br />
later collected by cardiac puncture which then was<br />
centrifuged at 8500 g for 25 min. The serum was<br />
separated out to measure the level of fasting glucose,<br />
insulin, triglycerides, total cholesterol, Low<br />
Density Lipoprotein (LDL), and High Density Lipoprotein<br />
(HDL). Mercodia Ultrasensitive Rat Insulin<br />
ELISA enzyme immunoassay (Uppsala, Sweden) and<br />
microplate reader (Bio-Rad) were used to measure<br />
the insulin level. Other tests were carried out using<br />
Semi Automated Clinical Chemistry Analyzer Microlab<br />
300 (Vital Scientific, Netherlands). In addition,<br />
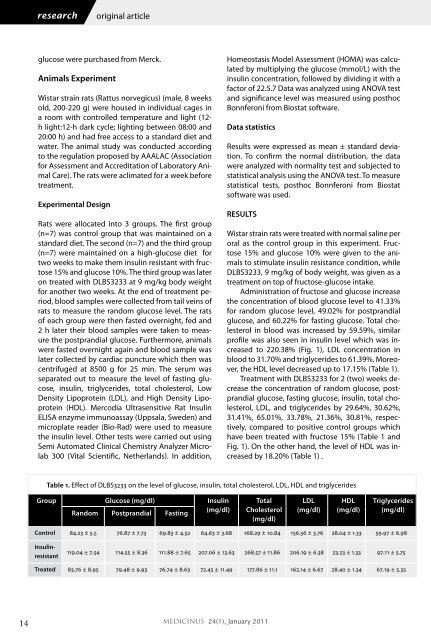
group glucose (mg/dl) Insulin<br />
Random Postprandial Fasting<br />
(mg/dl)<br />
MEDICINUS 24(1), January 2011<br />
Homeostasis Model Assessment (HOMA) was calculated<br />
by multiplying the glucose (mmol/L) with the<br />
insulin concentration, followed by dividing it with a<br />
factor of 22.5.7 Data was analyzed using ANOVA test<br />
and significance level was measured using posthoc<br />
Bonnferoni from Biostat software.<br />
Data statistics<br />
Results were expressed as mean ± standard deviation.<br />
To confirm the normal distribution, the data<br />
were analyzed with normality test and subjected to<br />
statistical analysis using the ANOVA test. To measure<br />
statistical tests, posthoc Bonnferoni from Biostat<br />
software was used.<br />
RESULTS<br />
Wistar strain rats were treated with normal saline per<br />
oral as the control group in this experiment. Fructose<br />
15% and glucose 10% were given to the animals<br />
to stimulate insulin resistance condition, while<br />
DLBS3233, 9 mg/kg of body weight, was given as a<br />
treatment on top of fructose-glucose intake.<br />
Administration of fructose and glucose increase<br />
the concentration of blood glucose level to 41.33%<br />
for random glucose level, 49.02% for postprandial<br />
glucose, and 60.22% for fasting glucose. Total cholesterol<br />
in blood was increased by 59.59%, similar<br />
profile was also seen in insulin level which was increased<br />
to 220.38% (Fig. 1), LDL concentration in<br />
blood to 31.70% and triglycerides to 61.39%. Moreover,<br />
the HDL level decreased up to 17.15% (Table 1).<br />
Treatment with DLBS3233 for 2 (two) weeks decrease<br />
the concentration of random glucose, postprandial<br />
glucose, fasting glucose, insulin, total cholesterol,<br />
LDL, and triglycerides by 29.64%, 30.62%,<br />
31.41%, 65.01%, 33.78%, 21.36%, 30.81%, respectively,<br />
compared to positive control groups which<br />
have been treated with fructose 15% (Table 1 and<br />
Fig. 1). On the other hand, the level of HDL was increased<br />
by 18.20% (Table 1) .<br />
Total<br />
Cholesterol<br />
(mg/dl)<br />
LDL<br />
(mg/dl)<br />
HDL<br />
(mg/dl)<br />
Triglycerides<br />
(mg/dl)<br />
Control 84.23 ± 5.5 76.87 ± 7.73 69.83 ± 4.52 64.63 ± 3.68 168.29 ± 10.84 156.56 ± 3.76 28.04 ± 1.33 59.97 ± 6.98<br />
Insulinresistant<br />
Table 1. Effect of DLBS3233 on the level of glucose, insulin, total cholesterol, LDL, HDL and triglycerides<br />
119.04 ± 7.54 114.55 ± 8.36 111.88 ± 7.65 207.06 ± 13.63 268.57 ± 11.86 206.19 ± 6.38 23.23 ± 1.33 97.11 ± 5.75<br />
Treated 83.76 ± 8.95 79.48 ± 9.93 76.74 ± 8.63 72.45 ± 11.49 177.86 ± 11.1 162.14 ± 6.67 28.40 ± 1.34 67.19 ± 5.35