Medicinus - Dexa Medica
Medicinus - Dexa Medica
Medicinus - Dexa Medica
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
NF-kB, TNFα, VCAM-1 and P-selectin. These markers<br />
were important in inflammation related to atherosclerosis.<br />
RAW 264.7 cells were able to down-regulate<br />
the expressions of NF-kB by 45% (Fig. 1a), TNFα by<br />
22% (Fig. 1b), VCAM-1 by 22% (Fig. 1c) and P-selectin<br />
(Fig. 1d) by 20%. To ascertain the effect of DLBS1033<br />
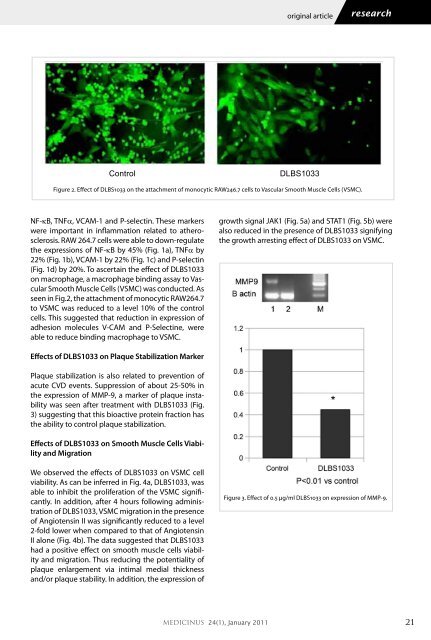
on macrophage, a macrophage binding assay to Vascular<br />
Smooth Muscle Cells (VSMC) was conducted. As<br />
seen in Fig.2, the attachment of monocytic RAW264.7<br />
to VSMC was reduced to a level 10% of the control<br />
cells. This suggested that reduction in expression of<br />
adhesion molecules V-CAM and P-Selectine, were<br />
able to reduce binding macrophage to VSMC.<br />
Effects of DLBS1033 on Plaque Stabilization Marker<br />
Plaque stabilization is also related to prevention of<br />
acute CVD events. Suppression of about 25-50% in<br />
the expression of MMP-9, a marker of plaque instability<br />
was seen after treatment with DLBS1033 (Fig.<br />
3) suggesting that this bioactive protein fraction has<br />
the ability to control plaque stabilization.<br />
Effects of DLBS1033 on Smooth Muscle Cells Viability<br />
and Migration<br />
We observed the effects of DLBS1033 on VSMC cell<br />
viability. As can be inferred in Fig. 4a, DLBS1033, was<br />
able to inhibit the proliferation of the VSMC significantly.<br />
In addition, after 4 hours following administration<br />
of DLBS1033, VSMC migration in the presence<br />
of Angiotensin II was significantly reduced to a level<br />
2-fold lower when compared to that of Angiotensin<br />
II alone (Fig. 4b). The data suggested that DLBS1033<br />
had a positive effect on smooth muscle cells viability<br />
and migration. Thus reducing the potentiality of<br />
plaque enlargement via intimal medial thickness<br />
and/or plaque stability. In addition, the expression of<br />
original article<br />
Control DLBS1033<br />
Figure 2. Effect of DLBS1033 on the attachment of monocytic RAW246.7 cells to Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells (VSMC).<br />
research<br />
growth signal JAK1 (Fig. 5a) and STAT1 (Fig. 5b) were<br />
also reduced in the presence of DLBS1033 signifying<br />
the growth arresting effect of DLBS1033 on VSMC.<br />
Figure 3. Effect of 0.5 μg/ml DLBS1033 on expression of MMP-9.<br />
MEDICINUS 24(1), January 2011 21