Medicinus - Dexa Medica
Medicinus - Dexa Medica
Medicinus - Dexa Medica
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
38<br />
technology<br />
cal characteristics, for chemical characteristics such<br />
as qualitative and quantitative standardization, and<br />
for potential impurities, and total aerobic microbial<br />
count. All three types of test are relevant at the time<br />
of formulation into dosage forms. The testing of<br />
physical properties of soft extracts determines formulation<br />
into dosage form, and its testing of chemical<br />
properties influencing the method of fabrication.<br />
For the preparation of solid dosage forms mostly<br />
dry extracts are used. Except in rare cases, dry extracts<br />
are hygroscopic and so they cannot be used<br />
without prior granulation for preparing tablets.<br />
Granulation is thus the critical stage in the process of<br />
preparing all solid dosage forms containing extracts.<br />
To overcome the problem of hygroscopic, Aerosil,<br />
a high porosity excipient, is widely used. Further<br />
when operating with wet granulation, it is advisable<br />
to use binders such us cellulose derivatives or polyvinylpirolidon<br />
in solution with organic solvents. If<br />
aqueous solutions of cellulose derivatives, gum arabic,<br />
gelatin, or aqueous gel such as starch mucilage<br />
are used, several problems may arise in the course<br />
of processing, especially if the formulation involves<br />
large quantities of extracts.<br />
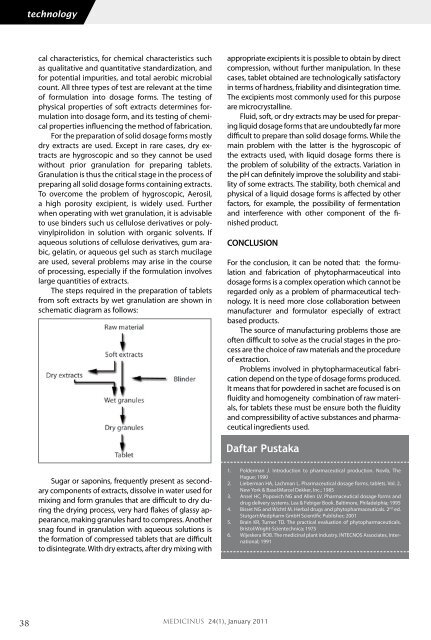
The steps required in the preparation of tablets<br />
from soft extracts by wet granulation are shown in<br />
schematic diagram as follows:<br />
Sugar or saponins, frequently present as secondary<br />
components of extracts, dissolve in water used for<br />
mixing and form granules that are difficult to dry during<br />
the drying process, very hard flakes of glassy appearance,<br />
making granules hard to compress. Another<br />
snag found in granulation with aqueous solutions is<br />
the formation of compressed tablets that are difficult<br />
to disintegrate. With dry extracts, after dry mixing with<br />
MEDICINUS 24(1), January 2011<br />
appropriate excipients it is possible to obtain by direct<br />
compression, without further manipulation. In these<br />
cases, tablet obtained are technologically satisfactory<br />
in terms of hardness, friability and disintegration time.<br />
The excipients most commonly used for this purpose<br />
are microcrystalline.<br />
Fluid, soft, or dry extracts may be used for preparing<br />
liquid dosage forms that are undoubtedly far more<br />
difficult to prepare than solid dosage forms. While the<br />
main problem with the latter is the hygroscopic of<br />
the extracts used, with liquid dosage forms there is<br />
the problem of solubility of the extracts. Variation in<br />
the pH can definitely improve the solubility and stability<br />
of some extracts. The stability, both chemical and<br />
physical of a liquid dosage forms is affected by other<br />
factors, for example, the possibility of fermentation<br />
and interference with other component of the finished<br />
product.<br />
CONCLUSION<br />
For the conclusion, it can be noted that: the formulation<br />
and fabrication of phytopharmaceutical into<br />
dosage forms is a complex operation which cannot be<br />
regarded only as a problem of pharmaceutical technology.<br />
It is need more close collaboration between<br />
manufacturer and formulator especially of extract<br />
based products.<br />
The source of manufacturing problems those are<br />
often difficult to solve as the crucial stages in the process<br />
are the choice of raw materials and the procedure<br />
of extraction.<br />
Problems involved in phytopharmaceutical fabrication<br />
depend on the type of dosage forms produced.<br />
It means that for powdered in sachet are focused is on<br />
fluidity and homogeneity combination of raw materials,<br />
for tablets these must be ensure both the fluidity<br />
and compressibility of active substances and pharmaceutical<br />
ingredients used.<br />
Daftar Pustaka<br />
1. Polderman J. Introduction to pharmaceutical production. Novib, The<br />
Hague; 1990<br />
2. Lieberman HA, Lachman L. Pharmaceutical dosage forms, tablets. Vol. 2,<br />
New York & Basel:Marcel Dekker, Inc.; 1985<br />
3. Ansel HC, Popovich NG and Allen LV. Pharmaceutical dosage forms and<br />
drug delivery systems. Lea & Febiger Book. Baltimore, Philadelphia; 1995<br />
4. Bisset NG and Wichtl M. Herbal drugs and phytopharmaceuticals. 2 nd ed.<br />
Stutgart:Medpharm GmbH Scientific Publisher; 2001<br />
5. Brain KR, Turner TD. The practical evaluation of phytopharmaceuticals.<br />
Bristol:Wright-Scientechnica; 1975<br />
6. Wijeskera ROB. The medicinal plant industry. INTECNOS Associates, International;<br />
1991