Dispensa in PDF - Dipartimento di Scienze Ambientali, Informatica e ...
Dispensa in PDF - Dipartimento di Scienze Ambientali, Informatica e ...
Dispensa in PDF - Dipartimento di Scienze Ambientali, Informatica e ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
C 1<br />
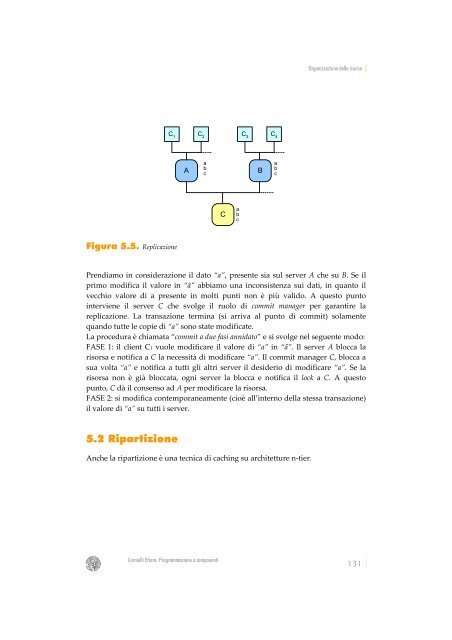
Figura 5.5. Replicazione<br />
A<br />
C 2<br />
a<br />
b<br />
c<br />
Carnielli Efrem: Programmazione a componenti<br />
C<br />
a<br />
b<br />
c<br />
C 3<br />
B<br />
C 4<br />
a<br />
b<br />
c<br />
Organizzazione delle risorse<br />
Pren<strong>di</strong>amo <strong>in</strong> considerazione il dato “a”, presente sia sul server A che su B. Se il<br />
primo mo<strong>di</strong>fica il valore <strong>in</strong> “ã” abbiamo una <strong>in</strong>consistenza sui dati, <strong>in</strong> quanto il<br />
vecchio valore <strong>di</strong> a presente <strong>in</strong> molti punti non è più valido. A questo punto<br />
<strong>in</strong>terviene il server C che svolge il ruolo <strong>di</strong> commit manager per garantire la<br />
replicazione. La transazione term<strong>in</strong>a (si arriva al punto <strong>di</strong> commit) solamente<br />
quando tutte le copie <strong>di</strong> “a” sono state mo<strong>di</strong>ficate.<br />
La procedura è chiamata “commit a due fasi annidato” e si svolge nel seguente modo:<br />
FASE 1: il client C1 vuole mo<strong>di</strong>ficare il valore <strong>di</strong> “a” <strong>in</strong> “ã”. Il server A blocca la<br />
risorsa e notifica a C la necessità <strong>di</strong> mo<strong>di</strong>ficare “a”. Il commit manager C, blocca a<br />
sua volta “a” e notifica a tutti gli altri server il desiderio <strong>di</strong> mo<strong>di</strong>ficare “a”. Se la<br />
risorsa non è già bloccata, ogni server la blocca e notifica il lock a C. A questo<br />
punto, C dà il consenso ad A per mo<strong>di</strong>ficare la risorsa.<br />
FASE 2: si mo<strong>di</strong>fica contemporaneamente (cioè all’<strong>in</strong>terno della stessa transazione)<br />
il valore <strong>di</strong> “a” su tutti i server.<br />
5.2 Ripartizione<br />
Anche la ripartizione è una tecnica <strong>di</strong> cach<strong>in</strong>g su architetture n-tier.<br />
131