Fokker-Planck-Gleichung
Fokker-Planck-Gleichung
Fokker-Planck-Gleichung
Sie wollen auch ein ePaper? Erhöhen Sie die Reichweite Ihrer Titel.
YUMPU macht aus Druck-PDFs automatisch weboptimierte ePaper, die Google liebt.
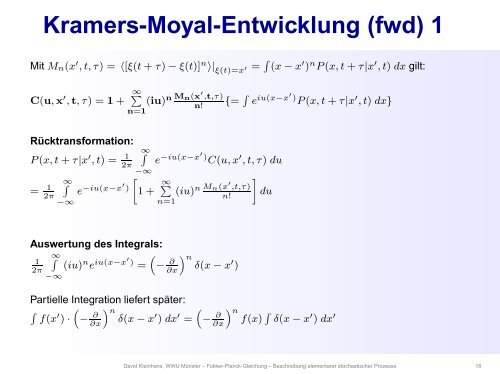
Kramers-Moyal-Entwicklung (fwd) 1<br />
Mit M n (x ′ , t, τ) = 〈[ξ(t + τ) − ξ(t)] n 〉| ξ(t)=x ′ = ∫ (x − x ′ ) n P(x, t + τ|x ′ , t) dx gilt:<br />
C(u,x ′ ,t, τ) = 1 + ∞ ∑<br />
(iu) n M n (x ′ ,t,τ)<br />
n=1<br />
n!<br />
{= ∫ e iu(x−x′) P(x, t + τ|x ′ , t) dx}<br />
Rücktransformation:<br />
P(x, t + τ|x ′ , t) = 1<br />
2π<br />
= 1<br />
2π<br />
∞∫<br />
−∞<br />
e −iu(x−x′ )<br />
∞∫<br />
−∞<br />
[<br />
1 + ∞ ∑<br />
e −iu(x−x′) C(u, x ′ , t, τ) du<br />
(iu) n M n (x ′ ,t,τ)<br />
n!<br />
n=1<br />
]<br />
du<br />
Auswertung des Integrals:<br />
∞∫<br />
(iu) n e iu(x−x′) =<br />
1<br />
2π<br />
−∞<br />
Partielle Integration liefert später:<br />
∫<br />
f(x ′ ) ·<br />
(− ∂<br />
∂x) n<br />
δ(x − x ′ ) dx ′ =<br />
(<br />
− ∂<br />
∂x) n<br />
δ(x − x ′ )<br />
( ) n<br />
− ∂ ∫<br />
∂x f(x) δ(x − x ′ ) dx ′<br />
David Kleinhans, WWU Münster – <strong>Fokker</strong>-<strong>Planck</strong>-<strong>Gleichung</strong> – Beschreibung elementarer stochastischer Prozesse 18