Fugacity: It is derived from Latin, expressed as fleetness or escaping ...
Fugacity: It is derived from Latin, expressed as fleetness or escaping ...
Fugacity: It is derived from Latin, expressed as fleetness or escaping ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Ph<strong>as</strong>e Diagram f<strong>or</strong> Binary solution<br />
Constant pressure equilibrium<br />
Consider a Binary system made up of component A and B. Where it <strong>is</strong> <strong>as</strong>sumed to be<br />
m<strong>or</strong>e volatile than B where vapour pressure ‘A’ <strong>is</strong> m<strong>or</strong>e than ‘B’. When the pressure <strong>is</strong><br />
fixed at the liquid composition can be changed the properities such <strong>as</strong> temperature and<br />
vapour compositions get quickly determined VLE at constant pressure <strong>is</strong> represented on<br />
T-xy diagram.<br />
Boiling point diagrams<br />
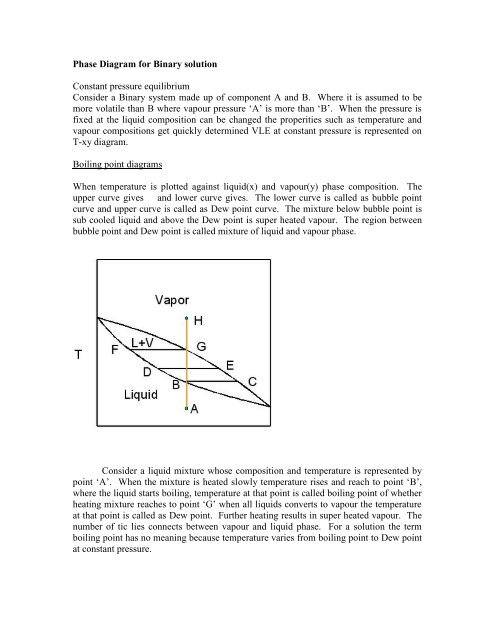
When temperature <strong>is</strong> plotted against liquid(x) and vapour(y) ph<strong>as</strong>e composition. The<br />
upper curve gives and lower curve gives. The lower curve <strong>is</strong> called <strong>as</strong> bubble point<br />
curve and upper curve <strong>is</strong> called <strong>as</strong> Dew point curve. The mixture below bubble point <strong>is</strong><br />
sub cooled liquid and above the Dew point <strong>is</strong> super heated vapour. The region between<br />
bubble point and Dew point <strong>is</strong> called mixture of liquid and vapour ph<strong>as</strong>e.<br />
Consider a liquid mixture whose composition and temperature <strong>is</strong> represented by<br />
point ‘A’. When the mixture <strong>is</strong> heated slowly temperature r<strong>is</strong>es and reach to point ‘B’,<br />
where the liquid starts boiling, temperature at that point <strong>is</strong> called boiling point of whether<br />
heating mixture reaches to point ‘G’ when all liquids converts to vapour the temperature<br />
at that point <strong>is</strong> called <strong>as</strong> Dew point. Further heating results in super heated vapour. The<br />
number of tic lies connects between vapour and liquid ph<strong>as</strong>e. F<strong>or</strong> a solution the term<br />
boiling point h<strong>as</strong> no meaning because temperature varies <strong>from</strong> boiling point to Dew point<br />
at constant pressure.