- Page 3 and 4:
Hacking FOR DUMmIES‰ 4TH EDITION
- Page 5 and 6:
About the Author Kevin Beaver is an
- Page 7 and 8:
Mega thanks to Queensrÿche, Rush,
- Page 9 and 10:
Contents at a Glance Introduction .
- Page 11 and 12:
Table of Contents Introduction ....
- Page 13 and 14:
Table of Contents Performing Social
- Page 15 and 16:
Table of Contents Gathering Informa
- Page 17 and 18:
Table of Contents Part VI: Ethical
- Page 19 and 20:
Introduction W elcome to Hacking Fo
- Page 21 and 22:
Introduction Before you start hacki
- Page 23 and 24:
Introduction well-known vulnerabili
- Page 25 and 26:
Part I Building the Foundation for
- Page 27 and 28:
Chapter 1 Introduction to Ethical H
- Page 29 and 30:
Chapter 1: Introduction to Ethical
- Page 31 and 32:
Chapter 1: Introduction to Ethical
- Page 33 and 34:
Chapter 1: Introduction to Ethical
- Page 35 and 36:
Obeying the Ethical Hacking Command
- Page 37 and 38:
Formulating your plan Chapter 1: In
- Page 39 and 40:
Chapter 1: Introduction to Ethical
- Page 41 and 42:
Chapter 1: Introduction to Ethical
- Page 43 and 44:
Chapter 2 Cracking the Hacker Minds
- Page 45 and 46:
Malicious attackers often think and
- Page 47 and 48:
Chapter 2: Cracking the Hacker Mind
- Page 49 and 50:
Chapter 2: Cracking the Hacker Mind
- Page 51 and 52:
Chapter 2: Cracking the Hacker Mind
- Page 53 and 54:
In This Chapter Chapter 3 Developin
- Page 55 and 56:
Chapter 3: Developing Your Ethical
- Page 57 and 58:
Attack tree analysis is the process
- Page 59 and 60:
Timing Chapter 3: Developing Your E
- Page 61 and 62:
Chapter 3: Developing Your Ethical
- Page 63 and 64:
Chapter 3: Developing Your Ethical
- Page 65 and 66:
In This Chapter Chapter 4 Hacking M
- Page 67 and 68:
Chapter 4: Hacking Methodology no o
- Page 69 and 70:
Chapter 4: Hacking Methodology ✓
- Page 71 and 72:
Chapter 4: Hacking Methodology One
- Page 73 and 74:
Chapter 4: Hacking Methodology test
- Page 75 and 76:
Figure 4-1: Netcraft’s web server
- Page 77 and 78:
Chapter 4: Hacking Methodology docu
- Page 79 and 80:
Penetrating the System Chapter 4: H
- Page 81 and 82:
Part II Putting Ethical Hacking in
- Page 83 and 84:
In This Chapter ▶ Discovering soc
- Page 85 and 86:
Chapter 5: Social Engineering A cas
- Page 87 and 88:
Chapter 5: Social Engineering Socia
- Page 89 and 90:
Chapter 5: Social Engineering Regar
- Page 91 and 92:
Chapter 5: Social Engineering years
- Page 93 and 94:
✓ Threatening reprimands if reque
- Page 95 and 96:
Chapter 5: Social Engineering In so
- Page 97 and 98:
Chapter 5: Social Engineering reque
- Page 99 and 100:
In This Chapter Chapter 6 Physical
- Page 101 and 102:
Chapter 6: Physical Security A Q&A
- Page 103 and 104:
Chapter 6: Physical Security ✓ Do
- Page 105 and 106:
Chapter 6: Physical Security ✓ Do
- Page 107 and 108:
Chapter 6: Physical Security cellul
- Page 109 and 110:
Chapter 6: Physical Security ✓ Ke
- Page 111 and 112:
In This Chapter ▶ Identifying pas
- Page 113 and 114:
Chapter 7: Passwords A case study i
- Page 115 and 116:
Chapter 7: Passwords The National V
- Page 117 and 118:
Chapter 7: Passwords they should’
- Page 119 and 120:
Chapter 7: Passwords ✓ John the R
- Page 121 and 122:
Chapter 7: Passwords Dictionary att
- Page 123 and 124:
Chapter 7: Passwords this password
- Page 125 and 126:
Chapter 7: Passwords Cracking UNIX/
- Page 127 and 128:
Chapter 7: Passwords The financial
- Page 129 and 130:
Chapter 7: Passwords (www.identityf
- Page 131 and 132:
Chapter 7: Passwords Weak BIOS pass
- Page 133 and 134:
Storing passwords Chapter 7: Passwo
- Page 135 and 136:
Chapter 7: Passwords your systems.
- Page 137 and 138:
Linux and UNIX Chapter 7: Passwords
- Page 139 and 140:
Part III Hacking Network Hosts
- Page 141 and 142:
In This Chapter ▶ Selecting tools
- Page 143 and 144:
Chapter 8: Network Infrastructure U
- Page 145 and 146:
Chapter 8: Network Infrastructure
- Page 147 and 148: Chapter 8: Network Infrastructure I
- Page 149 and 150: Chapter 8: Network Infrastructure 3
- Page 151 and 152: Figure 8-3: NetScan- Tools Pro OS F
- Page 153 and 154: Figure 8-5: Management interface us
- Page 155 and 156: Chapter 8: Network Infrastructure W
- Page 157 and 158: Chapter 8: Network Infrastructure C
- Page 159 and 160: Figure 8-8: Connecting a network an
- Page 161 and 162: Figure 8-9: OmniPeek can help uncov
- Page 163 and 164: Chapter 8: Network Infrastructure N
- Page 165 and 166: Figure 8-12: Selecting your victim
- Page 167 and 168: UNIX-based systems Chapter 8: Netwo
- Page 169 and 170: Chapter 8: Network Infrastructure W
- Page 171 and 172: Chapter 8: Network Infrastructure C
- Page 173 and 174: Figure 8-14: Cisco Global Exploiter
- Page 175 and 176: In This Chapter ▶ Understanding r
- Page 177 and 178: A case study with Joshua Wright on
- Page 179 and 180: Discovering Wireless LANs Figure 9-
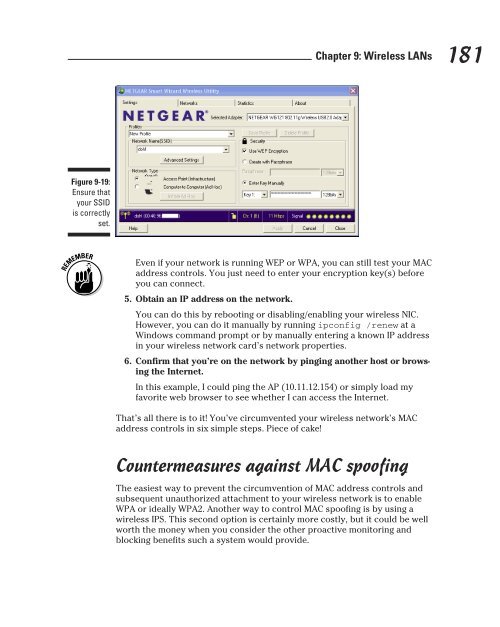
- Page 181 and 182: Figure 9-3: NetStumbler displays de
- Page 183 and 184: You undoubtedly have various Blueto
- Page 185 and 186: Chapter 9: Wireless LANs Airodump a
- Page 187 and 188: Figure 9-8: Using Elcomsoft Wireles
- Page 189 and 190: Figure 9-10: The Reaver startup win
- Page 191 and 192: Figure 9-12: NetStumbler showing po
- Page 193 and 194: Figure 9-15: CommView for Wifi show
- Page 195 and 196: Chapter 9: Wireless LANs ✓ If pos
- Page 197: Figure 9-17: Looking for the MAC ad
- Page 201 and 202: Chapter 9: Wireless LANs encryption
- Page 203 and 204: In This Chapter Chapter 10 Mobile D
- Page 205 and 206: Chapter 10: Mobile Devices You have
- Page 207 and 208: Figure 10-3: Usernames extracted vi
- Page 209 and 210: Chapter 10: Mobile Devices Power-on
- Page 211 and 212: Figure 10-5: iOS Forensic Toolkit
- Page 213 and 214: Chapter 10: Mobile Devices So, havi
- Page 215 and 216: Part IV Hacking Operating Systems
- Page 217 and 218: In This Chapter ▶ Port scanning W
- Page 219 and 220: Choosing Tools Chapter 11: Windows
- Page 221 and 222: Chapter 11: Windows Windows XP SP2
- Page 223 and 224: Figure 11-2: Gathering detailed vul
- Page 225 and 226: Figure 11-5: Using LanGuard to scan
- Page 227 and 228: Figure 11-6: Mapping a null session
- Page 229 and 230: ✓ Local usernames ✓ Drive share
- Page 231 and 232: Figure 11-9: Default local security
- Page 233 and 234: Figure 11-10: Using LanGuard’s sh
- Page 235 and 236: Figure 11-11: Exploitable vulnerabi
- Page 237 and 238: Figure 11-13: Browsing the availabl
- Page 239 and 240: Figure 11-17: Checking final parame
- Page 241 and 242: Figure 11-19: Metasploit Pro’s gr
- Page 243 and 244: Running Authenticated Scans Figure
- Page 245 and 246: In This Chapter ▶ Examining Linux
- Page 247 and 248: Chapter 12: Linux A tool such as Qu
- Page 249 and 250:
Figure 12-3: LanGuard revealing use
- Page 251 and 252:
Figure 12-6: Using NetScan Tools Pr
- Page 253 and 254:
Figure 12-7: Using Nmap to check ap
- Page 255 and 256:
Figure 12-9: Viewing the process ID
- Page 257 and 258:
Chapter 12: Linux Hacks using the .
- Page 259 and 260:
Chapter 12: Linux ✓ Block spoofed
- Page 261 and 262:
Chapter 12: Linux Manual testing Th
- Page 263 and 264:
Figure 12-11: /etc/inittab showing
- Page 265 and 266:
Figure 12-13: Partial output of the
- Page 267 and 268:
Part V Hacking Applications
- Page 269 and 270:
In This Chapter ▶ Attacking e-mai
- Page 271 and 272:
E-mail bombs Chapter 13: Communicat
- Page 273 and 274:
Figure 13-1: Limiting the number of
- Page 275 and 276:
Figure 13-4: smtpscan gathers versi
- Page 277 and 278:
Figure 13-7: Using EmailVerify to v
- Page 279 and 280:
Chapter 13: Communication and Messa
- Page 281 and 282:
Manual testing Chapter 13: Communic
- Page 283 and 284:
Figure 13-11: Critical information
- Page 285 and 286:
Chapter 13: Communication and Messa
- Page 287 and 288:
Chapter 13: Communication and Messa
- Page 289 and 290:
Chapter 13: Communication and Messa
- Page 291 and 292:
Figure 13-15: SiVuS discovered seve
- Page 293 and 294:
Figure 13-16: Using Cain & Abel to
- Page 295 and 296:
In This Chapter Chapter 14 Websites
- Page 297 and 298:
Chapter 14: Websites and Applicatio
- Page 299 and 300:
Figure 14-1: Using HTTrack to crawl
- Page 301 and 302:
Countermeasures against directory t
- Page 303 and 304:
Figure 14-2: Using Firefox Web Deve
- Page 305 and 306:
Figure 14-3: Using SPI Proxy to fin
- Page 307 and 308:
Figure 14-4: WebInspect discovered
- Page 309 and 310:
Figure 14-7: Script code reflected
- Page 311 and 312:
Chapter 14: Websites and Applicatio
- Page 313 and 314:
Figure 14-9: URL returns an error w
- Page 315 and 316:
Figure 14-11: The Brutus tool for t
- Page 317 and 318:
Chapter 14: Websites and Applicatio
- Page 319 and 320:
Chapter 14: Websites and Applicatio
- Page 321 and 322:
Figure 14-13: Using CxDeveloper to
- Page 323 and 324:
Chapter 15 Databases and Storage Sy
- Page 325 and 326:
The Situation Chapter 15: Databases
- Page 327 and 328:
Figure 15-2: Using Cain & Abel to c
- Page 329 and 330:
Chapter 15: Databases and Storage S
- Page 331 and 332:
Figure 15-3: Using FileLocator Pro
- Page 333 and 334:
Chapter 15: Databases and Storage S
- Page 335 and 336:
Part VI Ethical Hacking Aftermath
- Page 337 and 338:
In This Chapter Chapter 16 Reportin
- Page 339 and 340:
Chapter 16: Reporting Your Results
- Page 341 and 342:
✓ Summary of the vulnerabilities
- Page 343 and 344:
In This Chapter Chapter 17 Plugging
- Page 345 and 346:
Patch management Chapter 17: Pluggi
- Page 347 and 348:
I was once involved in an incident
- Page 349 and 350:
Chapter 18 Managing Security Proces
- Page 351 and 352:
Chapter 18: Managing Security Proce
- Page 353 and 354:
Chapter 18: Managing Security Proce
- Page 355 and 356:
Chapter 18: Managing Security Proce
- Page 357 and 358:
Part VII The Part of Tens
- Page 359 and 360:
Chapter 19 Ten Tips for Getting Upp
- Page 361 and 362:
Chapter 19: Ten Tips for Getting Up
- Page 363 and 364:
Chapter 19: Ten Tips for Getting Up
- Page 365 and 366:
Chapter 20 Ten Reasons Hacking Is t
- Page 367 and 368:
Chapter 20: Ten Reasons Hacking Is
- Page 369 and 370:
Chapter 21 Ten Deadly Mistakes S ev
- Page 371 and 372:
Thinking That You Know It All Chapt
- Page 373 and 374:
Appendix Tools and Resources T o st
- Page 375 and 376:
Exploits Appendix: Tools and Resour
- Page 377 and 378:
Keyloggers Appendix: Tools and Reso
- Page 379 and 380:
mailsnarf — www.monkey.org/~dugso
- Page 381 and 382:
Appendix: Tools and Resources PortS
- Page 383 and 384:
Appendix: Tools and Resources pwdum
- Page 385 and 386:
Source Code Analysis Storage Checkm
- Page 387 and 388:
Appendix: Tools and Resources NIST
- Page 389 and 390:
Windows Appendix: Tools and Resourc
- Page 391 and 392:
• A • aboveboard, 11 Abuse.net
- Page 393 and 394:
Cobb, Chey (author) Network Securit
- Page 395 and 396:
802.11 encryption protocols, 165, 1
- Page 397 and 398:
Health Insurance Portability and Ac
- Page 399 and 400:
malware, 151, 266-267, 355 Managing
- Page 401 and 402:
• P • packet filtering, 156 Pan
- Page 403 and 404:
Remember icon, 6 remote access serv
- Page 405 and 406:
SUSE, 247 SUSE Linux Security Alert
- Page 407 and 408:
Virtual Private Network (VPN) servi
- Page 409 and 410:
Apple & Mac iPad 2 For Dummies, 3rd