Advanced Wind Turbine Program Next Generation Turbine ... - NREL
Advanced Wind Turbine Program Next Generation Turbine ... - NREL
Advanced Wind Turbine Program Next Generation Turbine ... - NREL
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
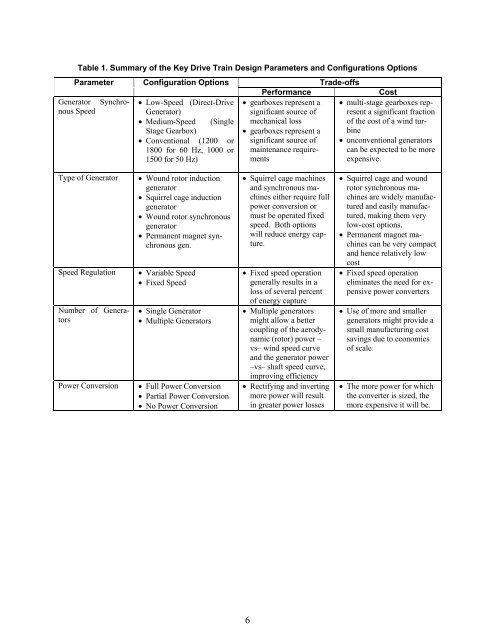
Table 1. Summary of the Key Drive Train Design Parameters and Configurations Options<br />
Parameter Configuration Options Trade-offs<br />
Performance Cost<br />
Generator Synchro • Low-Speed (Direct-Drive • gearboxes represent a • multi-stage gearboxes repnous<br />
Speed<br />
Generator)<br />
significant source of resent a significant fraction<br />
• Medium-Speed (Single mechanical loss<br />
of the cost of a wind tur<br />
Stage Gearbox)<br />
• gearboxes represent a bine<br />
• Conventional (1200 or significant source of • unconventional generators<br />
1800 for 60 Hz, 1000 or maintenance require can be expected to be more<br />
1500 for 50 Hz) ments expensive.<br />
Type of Generator • Wound rotor induction • Squirrel cage machines • Squirrel cage and wound<br />
generator and synchronous ma- rotor synchronous ma<br />
• Squirrel cage induction chines either require full chines are widely manufac<br />
generator<br />
power conversion or tured and easily manufac<br />
• Wound rotor synchronous must be operated fixed tured, making them very<br />
generator<br />
speed. Both options low-cost options.<br />
• Permanent magnet syn will reduce energy cap • Permanent magnet machronous<br />
gen.<br />
ture.chines<br />
can be very compact<br />
and hence relatively low<br />
cost<br />
Speed Regulation • Variable Speed • Fixed speed operation • Fixed speed operation<br />
• Fixed Speed generally results in a eliminates the need for ex<br />
loss of several percent<br />
of energy capture<br />
pensive power converters<br />
Number of Genera • Single Generator • Multiple generators • Use of more and smaller<br />
tors • Multiple Generators might allow a better generators might provide a<br />
coupling of the aerody small manufacturing cost<br />
namic (rotor) power – savings due to economies<br />
vs– wind speed curve<br />
and the generator power<br />
–vs– shaft speed curve,<br />
improving efficiency<br />
of scale<br />
Power Conversion • Full Power Conversion • Rectifying and inverting • The more power for which<br />
• Partial Power Conversion more power will result the converter is sized, the<br />
• No Power Conversion in greater power losses more expensive it will be.<br />
6