PROCEEDINGS OF THE 7 INTERNATIONAL ... - Fizika
PROCEEDINGS OF THE 7 INTERNATIONAL ... - Fizika
PROCEEDINGS OF THE 7 INTERNATIONAL ... - Fizika
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
N. Kazuchits et al. / Medical Physics in the Baltic States 7 (2009) 76 - 78<br />
results are in good agreement with mentioned above<br />
signal fluctuations. The same measurements carried out<br />
with integration time of 4,5 s correspond to the<br />
reference measurements with natural diamond detector.<br />
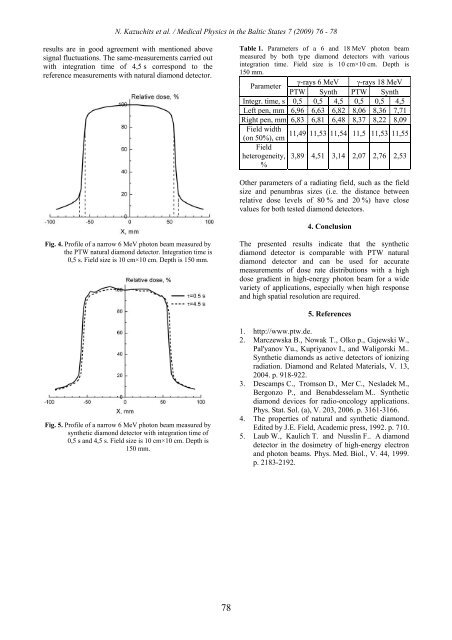
Fig. 4. Profile of a narrow 6 MeV photon beam measured by<br />
the PTW natural diamond detector. Integration time is<br />
0,5 s. Field size is 10 cm×10 cm. Depth is 150 mm.<br />
Fig. 5. Profile of a narrow 6 MeV photon beam measured by<br />
synthetic diamond detector with integration time of<br />
0,5 s and 4,5 s. Field size is 10 cm×10 cm. Depth is<br />
150 mm.<br />
78<br />
Table 1. Parameters of a 6 and 18 MeV photon beam<br />
measured by both type diamond detectors with various<br />
integration time. Field size is 10 cm×10 cm. Depth is<br />
150 mm.<br />
Parameter<br />
γ-rays 6 МeV<br />
PTW Synth<br />
γ-rays 18 МeV<br />
PTW Synth<br />
Integr. time, s 0,5 0,5 4,5 0,5 0,5 4,5<br />
Left pen, mm 6,96 6,63 6,82 8,06 8,36 7,71<br />
Right pen, mm 6,83 6,81 6,48 8,37 8,22 8,09<br />
Field width<br />
11,49 11,53 11,54 11,5 11,53 11,55<br />
(on 50%), cm<br />
Field<br />
heterogeneity,<br />
%<br />
3,89 4,51 3,14 2,07 2,76 2,53<br />
Other parameters of a radiating field, such as the field<br />
size and penumbras sizes (i.e. the distance between<br />
relative dose levels of 80 % and 20 %) have close<br />
values for both tested diamond detectors.<br />
4. Conclusion<br />
The presented results indicate that the synthetic<br />
diamond detector is comparable with PTW natural<br />
diamond detector and can be used for accurate<br />
measurements of dose rate distributions with a high<br />
dose gradient in high-energy photon beam for a wide<br />
variety of applications, especially when high response<br />
and high spatial resolution are required.<br />
5. References<br />
1. http://www.ptw.de.<br />
2. Marczewska B., Nowak T., Olko p., Gajewski W.,<br />
Pal'yanov Yu., Kupriyanov I., and Waligorski M..<br />
Synthetic diamonds as active detectors of ionizing<br />
radiation. Diamond and Related Materials, V. 13,<br />
2004. p. 918-922.<br />
3. Descamps C., Tromson D., Mer C., Nesladek M.,<br />
Bergonzo P., and Benabdesselam M.. Synthetic<br />
diamond devices for radio-oncology applications.<br />
Phys. Stat. Sol. (a), V. 203, 2006. p. 3161-3166.<br />
4. The properties of natural and synthetic diamond.<br />
Edited by J.E. Field, Academic press, 1992. p. 710.<br />
5. Laub W., Kaulich T. and Nusslin F.. A diamond<br />
detector in the dosimetry of high-energy electron<br />
and photon beams. Phys. Med. Biol., V. 44, 1999.<br />
p. 2183-2192.