View/Open - Università degli Studi di Milano-Bicocca
View/Open - Università degli Studi di Milano-Bicocca
View/Open - Università degli Studi di Milano-Bicocca
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Introduction<br />
response [54]. CTC1 is also one of the 8 telomere maintenance genes with<br />
mutations observed in patients with dyskeratosis congenita, a rare inherited<br />
bone marrow failure syndrome [55]. Altogether, the above data in<strong>di</strong>cates that<br />
CST complex is essential for telomere protection and maintenance from yeast<br />
to plants and humans.<br />
Telomeric duplex DNA bin<strong>di</strong>ng proteins<br />
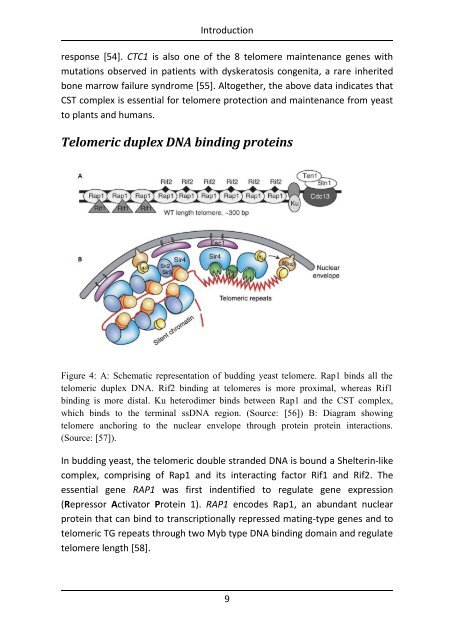
Figure 4: A: Schematic representation of bud<strong>di</strong>ng yeast telomere. Rap1 binds all the<br />
telomeric duplex DNA. Rif2 bin<strong>di</strong>ng at telomeres is more proximal, whereas Rif1<br />
bin<strong>di</strong>ng is more <strong>di</strong>stal. Ku hetero<strong>di</strong>mer binds between Rap1 and the CST complex,<br />
which binds to the terminal ssDNA region. (Source: [56]) B: Diagram showing<br />
telomere anchoring to the nuclear envelope through protein protein interactions.<br />
(Source: [57]).<br />
In bud<strong>di</strong>ng yeast, the telomeric double stranded DNA is bound a Shelterin-like<br />
complex, comprising of Rap1 and its interacting factor Rif1 and Rif2. The<br />
essential gene RAP1 was first indentified to regulate gene expression<br />
(Repressor Activator Protein 1). RAP1 encodes Rap1, an abundant nuclear<br />
protein that can bind to transcriptionally repressed mating-type genes and to<br />
telomeric TG repeats through two Myb type DNA bin<strong>di</strong>ng domain and regulate<br />
telomere length [58].<br />
9