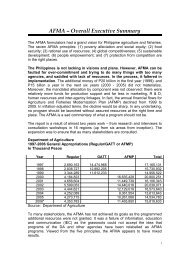
5. Key Commodity Performance - National Agricultural and Fishery ...
5. Key Commodity Performance - National Agricultural and Fishery ...
5. Key Commodity Performance - National Agricultural and Fishery ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
<strong>5.</strong>6.8 The country is a net exporter of mangoes. Total export receipts<br />
increased by 2% per year from US$42.3 million in 1993 to US$51 million in<br />
2004. About 60% of the total value of exports in 2004 were in fresh form <strong>and</strong><br />
the rest are processed mango products such as puree, juice, dried, frozen,<br />
concentrates, drained or crystallized, in brine <strong>and</strong> pickled. Exports increased<br />
by 5% per year from 1993-1998 <strong>and</strong> picked up further in 1999-2004, growing<br />
by 7.6% per annum. The growth driver in the earlier years were fresh<br />
mangoes but processed exports propelled growth in the latter period. In<br />
particular, puree, dried <strong>and</strong> frozen mangoes posted substantial increases in<br />
2003 because of strong dem<strong>and</strong> overseas.<br />
<strong>5.</strong>6.9 The country exported 33,662 tons of fresh mangoes worth US$28.7<br />
million in 2004. The leading market volume-wise was Hong Kong, absorbing<br />
61% of total exports during the year. Japan was a far second with a 30% share.<br />
In terms of value, however, Japan was a far bigger market than Hong Kong since<br />
it offers a price premium. It accounted for 62% of the total value of fresh mango<br />
exports during the same year. Growth in these markets, however, has been<br />
rather anemic.<br />
<strong>5.</strong>6.10 Puree exports, meanwhile, totaled 9,291 tons in 2004, generating<br />
US$9.2 million in foreign exchange earnings. The leading buyers were South<br />
Korea (47% of volume), Japan (19%) <strong>and</strong> the USA. On the other h<strong>and</strong>, juice<br />
exports amounted to 3,360 tons during the same year, valued at US$3 million.<br />
The primary destination was the USA (44% of volume), followed distantly by<br />
Canada (10%) <strong>and</strong> Japan (9%). In the case of dried mangoes, exports reached<br />
1,912 tons valued at US$8.1 million also in 2004. Some 41% of the volume went<br />
to the USA, followed by Singapore (12%) <strong>and</strong> Japan (10%).<br />
<strong>5.</strong>6.11 Considering the two leading mango exports – fresh <strong>and</strong> puree – the<br />
volume indices relative to 1993 levels were generally increasing for puree but<br />
was decreasing for fresh mangoes especially from 2000-2004. This could<br />
imply that more <strong>and</strong> more of production are going into processed rather than<br />
fresh exports.<br />
Figure <strong>5.</strong>6.<strong>5.</strong> MANGO: Production <strong>and</strong> Export Volume Index by Product<br />
Form, 1993-2004<br />
Index (1993=100)<br />
450<br />
400<br />
350<br />
300<br />
250<br />
200<br />
150<br />
100<br />
50<br />
-<br />
Production Fresh ex ports Puree ex ports<br />
93 94 95 96 97 98 99 00 01 02 03 04<br />
5- 44