View/Open - University of Zululand Institutional Repository
View/Open - University of Zululand Institutional Repository
View/Open - University of Zululand Institutional Repository
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
5.11 SECTION J: REHABILITATION AIDS<br />
The inclusion <strong>of</strong>this section is important because rehabilitation aids help the people with<br />
amputations to become fully participating members <strong>of</strong> society, with access to all the<br />
benefits and opportunities <strong>of</strong>that society. It was also included to determine whether the<br />
amputees were using rehabilitation aids or not and to find out if they were managing to<br />
purchase them and use them. Ifthey are not able to purchase them, who provides them<br />
and maintain them.<br />
5.11.1 ITEM 43<br />
TYPES OF REHABILITATION AIDS USED BY<br />
AMPUTEES<br />
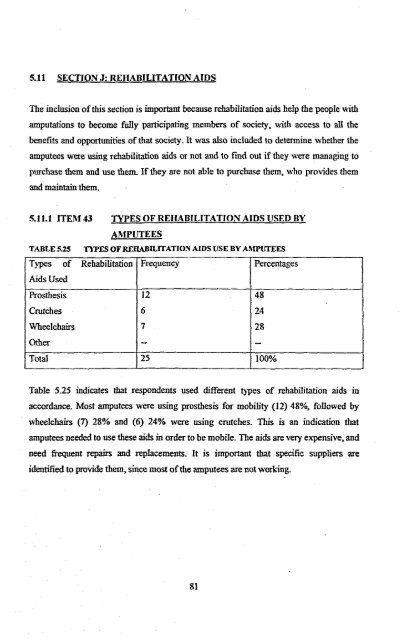
TABLE 5.25 TYPES OF REHABILITATION AIDS USE BY AMPUTEES<br />
Types <strong>of</strong> Rehabilitation Frequency Percentages<br />
Aids Used<br />
Prosthesis 12 48<br />
Crutches 6 24<br />
Wheelchairs 7 28<br />
Other - -<br />
Total 25 100%<br />
Table 5.25 indicates that respondents used different types <strong>of</strong> rehabilitation aids in<br />
accordance. Most amputees were using prosthesis for mobility (12) 48%, followed by<br />
wheelchairs (7) 28% and (6) 24% were using crutches. This is an indication that<br />
amputees needed to use these aids in order to be mobile. The aids are very expensive, and<br />
need frequent repairs and replacements. It is important that specific suppliers are<br />
identified to provide them, since most <strong>of</strong>the amputees are not working.<br />
81