Summer Undergraduate Research Program - Fred Hutchinson ...
Summer Undergraduate Research Program - Fred Hutchinson ...
Summer Undergraduate Research Program - Fred Hutchinson ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
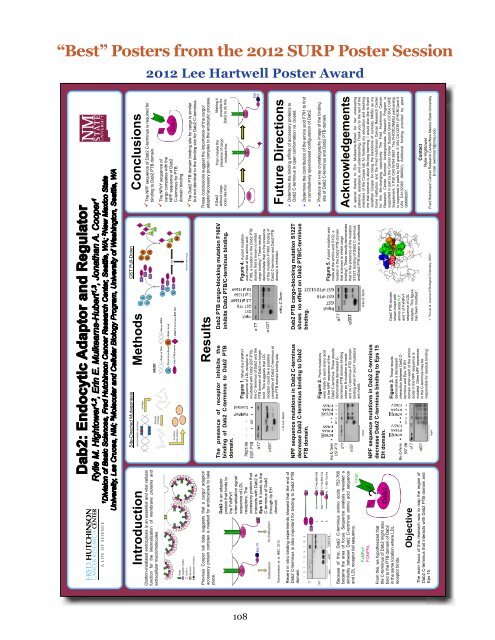
“Best” Posters from the 2012 SURP Poster Session<br />
Conclusions<br />
Site-Directed Mutagenesis GST Pull-Down<br />
Methods<br />
Introduction<br />
2012 Lee Hartwell Poster Award<br />
The NPF sequence of Dab2 C-terminus is required for<br />
binding to Dab2 PTB domain.<br />
Clathrin-mediated endocytosis is an essential and vital cellular<br />
function for the internalization of membrane proteins and<br />
extracellular macromolecules.<br />
The NPxY sequence of<br />
cargo competes with the<br />
NPF sequence of Dab2<br />
C-terminus for PTB<br />
domain binding.<br />
The Dab2 PTB domain binding site for cargo is similar<br />
but not identical to the binding site for Dab2 C-terminus.<br />
These conclusions suggest the importance of the cargo/<br />
adaptor/accessory protein complex to the endocytic process.<br />
Results<br />
Making it<br />
possible for<br />
Dab2 to do this:<br />
Then maybe the<br />
presence of cargo<br />
initiates this:<br />
If Dab2<br />
without cargo<br />
looks like this:<br />
Dab2 PTB cargo-blocking mutation F166V<br />
inhibits Dab2 PTB/C-terminus binding.<br />
The presence of receptor inhibits the<br />
binding of Dab2 C-terminus to Dab2 PTB<br />
domain.<br />
Figure 4. A point mutation<br />
was made at the amino acid<br />
F166, a location in the Dab2 PTB<br />
domain that is known to inhibit<br />
cargo binding1 . These results<br />
demonstrate that in the presence<br />
of the mutation F166V, binding of<br />
Dab2 C-terminus and Dab2 PTB<br />
domain is inhibited.<br />
Figure 1. When the FxNPxY<br />
sequence of LDL receptor is<br />
incubated with Dab2 GST-PTB,<br />
the C- terminus of Dab2 and the<br />
PTB domain of Dab2 no longer<br />
bind. This suggests that LDL<br />
receptor could be a possible<br />
competitor of Dab2 C-terminus at<br />
the PTB domain binding site.<br />
108<br />
Eps<br />
15<br />
Previous Cooper lab data suggests that a cargo/ adaptor/<br />
accessory protein complex is needed for endocytosis to take<br />
place.<br />
Dab2 is an adaptor<br />
protein that binds to<br />
the FxNPxY<br />
internalization signal<br />
sequence of LDL<br />
receptors. The<br />
accessory protein that<br />
Eps 15<br />
interacts with Dab2 is<br />
Eps 15. It binds to the<br />
C-terminus of Dab2<br />
through its EH<br />
domain.<br />
Teckchandani, et. al, MBC. 2012.<br />
Future Directions<br />
Determine the binding affinity of accessory proteins to<br />
Dab2 C-terminus in open conformation vs. closed.<br />
Dab2 PTB cargo-blocking mutation S122T<br />
shows no effect on Dab2 PTB/C-terminus<br />
binding.<br />
NPF sequence mutations in Dab2 C-terminus<br />
decrease Dab2 C-terminus binding to Dab2<br />
PTB domain.<br />
Recent in vitro binding experiments showed that the end of<br />
Dab2 C-terminus is also important for binding to Dab2 PTB<br />
domain.<br />
Determine the contribution of the amino acid F761 to find<br />
a constitutively open/closed configuration of Dab2.<br />
Produce an x-ray crystallography image of the binding<br />
site of Dab2 C-terminus and Dab2 PTB domain.<br />
Acknowledgements<br />
Figure 5. A point mutation was<br />
made at the amino acid S122, a<br />
location in the Dab2 PTB domain<br />
that is known to inhibit cargo<br />
binding1 . These results demonstrate<br />
that in the presence of the mutation<br />
S122T, binding of Dab2 C-terminus<br />
andDab2 PTB domain is unaffected.<br />
Figure 2. Point mutations<br />
were made to each amino acid<br />
in the NPF sequence of the<br />
Dab2 C-terminus. These results<br />
demonstrate decreased Cterminus-PTB<br />
domain binding<br />
when an N mutation is made<br />
and no C-terminus-PTB domain<br />
binding when P and F mutations<br />
are made.<br />
Because of this, Dab2 C-terminus amino acids 752-766<br />
became the area of focus. Sequence analysis revealed a<br />
similarity between Dab2 C-terminus amino acid sequence<br />
and LDL receptor tail sequence.<br />
Cargo<br />
A special thanks to Erin Mulkearns-Hubert for her unwavering<br />
patience, assistance, and understanding. Thank you to the rest of the<br />
members of the Cooper lab for fostering my education and teaching<br />
me that science is about life-long learning. I would also like to thank<br />
Jonathan Cooper for being the backbone of curiosity, NMSU as my<br />
home institution, and the <strong>Fred</strong> <strong>Hutchinson</strong> Cancer <strong>Research</strong> Center<br />
for this life-changing opportunity. The <strong>Fred</strong> <strong>Hutchinson</strong> Cancer<br />
<strong>Research</strong> Center <strong>Summer</strong> <strong>Undergraduate</strong> <strong>Research</strong> <strong>Program</strong> is<br />
supported in part by the Cancer Center Support Grant (CCSG) CURE<br />
Supplement: 3 P30 CA015704-38S1. The FHCRC/NMSU partnership<br />
is supported in parts by NCI grants: 5 U54 CA132381 (FHCRC)and 5<br />
U54 CA132383 (NMSU). Additional funding provided by grant<br />
GM066257.<br />
+His-C-Term<br />
?<br />
FxNPxY<br />
FGNPFA<br />
NPF sequence mutations in Dab2 C-terminus<br />
decrease Dab2 C-terminus binding to Eps 15<br />
EH domain.<br />
F166<br />
P<br />
Y<br />
S122<br />
Y<br />
From this, we hypothesized that<br />
the C-terminus of Dab2 might also<br />
bind to the PTB domain of Dab2<br />
in the same location where LDL<br />
Dab2 PTB domain<br />
shown inlaid with<br />
amino acids N,P,<br />
and Y of FxNPxY<br />
sequence of LDL<br />
receptor. This figure<br />
has been modified1 .<br />
Figure 3. These results<br />
demonstrate a decreased<br />
interaction between Dab2 Cterminus<br />
and Eps 15 EH<br />
domain when each of the amino<br />
acids in the NPF sequence is<br />
mutated. Other NPF sequences<br />
in the C-terminus may be<br />
responsible for residual binding.<br />
receptor binds.<br />
Objective<br />
Contact<br />
Rylie Hightower<br />
<strong>Fred</strong> <strong>Hutchinson</strong> Cancer <strong>Research</strong> Center/New Mexico State University<br />
E-mail: swimmer1@nmsu.edu<br />
The main focus of this research was to map the region of<br />
Dab2 C-terminus that interacts with Dab2 PTB domain and<br />
Eps 15.<br />
1. "Yun et al. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2003."