Combined Actions and Interactions of Chemicals in Mixtures
Combined Actions and Interactions of Chemicals in Mixtures
Combined Actions and Interactions of Chemicals in Mixtures
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
octylt<strong>in</strong> dichloride). A number <strong>of</strong> adverse effects seen at the LOAEL, such as<br />
decreased prothromb<strong>in</strong> time, <strong>in</strong>creased liver enzyme activity (ALAT <strong>and</strong> ASAT) <strong>in</strong><br />
plasma, <strong>in</strong>creased kidney weights, reduced number <strong>of</strong> corpora lutea <strong>in</strong> ovaries, <strong>and</strong><br />
<strong>in</strong>creased numbers <strong>of</strong> mult<strong>in</strong>ucleated giant cells <strong>in</strong> the epididymides had not been<br />
seen at all or had been found at doses higher than the LOAEL <strong>of</strong> the <strong>in</strong>dividual<br />
compounds. Although some <strong>of</strong> these changes may be related to the severe growth<br />
retardation, they suggested some k<strong>in</strong>d <strong>of</strong> <strong>in</strong>teraction result<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong> a slightly more<br />
severe <strong>and</strong> maybe broader range <strong>of</strong> toxic response. On the other h<strong>and</strong> the changes<br />
<strong>in</strong> the thymus were less pronounced on comb<strong>in</strong>ed exposure than after exposure to<br />
di-n-octylt<strong>in</strong> dichloride alone, suggest<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong>teraction lead<strong>in</strong>g to less severe toxicity.<br />
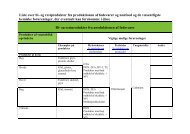
Table 5.2.1. Toxicological studies <strong>of</strong> chemicals with different target organs <strong>and</strong>/or modes <strong>of</strong><br />
action.<br />
Compound<br />
Potassium<br />
nitrate<br />
Stannous<br />
chloride<br />
Sodium<br />
metabisulphiteMetalde-<br />
hyde<br />
62<br />
NOAEL/10 NOAEL/3 NOAEL LOAEL<br />
Mg/kg bw/day<br />
Target<br />
organ<br />
10 33 100 300 Adrenals<br />
100 330 1000 3000 Body<br />
weight,<br />
blood, liver<br />
500 1670 5000 20000 Blood,<br />
stomach,<br />
liver<br />
20 70 200 1000 Liver<br />
Loperamide 0.5 1.7 5 25 Body weight<br />
Mirex 0.5 1.7 5 80 Body<br />
weight, liver<br />
blood<br />
Lys<strong>in</strong>o- 3 10 30 100 Kidneys<br />
alan<strong>in</strong>e<br />
Di-n-octylt<strong>in</strong><br />
dichloride<br />
0.6 2 6 30 Thymus,<br />
liver<br />
The authors concluded that the study demonstrates absence <strong>of</strong> a simple additive<br />
effect <strong>and</strong> synergism, <strong>and</strong> provides some, but no conv<strong>in</strong>c<strong>in</strong>g evidence for an<br />
<strong>in</strong>creased risk from exposure to a comb<strong>in</strong>ation <strong>of</strong> chemicals when each chemical is<br />
adm<strong>in</strong>istered at its own <strong>in</strong>dividual NOAEL. At lower dose levels no <strong>in</strong>creased risk<br />
appeared to exist.<br />
The other experiment (Feron et al. 1995a, Groten et al. 1997) was a 4-week<br />
oral/<strong>in</strong>halatory study <strong>in</strong> male Wistar rats <strong>in</strong> which the toxicity <strong>of</strong> comb<strong>in</strong>ations <strong>of</strong><br />
n<strong>in</strong>e compounds was exam<strong>in</strong>ed (Table 5.2.2). In this study a comb<strong>in</strong>ation was used<br />
<strong>of</strong> compounds highly relevant to the general population <strong>in</strong> terms <strong>of</strong> use patterns <strong>and</strong><br />
levels <strong>and</strong> frequency <strong>of</strong> exposure. The study <strong>in</strong>cluded 20 experimental groups, four<br />
groups <strong>of</strong> eight rats <strong>in</strong> the ma<strong>in</strong> study <strong>and</strong> 16 groups <strong>of</strong> five rats <strong>in</strong> a satellite study.<br />
In the ma<strong>in</strong> study, the rats were simultaneously exposed to mixtures <strong>of</strong> all n<strong>in</strong>e<br />
chemicals. Dichloromethane <strong>and</strong> formaldehyde were adm<strong>in</strong>istered by <strong>in</strong>halation<br />
<strong>and</strong> aspir<strong>in</strong>, di(2- ethylhexyl)phthalate (DEHP), cadmium chloride, stannous<br />
chloride, butyl hydroxyanisol (BHA), loperamide, <strong>and</strong> sperm<strong>in</strong>e were given <strong>in</strong> the<br />
diet at concentrations equal to the "m<strong>in</strong>imum-observed-adverse-effect level"<br />
(LOAEL), the NOAEL, or one third the NOAEL. The satellite study was designed<br />
as a fractionated two-level factorial study <strong>in</strong> which the rats were simultaneously<br />
exposed to comb<strong>in</strong>ations <strong>of</strong> maximally five compounds at their LOAEL. These 16