- Page 1 and 2:
The Global Mycological Journal Volu
- Page 3 and 4:
Mycospeak and Biobabble “There ar
- Page 5 and 6:
Cultures of lichen-forming fungi av
- Page 7 and 8:
Interested in hosting IMC11 (2018)?
- Page 9 and 10:
International Commission on the Tax
- Page 11 and 12:
Sustainable, quality production, wa
- Page 13 and 14:
REPORTS Scenes from the One Fungus
- Page 15 and 16:
which were, as is tradition, rounde
- Page 17 and 18:
Alexopoulos Award for Research from
- Page 19 and 20:
their involvement in dandruff, but
- Page 21 and 22:
The road to stability Stability and
- Page 23 and 24:
INTERVIEW With Jens H. Petersen, au
- Page 25 and 26:
Fungal Biology in the Origin and Em
- Page 27 and 28:
1993 volume, and now covers 646 spe
- Page 29 and 30:
through ectomycorrhizal fungi. A te
- Page 31 and 32:
that time. The new list covers all
- Page 33 and 34:
9 th International Conference on Cr
- Page 35 and 36:
doi:10.5598/imafungus.2013.04.01.01
- Page 37 and 38:
Taiwanascus samuelsii sp. nov. ARTI
- Page 39 and 40:
doi:10.5598/imafungus.2013.04.01.02
- Page 41 and 42:
Antherospora on Muscari phylogeneti
- Page 43 and 44:
Antherospora on Muscari gamma distr
- Page 45 and 46:
Antherospora on Muscari ARTICLE Fig
- Page 47 and 48:
Antherospora on Muscari Basionym: U
- Page 49 and 50:
Antherospora on Muscari (Zundel 195
- Page 51 and 52:
Antherospora on Muscari any authori
- Page 53 and 54:
Antherospora on Muscari Führung Ad
- Page 55 and 56:
doi:10.5598/imafungus.2013.04.01.03
- Page 57 and 58:
Brevicellicium in Trechisporales re
- Page 59 and 60:
Brevicellicium in Trechisporales 0.
- Page 61 and 62:
Brevicellicium in Trechisporales Th
- Page 63 and 64:
doi:10.5598/imafungus.2013.04.01.04
- Page 65 and 66:
Microbotryum silenes-saxifragae sp.
- Page 67 and 68:
Microbotryum silenes-saxifragae sp.
- Page 69 and 70:
Microbotryum silenes-saxifragae sp.
- Page 71 and 72:
Microbotryum silenes-saxifragae sp.
- Page 73 and 74:
Microbotryum silenes-saxifragae sp.
- Page 75 and 76:
doi:10.5598/imafungus.2013.04.01.05
- Page 77 and 78:
Genera in Hypocreales proposed for
- Page 79 and 80:
Genera in Hypocreales proposed for
- Page 81 and 82:
Genera in Hypocreales proposed for
- Page 83 and 84:
Genera in Hypocreales proposed for
- Page 85 and 86:
Genera in Hypocreales proposed for
- Page 87 and 88:
doi:10.5598/imafungus.2013.04.01.06
- Page 89 and 90:
Names of fungal species with the sa
- Page 91 and 92:
doi:10.5598/imafungus.2013.04.01.07
- Page 93 and 94:
Durotheca gen. nov. and Theissenia
- Page 95 and 96:
Durotheca gen. nov. and Theissenia
- Page 97 and 98:
Durotheca gen. nov. and Theissenia
- Page 99 and 100:
Durotheca gen. nov. and Theissenia
- Page 101 and 102:
Durotheca gen. nov. and Theissenia
- Page 103 and 104:
Durotheca gen. nov. and Theissenia
- Page 105 and 106:
doi:10.5598/imafungus.2013.04.01.08
- Page 107 and 108:
Gelatinomyces siamensis gen. sp. no
- Page 109 and 110:
Gelatinomyces siamensis gen. sp. no
- Page 111 and 112:
Gelatinomyces siamensis gen. sp. no
- Page 113 and 114:
Gelatinomyces siamensis gen. sp. no
- Page 115 and 116:
Gelatinomyces siamensis gen. sp. no
- Page 117 and 118:
Gelatinomyces siamensis gen. sp. no
- Page 119 and 120:
Gelatinomyces siamensis gen. sp. no
- Page 121 and 122:
Gelatinomyces siamensis gen. sp. no
- Page 123 and 124:
doi:10.5598/imafungus.2013.04.01.09
- Page 125 and 126: Auxarthronopsis gen. sp. nov. Table
- Page 127 and 128: Auxarthronopsis gen. sp. nov. in th
- Page 129 and 130: Auxarthronopsis gen. sp. nov. ARTIC
- Page 131 and 132: Auxarthronopsis gen. sp. nov. ARTIC
- Page 133 and 134: Auxarthronopsis gen. sp. nov. ARTIC
- Page 135 and 136: Auxarthronopsis gen. sp. nov. 4(3)
- Page 137 and 138: doi:10.5598/imafungus.2013.04.01.10
- Page 139 and 140: Anthracoidea kenaica comb. nov. on
- Page 141 and 142: Anthracoidea kenaica comb. nov. on
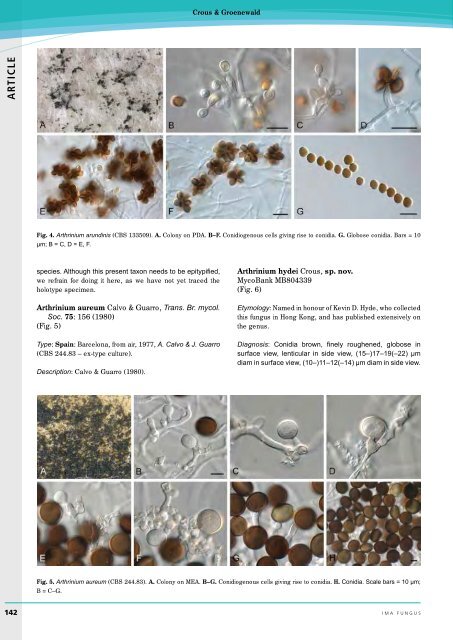
- Page 143 and 144: Anthracoidea kenaica comb. nov. on
- Page 145 and 146: doi:10.5598/imafungus.2013.04.01.11
- Page 147 and 148: Luteocirrhus shearii gen. sp. nov.
- Page 149 and 150: Luteocirrhus shearii gen. sp. nov.
- Page 151 and 152: Luteocirrhus shearii gen. sp. nov.
- Page 153 and 154: Luteocirrhus shearii gen. sp. nov.
- Page 155 and 156: Luteocirrhus shearii gen. sp. nov.
- Page 157 and 158: doi:10.5598/imafungus.2013.04.01.12
- Page 159 and 160: Phytophthora diversity in South Afr
- Page 161 and 162: Phytophthora diversity in South Afr
- Page 163 and 164: Phytophthora diversity in South Afr
- Page 165 and 166: Phytophthora diversity in South Afr
- Page 167 and 168: doi:10.5598/imafungus.2013.04.01.13
- Page 169 and 170: Re-evaluation of Arthrinium (syn. A
- Page 171 and 172: Re-evaluation of Arthrinium (syn. A
- Page 173 and 174: Re-evaluation of Arthrinium (syn. A
- Page 175: Re-evaluation of Arthrinium (syn. A
- Page 179 and 180: Re-evaluation of Arthrinium (syn. A
- Page 181 and 182: Re-evaluation of Arthrinium (syn. A
- Page 183 and 184: Re-evaluation of Arthrinium (syn. A
- Page 185 and 186: Re-evaluation of Arthrinium (syn. A
- Page 187 and 188: Re-evaluation of Arthrinium (syn. A
- Page 189 and 190: doi:10.5598/imafungus.2013.04.01.14
- Page 191 and 192: Puccinia psidii in Africa Table 1.
- Page 193 and 194: Puccinia psidii in Africa ACKNOWLED
- Page 195: Editorial Mycospeak and Biobabble (