Korg Microkorg Owner's Manual - zZounds.com
Korg Microkorg Owner's Manual - zZounds.com
Korg Microkorg Owner's Manual - zZounds.com
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
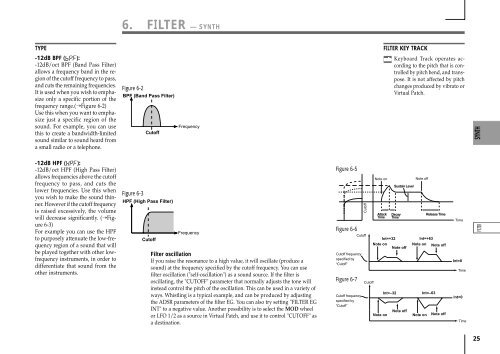
6. FILTER — SYNTH<br />
TYPE<br />
-12dB BPF ( ):<br />
-12dB/oct BPF (Band Pass Filter)<br />
allows a frequency band in the region<br />
of the cutoff frequency to pass,<br />
and cuts the remaining frequencies.<br />
It is used when you wish to emphasize<br />
only a specific portion of the<br />
frequency range.(➝Figure 6-2)<br />
Use this when you want to emphasize<br />
just a specific region of the<br />
sound. For example, you can use<br />
this to create a bandwidth-limited<br />
sound similar to sound heard from<br />
a small radio or a telephone.<br />
Figure 6-2<br />
BPF (Band Pass Filter)<br />
Cutoff<br />
Frequency<br />
FILTER KEY TRACK<br />
Keyboard Track operates according<br />
to the pitch that is controlled<br />
by pitch bend, and transpose.<br />
It is not affected by pitch<br />
changes produced by vibrato or<br />
Virtual Patch.<br />
-12dB HPF ( ):<br />
-12dB/oct HPF (High Pass Filter)<br />
allows frequencies above the cutoff<br />
frequency to pass, and cuts the<br />
lower frequencies. Use this when<br />
you wish to make the sound thinner.<br />
However if the cutoff frequency<br />
is raised excessively, the volume<br />
will decrease significantly. (➝Figure<br />
6-3)<br />
For example you can use the HPF<br />
to purposely attenuate the low-frequency<br />
region of a sound that will<br />
be played together with other lowfrequency<br />
instruments, in order to<br />
differentiate that sound from the<br />
other instruments.<br />
Figure 6-3<br />
HPF (High Pass Filter)<br />
Cutoff<br />
Frequency<br />
Filter oscillation<br />
If you raise the resonance to a high value, it will oscillate (produce a<br />
sound) at the frequency specified by the cutoff frequency. You can use<br />
filter oscillation ("self-oscillation") as a sound source. If the filter is<br />
oscillating, the "CUTOFF" parameter that normally adjusts the tone will<br />
instead control the pitch of the oscillation. This can be used in a variety of<br />
ways. Whistling is a typical example, and can be produced by adjusting<br />
the ADSR parameters of the filter EG. You can also try setting "FILTER EG<br />
INT" to a negative value. Another possibility is to select the MOD wheel<br />
or LFO 1/2 as a source in Virtual Patch, and use it to control "CUTOFF" as<br />
a destination.<br />
Figure 6-5<br />
Figure 6-6<br />
Cutoff<br />
Cutoff<br />
Cutoff frequency<br />
specified by<br />
“Cutoff”<br />
Figure 6-7<br />
Cutoff frequency<br />
specified by<br />
“Cutoff”<br />
Cutoff<br />
Note on<br />
Attack<br />
Time<br />
Sustain Level<br />
Decay<br />
Time<br />
Int=+32<br />
Note on<br />
Note off<br />
Note on<br />
Int=–32<br />
Note off<br />
Note off<br />
Release Time<br />
Int=+63<br />
Note on Note off<br />
Note on<br />
Int=–63<br />
Note off<br />
Time<br />
Int=0<br />
Time<br />
Int=0<br />
Time<br />
25