download the full article here - E-International Scientific Research ...
download the full article here - E-International Scientific Research ...
download the full article here - E-International Scientific Research ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
E-<strong>International</strong> <strong>Scientific</strong> <strong>Research</strong> Journal<br />
ISSN: 2094-1749 Volume: 3 Issue: 2, 2011<br />
22<br />
4<br />
1<br />
Dabka Watershed<br />
Erosion Hazard Vulnerability<br />
2<br />
3<br />
23<br />
13<br />
14<br />
16<br />
15<br />
0 0.5 1 2<br />
Km<br />
1:25000<br />
22<br />
4<br />
1<br />
Dabka Watershed<br />
Landslide Hazard Vulnerability<br />
2<br />
3<br />
23<br />
13<br />
14<br />
16<br />
15<br />
7<br />
5<br />
6<br />
9<br />
10<br />
11<br />
12<br />
21<br />
17<br />
Index<br />
High<br />
19<br />
18<br />
20<br />
7<br />
5<br />
6<br />
9<br />
10<br />
11<br />
12<br />
21<br />
17<br />
Index<br />
High<br />
19<br />
18<br />
20<br />
8<br />
Moderate<br />
Low<br />
8<br />
Moderate<br />
Low<br />
22<br />
4<br />
5<br />
6<br />
7<br />
1<br />
Dabka Watershed<br />
Multiple Hazard Vulnerability<br />
8<br />
2<br />
3<br />
23<br />
9<br />
13<br />
10<br />
11<br />
14<br />
12<br />
16<br />
21<br />
15<br />
17<br />
Index<br />
High<br />
19<br />
Moderate<br />
Low<br />
18<br />
20<br />
22<br />
4<br />
5<br />
6<br />
7<br />
1<br />
Dabka Watershed<br />
FloodHazard Vulnerability<br />
8<br />
2<br />
3<br />
23<br />
9<br />
13<br />
10<br />
11<br />
14<br />
12<br />
16<br />
21<br />
15<br />
17<br />
Index<br />
High<br />
19<br />
Moderate<br />
Low<br />
18<br />
20<br />
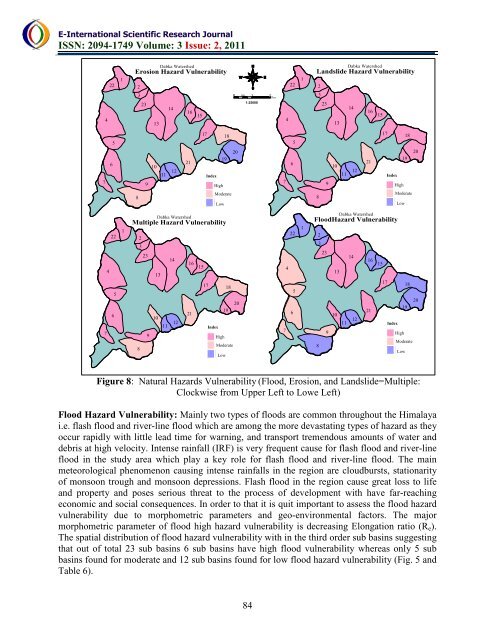
Figure 8: Natural Hazards Vulnerability (Flood, Erosion, and Landslide=Multiple:<br />
Clockwise from Upper Left to Lowe Left)<br />
Flood Hazard Vulnerability: Mainly two types of floods are common throughout <strong>the</strong> Himalaya<br />
i.e. flash flood and river-line flood which are among <strong>the</strong> more devastating types of hazard as <strong>the</strong>y<br />
occur rapidly with little lead time for warning, and transport tremendous amounts of water and<br />
debris at high velocity. Intense rainfall (IRF) is very frequent cause for flash flood and river-line<br />
flood in <strong>the</strong> study area which play a key role for flash flood and river-line flood. The main<br />
meteorological phenomenon causing intense rainfalls in <strong>the</strong> region are cloudbursts, stationarity<br />
of monsoon trough and monsoon depressions. Flash flood in <strong>the</strong> region cause great loss to life<br />
and property and poses serious threat to <strong>the</strong> process of development with have far-reaching<br />
economic and social consequences. In order to that it is quit important to assess <strong>the</strong> flood hazard<br />
vulnerability due to morphometric parameters and geo-environmental factors. The major<br />
morphometric parameter of flood high hazard vulnerability is decreasing Elongation ratio (R e ).<br />
The spatial distribution of flood hazard vulnerability with in <strong>the</strong> third order sub basins suggesting<br />
that out of total 23 sub basins 6 sub basins have high flood vulnerability w<strong>here</strong>as only 5 sub<br />
basins found for moderate and 12 sub basins found for low flood hazard vulnerability (Fig. 5 and<br />
Table 6).<br />
84