MV design guide - Schneider Electric
MV design guide - Schneider Electric
MV design guide - Schneider Electric
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Switchgear<br />
definition<br />
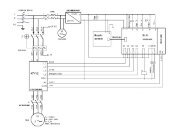
Current transformer<br />
Please note!<br />
Never leave a CT in<br />
an open circuit.<br />
This is intended to provide a secondary circuit with a current<br />
proportional to the primary current.<br />
Transformation ratio (Kn)<br />
Ipr<br />
Kn = = N2<br />
Isr N1<br />
N.B.: current transformers must be in conformity with standard IEC 185 but can also be defined<br />
by standards BS 3938 and ANSI.<br />
c It comprises one or several primary windings around one or several<br />
secondary windings each having their own magnetic circuit, and all being<br />
encapsulated in an insulating resin.<br />
c It is dangerous to leave a CT in an open circuit because dangerous<br />
voltages for both people and equipment may appear across its terminals.<br />
Primary circuit characteristics<br />
according to IEC standards<br />
Rated frequency (fr)<br />
A CT defined at 50 Hz can be installed on a 60 Hz network.<br />
Its precision is retained. The opposite is not true.<br />
Rated primary circuit voltage (Upr)<br />
c General case:<br />
Rated CT voltage ≥ rated installation voltage<br />
The rated voltage sets the equipment insulation level (see "Introduction"<br />
chapter of this <strong>guide</strong>). Generally, we would choose the rated CT voltage<br />
based on the installation operating voltage U, according to the chart:<br />
U 3.3 5 5.5 6 6.6 10 11 13.8 15 20 22 30 33<br />
Upr<br />
7.2 kV<br />
cable or busduct<br />
Core balance CT<br />
(sheathed or not sheathed busduct)<br />
insulator<br />
air<br />
insulator<br />
12 kV<br />
17.5 kV<br />
24 kV<br />
36 kV<br />
c Special case:<br />
If the CT is a core balance CT installed on a busduct or on a cable.<br />
The dielectric insulation is provided by the cable or busducting insulation<br />
and the air located between them. The core balance CT is itself insulated.<br />
54 Merlin Gerin <strong>MV</strong> <strong>design</strong> <strong>guide</strong> <strong>Schneider</strong> <strong>Electric</strong>