COMNET III
COMNET III
COMNET III
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
<strong>COMNET</strong> <strong>III</strong> Reports and Statistics<br />
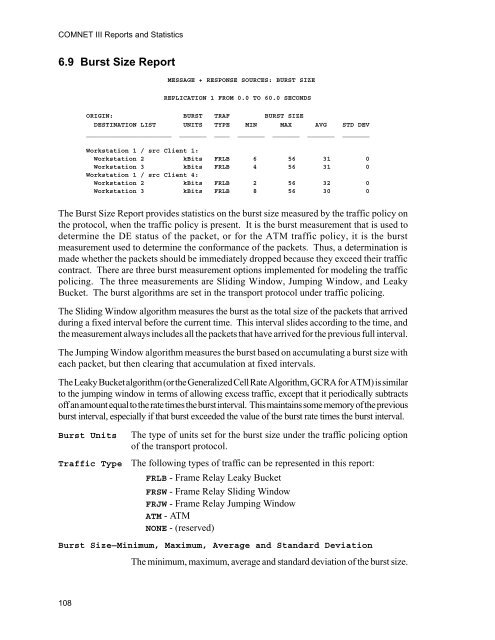
6.9 Burst Size Report<br />
MESSAGE + RESPONSE SOURCES: BURST SIZE<br />
REPLICATION 1 FROM 0.0 TO 60.0 SECONDS<br />
ORIGIN: BURST TRAF BURST SIZE<br />
DESTINATION LIST UNITS TYPE MIN MAX AVG STD DEV<br />
______________________ _______ ____ _______ _______ _______ _______<br />
Workstation 1 / src Client 1:<br />
Workstation 2 kBits FRLB 6 56 31 0<br />
Workstation 3 kBits FRLB 4 56 31 0<br />
Workstation 1 / src Client 4:<br />
Workstation 2 kBits FRLB 2 56 32 0<br />
Workstation 3 kBits FRLB 8 56 30 0<br />
The Burst Size Report provides statistics on the burst size measured by the traffic policy on<br />
the protocol, when the traffic policy is present. It is the burst measurement that is used to<br />
determine the DE status of the packet, or for the ATM traffic policy, it is the burst<br />
measurement used to determine the conformance of the packets. Thus, a determination is<br />
made whether the packets should be immediately dropped because they exceed their traffic<br />
contract. There are three burst measurement options implemented for modeling the traffic<br />
policing. The three measurements are Sliding Window, Jumping Window, and Leaky<br />
Bucket. The burst algorithms are set in the transport protocol under traffic policing.<br />
The Sliding Window algorithm measures the burst as the total size of the packets that arrived<br />
during a fixed interval before the current time. This interval slides according to the time, and<br />
the measurement always includes all the packets that have arrived for the previous full interval.<br />
The Jumping Window algorithm measures the burst based on accumulating a burst size with<br />
each packet, but then clearing that accumulation at fixed intervals.<br />
The Leaky Bucket algorithm (or the Generalized Cell Rate Algorithm, GCRA for ATM) is similar<br />
to the jumping window in terms of allowing excess traffic, except that it periodically subtracts<br />
off an amount equal to the rate times the burst interval. This maintains some memory of the previous<br />
burst interval, especially if that burst exceeded the value of the burst rate times the burst interval.<br />
Burst Units<br />
Traffic Type<br />
The type of units set for the burst size under the traffic policing option<br />
of the transport protocol.<br />
The following types of traffic can be represented in this report:<br />
FRLB - Frame Relay Leaky Bucket<br />
FRSW - Frame Relay Sliding Window<br />
FRJW - Frame Relay Jumping Window<br />
ATM - ATM<br />
NONE - (reserved)<br />
Burst Size—Minimum, Maximum, Average and Standard Deviation<br />
The minimum, maximum, average and standard deviation of the burst size.<br />
108