Chitosan Loaded Mucoadhesive Microspheres of Gliclazide - Journal
Chitosan Loaded Mucoadhesive Microspheres of Gliclazide - Journal
Chitosan Loaded Mucoadhesive Microspheres of Gliclazide - Journal
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Prakash Rao B et al./ Formulation and Evaluation <strong>of</strong> <strong>Mucoadhesive</strong> Buccal Drug Delivery System <strong>of</strong> Metoprolol Tartrate by Using Central Composite Design<br />
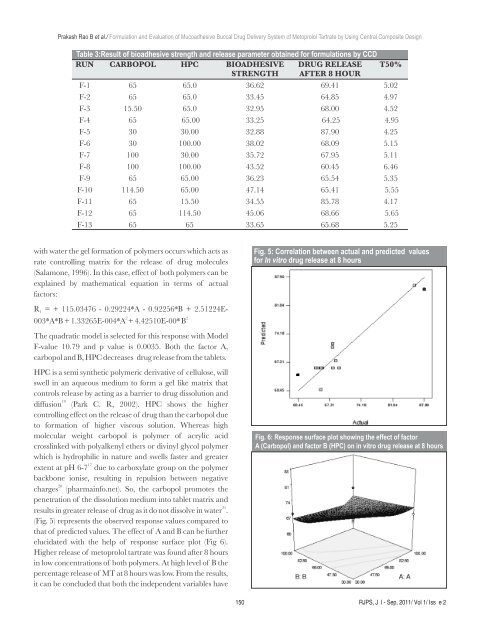
Table 3:Result <strong>of</strong> bioadhesive strength and release parameter obtained for formulations by CCD<br />
RUN CARBOPOL HPC BIOADHESIVE DRUG RELEASE T50%<br />
STRENGTH AFTER 8 HOUR<br />
F-1 65 65.0 36.62 69.41 5.02<br />
F-2 65 65.0 33.45 64.85 4.97<br />
F-3 15.50 65.0 32.95 68.00 4.52<br />
F-4 65 65.00 33.25 64.25 4.95<br />
F-5 30 30.00 32.88 87.90 4.25<br />
F-6 30 100.00 38.02 68.09 5.15<br />
F-7 100 30.00 35.72 67.95 5.11<br />
F-8 100 100.00 43.52 60.45 6.46<br />
F-9 65 65.00 36.23 65.54 5.35<br />
F-10 114.50 65.00 47.14 65.41 5.55<br />
F-11 65 15.50 34.55 85.78 4.17<br />
F-12 65 114.50 45.06 68.66 5.65<br />
F-13 65 65 33.65 65.68 5.25<br />
with water the gel formation <strong>of</strong> polymers occurs which acts as<br />
rate controlling matrix for the release <strong>of</strong> drug molecules<br />
(Salamone, 1996). In this case, effect <strong>of</strong> both polymers can be<br />
explained by mathematical equation in terms <strong>of</strong> actual<br />
factors:<br />
R 1 = + 115.03476 - 0.29224*A - 0.92256*B + 2.51224E-<br />
2 2<br />
003*A*B + 1.33265E-004*A + 4.42510E-00* B<br />
The quadratic model is selected for this response with Model<br />
F-value 10.79 and p value is 0.0035. Both the factor A,<br />
carbopol and B, HPC decreases drug release from the tablets.<br />
HPC is a semi synthetic polymeric derivative <strong>of</strong> cellulose, will<br />
swell in an aqueous medium to form a gel like matrix that<br />
controls release by acting as a barrier to drug dissolution and<br />
19<br />
diffusion (Park C. R, 2002). HPC shows the higher<br />
controlling effect on the release <strong>of</strong> drug than the carbopol due<br />
to formation <strong>of</strong> higher viscous solution. Whereas high<br />
molecular weight carbopol is polymer <strong>of</strong> acrylic acid<br />
crosslinked with polyalkenyl ethers or divinyl glycol polymer<br />
which is hydrophilic in nature and swells faster and greater<br />
17<br />
extent at pH 6-7 due to carboxylate group on the polymer<br />
backbone ionise, resulting in repulsion between negative<br />
20<br />
charges (pharmainfo.net). So, the carbopol promotes the<br />
penetration <strong>of</strong> the dissolution medium into tablet matrix and<br />
21<br />
results in greater release <strong>of</strong> drug as it do not dissolve in water .<br />
(Fig. 5) represents the observed response values compared to<br />
that <strong>of</strong> predicted values. The effect <strong>of</strong> A and B can be further<br />
elucidated with the help <strong>of</strong> response surface plot (Fig 6).<br />
Higher release <strong>of</strong> metoprolol tartrate was found after 8 hours<br />
in low concentrations <strong>of</strong> both polymers. At high level <strong>of</strong> B the<br />
percentage release <strong>of</strong> MT at 8 hours was low. From the results,<br />
it can be concluded that both the independent variables have<br />
Fig. 5: Correlation between actual and predicted values<br />
for In vitro drug release at 8 hours<br />
Fig. 6: Response surface plot showing the effect <strong>of</strong> factor<br />
A (Carbopol) and factor B (HPC) on in vitro drug release at 8 hours<br />
150 RJPS, Jul - Sep, 2011/ Vol 1/ Issue 2