pdf download - Software and Computer Technology - TU Delft
pdf download - Software and Computer Technology - TU Delft
pdf download - Software and Computer Technology - TU Delft
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Introduction<br />
1.4 Contributions<br />
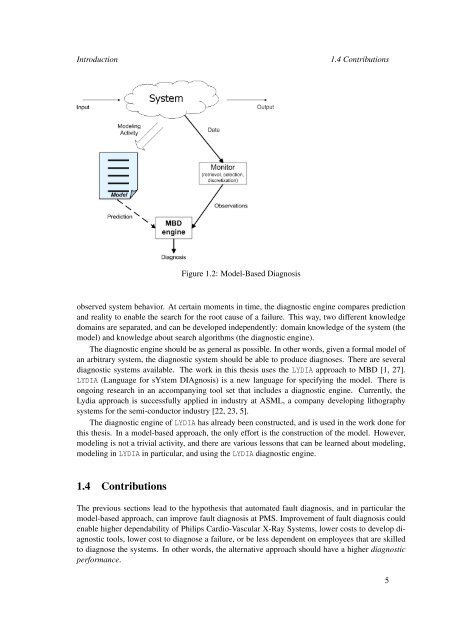
Figure 1.2: Model-Based Diagnosis<br />
observed system behavior. At certain moments in time, the diagnostic engine compares prediction<br />
<strong>and</strong> reality to enable the search for the root cause of a failure. This way, two different knowledge<br />
domains are separated, <strong>and</strong> can be developed independently: domain knowledge of the system (the<br />
model) <strong>and</strong> knowledge about search algorithms (the diagnostic engine).<br />
The diagnostic engine should be as general as possible. In other words, given a formal model of<br />
an arbitrary system, the diagnostic system should be able to produce diagnoses. There are several<br />
diagnostic systems available. The work in this thesis uses the LYDIA approach to MBD [1, 27].<br />
LYDIA (Language for sYstem DIAgnosis) is a new language for specifying the model. There is<br />
ongoing research in an accompanying tool set that includes a diagnostic engine. Currently, the<br />
Lydia approach is successfully applied in industry at ASML, a company developing lithography<br />
systems for the semi-conductor industry [22, 23, 5].<br />
The diagnostic engine of LYDIA has already been constructed, <strong>and</strong> is used in the work done for<br />
this thesis. In a model-based approach, the only effort is the construction of the model. However,<br />
modeling is not a trivial activity, <strong>and</strong> there are various lessons that can be learned about modeling,<br />
modeling in LYDIA in particular, <strong>and</strong> using the LYDIA diagnostic engine.<br />
1.4 Contributions<br />
The previous sections lead to the hypothesis that automated fault diagnosis, <strong>and</strong> in particular the<br />
model-based approach, can improve fault diagnosis at PMS. Improvement of fault diagnosis could<br />
enable higher dependability of Philips Cardio-Vascular X-Ray Systems, lower costs to develop diagnostic<br />
tools, lower cost to diagnose a failure, or be less dependent on employees that are skilled<br />
to diagnose the systems. In other words, the alternative approach should have a higher diagnostic<br />
performance.<br />
5