Annual Report 2006
Annual Report 2006
Annual Report 2006
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Fig. 1<br />
Phylogenetic relationships among species<br />
A strict consensus tree was calculated using the<br />
maximum parsimony method based on the sequence<br />
data of 18 chloroplast DNA regions. Tree length = 264,<br />
confidence interval =0.8659, retention index =0.9299,<br />
rescaled consistency index =0.8912. Species names<br />
and abbreviations of each accession (in parentheses)<br />
are shown. If two accessions of the same species have<br />
identical sequences, they are shown as 2 acc. The<br />
numbers above the nodes represent bootstrap values<br />
expressed as the percentage of 1,000 bootstrap<br />
replications.<br />
and <br />
form an independent clade; (2) <br />
has a paraphyletic relationship<br />
with the other five species; and (3) no or very<br />
low intraspecific variation was observed in <br />
<br />
and whereas higher intraspecific<br />
variation was observed in <br />
Based on the number of nucleotide<br />
substitutions, the divergence time between <br />
and and between <br />
and maize were calculated to be<br />
about 730-780 thousand years ago and about 5.9<br />
million years ago, respectively. These results<br />
suggest that the cytoplasm of <br />
species are very closely related.<br />
Analysis of a large seeded<br />
mutant in black gram<br />
<br />
The Asian consists of domesticated<br />
species among them is black gram. A mutant of<br />
this species has a seed size about double that of<br />
traditional cultivated black gram and six times<br />
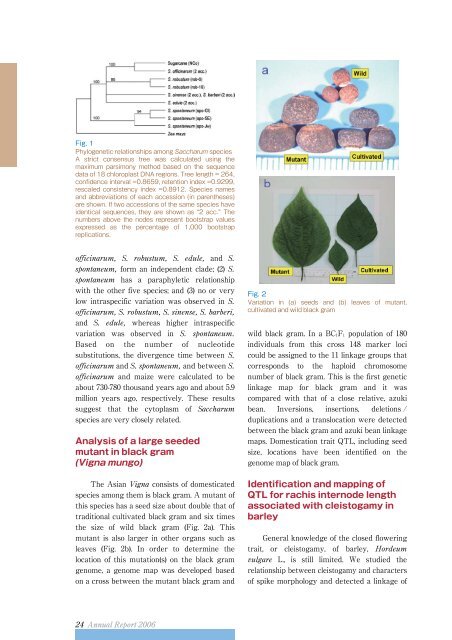
the size of wild black gram (Fig. 2a). This<br />
mutant is also larger in other organs such as<br />
leaves (Fig. 2b). In order to determine the<br />
location of this mutation(s) on the black gram<br />
genome, a genome map was developed based<br />
on a cross between the mutant black gram and<br />
Fig. 2<br />
Variation in (a) seeds and (b) leaves of mutant,<br />
cultivated and wild black gram<br />
wild black gram. In a BC1F1 population of 180<br />
individuals from this cross 148 marker loci<br />
could be assigned to the 11 linkage groups that<br />
corresponds to the haploid chromosome<br />
number of black gram. This is the first genetic<br />
linkage map for black gram and it was<br />
compared with that of a close relative, azuki<br />
bean. Inversions, insertions, deletions /<br />
duplications and a translocation were detected<br />
between the black gram and azuki bean linkage<br />
maps. Domestication trait QTL, including seed<br />
size, locations have been identified on the<br />
genome map of black gram.<br />
Identification and mapping of<br />
QTL for rachis internode length<br />
associated with cleistogamy in<br />
barley<br />
General knowledge of the closed flowering<br />
trait, or cleistogamy, of barley, <br />
L., is still limited. We studied the<br />
relationship between cleistogamy and characters<br />
of spike morphology and detected a linkage of