Crisman Annual Report 2009 - Harold Vance Department of ...
Crisman Annual Report 2009 - Harold Vance Department of ...
Crisman Annual Report 2009 - Harold Vance Department of ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Rheological Properties <strong>of</strong> a New Class <strong>of</strong> Viscoelastic Surfactant<br />
Objectives<br />
Surfactant-based acid systems were developed over<br />
the last few years for diversion, to overcome the<br />
severe problems caused by polymer residue and<br />
crosslinker precipitate after polymer-based system<br />
treatments during matrix and fracture acidizing.<br />
Surfactant molecules can form rod-like micelles and<br />
significantly increase the viscosity in the presence <strong>of</strong><br />
salts. After acid treatments, the surfactant gel can<br />
be broken by mixing with hydrocarbons, external<br />
breakers, or internal breakers or by reducing the<br />
concentration <strong>of</strong> salts via dilution with water. Acid<br />
additives and Fe (III) contamination can influence<br />
the formation <strong>of</strong> the rod-shaped micelles and result<br />
in different rheological properties from what we<br />
want. A new class <strong>of</strong> viscoelastic surfactant (VES)-<br />
amidoamine oxide has been tested in this study.<br />
The effects <strong>of</strong> acid additives, Fe (III) contamination,<br />
temperatures and shear rates need to be examined<br />
on the rheological properties <strong>of</strong> this new surfactant.<br />
Approach<br />
Acid additives studied included corrosion inhibitors,<br />
mutual solvents, non-emulsifying surfactants, iron<br />
control agents and a hydrogen sulfide scavenger.<br />
The Grace Instrument M5600 HPHT Rheometer was<br />
used to measure the apparent viscosity <strong>of</strong> live and<br />
spent acids under different conditions. The wetted<br />
material is Hastelloy C-276, which is acid-resistant.<br />
Measurements were made at temperatures from 75-<br />
220°F, and 300 psi at various shear rates from 0.01-<br />
935 s -1 . An Orion 950 analytical titrator was used to<br />
measure HCl concentration. The centrifuge used in<br />
this study was Z 206 A from Labnet International.<br />
Apparent Viscosity (cp)<br />
1200<br />
1000<br />
800<br />
600<br />
400<br />
200<br />
0<br />
5<br />
10<br />
15<br />
<strong>Crisman</strong> <strong>Annual</strong> <strong>Report</strong> <strong>2009</strong><br />
C HCl<br />
(wt%)<br />
20<br />
8<br />
10<br />
12<br />
15<br />
18<br />
20<br />
25<br />
28<br />
Acid Concentration (wt%)<br />
Viscosity (cp)<br />
108.8632<br />
706.438<br />
984.783<br />
175.0444<br />
12.1892<br />
5.8126<br />
2.8148<br />
2.896<br />
25 30<br />
Fig. 1. Apparent viscosity (10 s -1 ) <strong>of</strong> surfactant-based live acids that contained<br />
4 wt% surfactant, 1 wt% CI-A and various HCl concentrations.<br />
Apparent Viscosity (cp)<br />
1800<br />
1600<br />
1400<br />
1200<br />
1000<br />
800<br />
600<br />
400<br />
200<br />
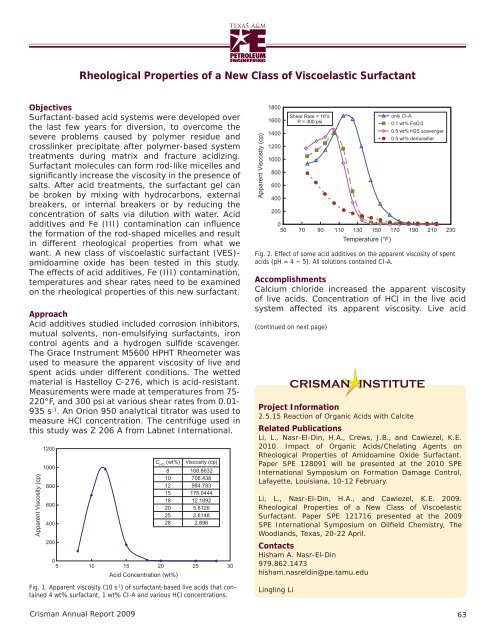
Accomplishments<br />
Calcium chloride increased the apparent viscosity<br />
<strong>of</strong> live acids. Concentration <strong>of</strong> HCl in the live acid<br />
system affected its apparent viscosity. Live acid<br />
Project Information<br />
2.5.15 Reaction <strong>of</strong> Organic Acids with Calcite<br />
Related Publications<br />
Li, L., Nasr-El-Din, H.A., Crews, J.B., and Cawiezel, K.E.<br />
2010. Impact <strong>of</strong> Organic Acids/Chelating Agents on<br />
Rheological Properties <strong>of</strong> Amidoamine Oxide Surfactant.<br />
Paper SPE 128091 will be presented at the 2010 SPE<br />
International Symposium on Formation Damage Control,<br />
Lafayette, Louisiana, 10-12 February.<br />
Li, L., Nasr-El-Din, H.A., and Cawiezel, K.E. <strong>2009</strong>.<br />
Rheological Properties <strong>of</strong> a New Class <strong>of</strong> Viscoelastic<br />
Surfactant. Paper SPE 121716 presented at the <strong>2009</strong><br />
SPE International Symposium on Oilfield Chemistry, The<br />
Woodlands, Texas, 20-22 April.<br />
Contacts<br />
Hisham A. Nasr-El-Din<br />
979.862.1473<br />
hisham.nasreldin@pe.tamu.edu<br />
Lingling Li<br />
-1<br />
Shear Rate = 10 s<br />
P = 300 psi<br />
0<br />
50 70 90 110 130 150 170 190 210 230<br />
Temperature (°F)<br />
only CI-A<br />
0.1 wt% FeCl3<br />
0.5 wt% H2S scavenger<br />
0.5 wt% demulsifier<br />
Fig. 2. Effect <strong>of</strong> some acid additives on the apparent viscosity <strong>of</strong> spent<br />
acids (pH = 4 ~ 5). All solutions contained CI-A.<br />
(continued on next page)<br />
CRISMAN INSTITUTE<br />
63