Xeon-Phi-Coprocessor-Datasheet
Xeon-Phi-Coprocessor-Datasheet
Xeon-Phi-Coprocessor-Datasheet
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
sense monitoring for system fan and power control. This information is forwarded to<br />
the coprocessor for power state control. The SMBus interface can be used by system<br />
for chassis fan control with the passive heat sink card and for integration with the Node<br />
Management controller in the platform. Communication with the system baseboard<br />
management controller (BMC) or peripheral control hub (PCH) occurs over the SMBus<br />
using the standard IPMB protocol. See chapter on manageability for more details.<br />
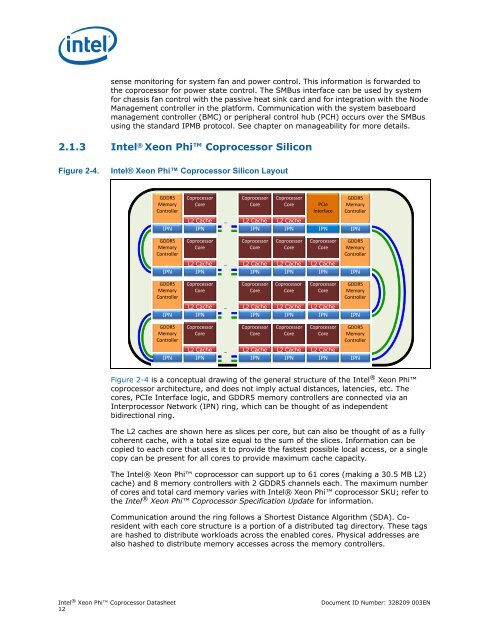
2.1.3 Intel ® <strong>Xeon</strong> <strong>Phi</strong> <strong>Coprocessor</strong> Silicon<br />
Figure 2-4.<br />
Intel® <strong>Xeon</strong> <strong>Phi</strong> <strong>Coprocessor</strong> Silicon Layout<br />
GDDR5<br />
Memory<br />
Controller<br />
<strong>Coprocessor</strong><br />
Core<br />
<strong>Coprocessor</strong><br />
Core<br />
<strong>Coprocessor</strong><br />
Core<br />
PCIe<br />
Interface<br />
GDDR5<br />
Memory<br />
Controller<br />
IPN<br />
L2 Cache<br />
IPN<br />
…<br />
L2 Cache<br />
IPN<br />
L2 Cache<br />
IPN<br />
IPN<br />
IPN<br />
GDDR5<br />
Memory<br />
Controller<br />
<strong>Coprocessor</strong><br />
Core<br />
<strong>Coprocessor</strong><br />
Core<br />
<strong>Coprocessor</strong><br />
Core<br />
<strong>Coprocessor</strong><br />
Core<br />
GDDR5<br />
Memory<br />
Controller<br />
IPN<br />
L2 Cache<br />
IPN<br />
…<br />
L2 Cache<br />
IPN<br />
L2 Cache<br />
IPN<br />
L2 Cache<br />
IPN<br />
IPN<br />
GDDR5<br />
Memory<br />
Controller<br />
<strong>Coprocessor</strong><br />
Core<br />
<strong>Coprocessor</strong><br />
Core<br />
<strong>Coprocessor</strong><br />
Core<br />
<strong>Coprocessor</strong><br />
Core<br />
GDDR5<br />
Memory<br />
Controller<br />
IPN<br />
L2 Cache<br />
IPN<br />
…<br />
L2 Cache<br />
IPN<br />
L2 Cache<br />
IPN<br />
L2 Cache<br />
IPN<br />
IPN<br />
GDDR5<br />
Memory<br />
Controller<br />
<strong>Coprocessor</strong><br />
Core<br />
<strong>Coprocessor</strong><br />
Core<br />
<strong>Coprocessor</strong><br />
Core<br />
<strong>Coprocessor</strong><br />
Core<br />
GDDR5<br />
Memory<br />
Controller<br />
IPN<br />
L2 Cache<br />
IPN<br />
…<br />
L2 Cache<br />
IPN<br />
L2 Cache<br />
IPN<br />
L2 Cache<br />
IPN<br />
IPN<br />
Figure 2-4 is a conceptual drawing of the general structure of the Intel ® <strong>Xeon</strong> <strong>Phi</strong><br />
coprocessor architecture, and does not imply actual distances, latencies, etc. The<br />
cores, PCIe Interface logic, and GDDR5 memory controllers are connected via an<br />
Interprocessor Network (IPN) ring, which can be thought of as independent<br />
bidirectional ring.<br />
The L2 caches are shown here as slices per core, but can also be thought of as a fully<br />
coherent cache, with a total size equal to the sum of the slices. Information can be<br />
copied to each core that uses it to provide the fastest possible local access, or a single<br />
copy can be present for all cores to provide maximum cache capacity.<br />
The Intel® <strong>Xeon</strong> <strong>Phi</strong> coprocessor can support up to 61 cores (making a 30.5 MB L2)<br />
cache) and 8 memory controllers with 2 GDDR5 channels each. The maximum number<br />
of cores and total card memory varies with Intel® <strong>Xeon</strong> <strong>Phi</strong> coprocessor SKU; refer to<br />
the Intel ® <strong>Xeon</strong> <strong>Phi</strong> <strong>Coprocessor</strong> Specification Update for information.<br />
Communication around the ring follows a Shortest Distance Algorithm (SDA). Coresident<br />
with each core structure is a portion of a distributed tag directory. These tags<br />
are hashed to distribute workloads across the enabled cores. Physical addresses are<br />
also hashed to distribute memory accesses across the memory controllers.<br />
Intel ® <strong>Xeon</strong> <strong>Phi</strong> <strong>Coprocessor</strong> <strong>Datasheet</strong><br />
12<br />
Document ID Number: 328209 003EN