NHMRC Glaucoma Guidelines - ANZGIG
NHMRC Glaucoma Guidelines - ANZGIG
NHMRC Glaucoma Guidelines - ANZGIG
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
<strong>NHMRC</strong> GUIDELINES FOR THE SCREENING, PROGNOSIS, DIAGNOSIS, MANAGEMENT AND PREVENTION OF GLAUCOMA<br />
Chapter 9 – Medication<br />
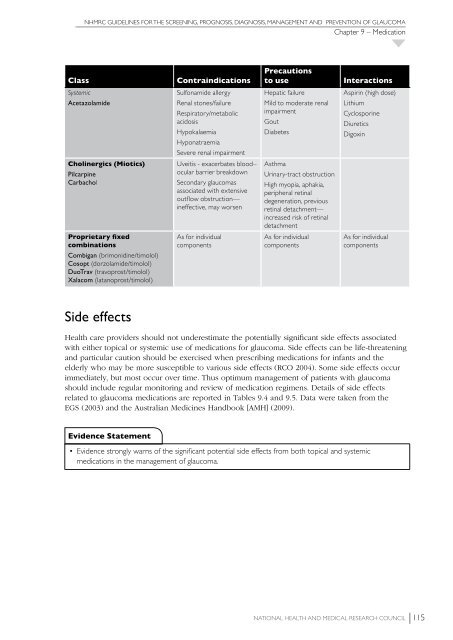
Class<br />
Contraindications<br />
Precautions<br />
to use<br />
Interactions<br />
Systemic<br />
Acetazolamide<br />
Sulfonamide allergy<br />
Renal stones/failure<br />
Respiratory/metabolic<br />
acidosis<br />
Hypokalaemia<br />
Hyponatraemia<br />
Severe renal impairment<br />
Hepatic failure<br />
Mild to moderate renal<br />
impairment<br />
Gout<br />
Diabetes<br />
Aspirin (high dose)<br />
Lithium<br />
Cyclosporine<br />
Diuretics<br />
Digoxin<br />
Cholinergics (Miotics)<br />
Pilcarpine<br />
Carbachol<br />
Uveitis - exacerbates blood–<br />
ocular barrier breakdown<br />
Secondary glaucomas<br />
associated with extensive<br />
outflow obstruction—<br />
ineffective, may worsen<br />
Asthma<br />
Urinary-tract obstruction<br />
High myopia, aphakia,<br />
peripheral retinal<br />
degeneration, previous<br />
retinal detachment—<br />
increased risk of retinal<br />
detachment<br />
Proprietary fixed<br />
combinations<br />
Combigan (brimonidine/timolol)<br />
Cosopt (dorzolamide/timolol)<br />
DuoTrav (travoprost/timolol)<br />
Xalacom (latanoprost/timolol)<br />
As for individual<br />
components<br />
As for individual<br />
components<br />
As for individual<br />
components<br />
Side effects<br />
Health care providers should not underestimate the potentially significant side effects associated<br />
with either topical or systemic use of medications for glaucoma. Side effects can be life-threatening<br />
and particular caution should be exercised when prescribing medications for infants and the<br />
elderly who may be more susceptible to various side effects (RCO 2004). Some side effects occur<br />
immediately, but most occur over time. Thus optimum management of patients with glaucoma<br />
should include regular monitoring and review of medication regimens. Details of side effects<br />
related to glaucoma medications are reported in Tables 9.4 and 9.5. Data were taken from the<br />
EGS (2003) and the Australian Medicines Handbook [AMH] (2009).<br />
Evidence Statement<br />
• Evidence strongly warns of the significant potential side effects from both topical and systemic<br />
medications in the management of glaucoma.<br />
National Health and Medical Research Council 115