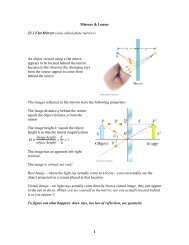
Astronomical Spectroscopy - Physics - University of Cincinnati
Astronomical Spectroscopy - Physics - University of Cincinnati
Astronomical Spectroscopy - Physics - University of Cincinnati
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
– 23 –<br />
Fig. 8.— Optical layout <strong>of</strong> Magellan’s IMACS. This is based upon an illustration in the<br />
IMACS user manual.<br />
2.4.2. Fiber-fed Bench-Mounted Spectrographs<br />
As an alternative to multi-slit masks, a spectrograph can be fed by multiple optical<br />
fibers. The fibers can be arranged in the focal plane so that light from the objects <strong>of</strong> interest<br />
enter the fibers, while at the spectrograph end the fibers are arranged in a line, with the<br />
ends acting like the slit in the model <strong>of</strong> the basic spectrograph (Figure 1). Fibers were first<br />
commonly used for multi-object spectroscopy in the 1980s, prior even to the advent <strong>of</strong> CCDs;<br />
for example, the Boller and Chivens spectrograph on the Las Campanas du Pont 100-inch<br />
telescope was used with a plug-board fiber system when the detector was an intensified<br />
Reticon system. Plug-boards are like multi-slit masks in that there are a number <strong>of</strong> holes<br />
pre-drilled at specific locations in which the fibers are then “plugged”. For most modern<br />
fiber systems, the fibers are positioned robotically in the focal plane, although the Sloan<br />
Digital Sky Survey used a plug-board system. A major advantage <strong>of</strong> a fiber system is that<br />
the spectrograph can be mounted on a laboratory air-supported optical bench in a clean<br />
room, and thus not suffer flexure as the telescope is moved. This can result in high stability,<br />
needed for precision radial velocities. The fibers themselves provide additional “scrambling”<br />
<strong>of</strong> the light, also significantly improving the radial velocity precision, as otherwise the exact<br />
placement <strong>of</strong> a star on the slit may bias the measured velocities.<br />
There are three down sides to fiber systems. First, the fibers themselves tend to have<br />
significant losses <strong>of</strong> light at the slit end; i.e., not all <strong>of</strong> the light falling on the entrance