Train the Trainer Course book - Cochrane Public Health Group
Train the Trainer Course book - Cochrane Public Health Group
Train the Trainer Course book - Cochrane Public Health Group
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
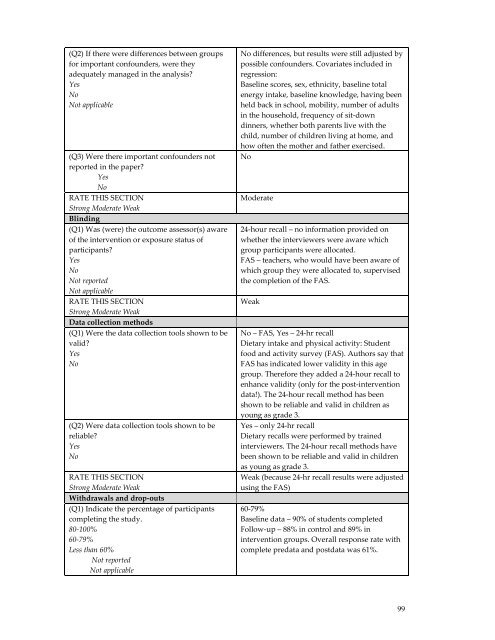
(Q2) If <strong>the</strong>re were differences between groups<br />
for important confounders, were <strong>the</strong>y<br />
adequately managed in <strong>the</strong> analysis?<br />
Yes<br />
No<br />
Not applicable<br />
(Q3) Were <strong>the</strong>re important confounders not<br />
reported in <strong>the</strong> paper?<br />
Yes<br />
No<br />
RATE THIS SECTION<br />
Strong Moderate Weak<br />
Blinding<br />
(Q1) Was (were) <strong>the</strong> outcome assessor(s) aware<br />
of <strong>the</strong> intervention or exposure status of<br />
participants?<br />
Yes<br />
No<br />
Not reported<br />
Not applicable<br />
RATE THIS SECTION<br />
Strong Moderate Weak<br />
Data collection methods<br />
(Q1) Were <strong>the</strong> data collection tools shown to be<br />
valid?<br />
Yes<br />
No<br />
(Q2) Were data collection tools shown to be<br />
reliable?<br />
Yes<br />
No<br />
RATE THIS SECTION<br />
Strong Moderate Weak<br />
Withdrawals and drop-outs<br />
(Q1) Indicate <strong>the</strong> percentage of participants<br />
completing <strong>the</strong> study.<br />
80-100%<br />
60-79%<br />
Less than 60%<br />
Not reported<br />
Not applicable<br />
No differences, but results were still adjusted by<br />
possible confounders. Covariates included in<br />
regression:<br />
Baseline scores, sex, ethnicity, baseline total<br />
energy intake, baseline knowledge, having been<br />
held back in school, mobility, number of adults<br />
in <strong>the</strong> household, frequency of sit-down<br />
dinners, whe<strong>the</strong>r both parents live with <strong>the</strong><br />
child, number of children living at home, and<br />
how often <strong>the</strong> mo<strong>the</strong>r and fa<strong>the</strong>r exercised.<br />
No<br />
Moderate<br />
24-hour recall – no information provided on<br />
whe<strong>the</strong>r <strong>the</strong> interviewers were aware which<br />
group participants were allocated.<br />
FAS – teachers, who would have been aware of<br />
which group <strong>the</strong>y were allocated to, supervised<br />
<strong>the</strong> completion of <strong>the</strong> FAS.<br />
Weak<br />
No – FAS, Yes – 24-hr recall<br />
Dietary intake and physical activity: Student<br />
food and activity survey (FAS). Authors say that<br />
FAS has indicated lower validity in this age<br />
group. Therefore <strong>the</strong>y added a 24-hour recall to<br />
enhance validity (only for <strong>the</strong> post-intervention<br />
data!). The 24-hour recall method has been<br />
shown to be reliable and valid in children as<br />
young as grade 3.<br />
Yes – only 24-hr recall<br />
Dietary recalls were performed by trained<br />
interviewers. The 24-hour recall methods have<br />
been shown to be reliable and valid in children<br />
as young as grade 3.<br />
Weak (because 24-hr recall results were adjusted<br />
using <strong>the</strong> FAS)<br />
60-79%<br />
Baseline data – 90% of students completed<br />
Follow-up – 88% in control and 89% in<br />
intervention groups. Overall response rate with<br />
complete predata and postdata was 61%.<br />
99