Full Report
Full Report
Full Report
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
DISCUSSIONS &<br />
RECOMENDATIONS<br />
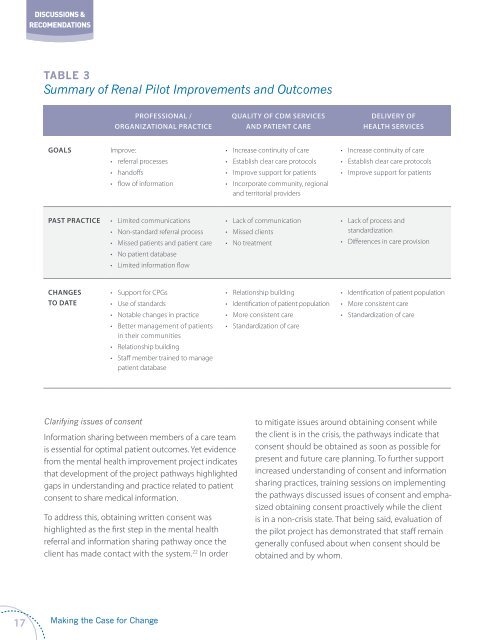
Table 3<br />
Summary of Renal Pilot Improvements and Outcomes<br />
PROFESSIONAL /<br />
ORGANIZATIONAL PRACTICE<br />
QUALITY OF CDM SERVICES<br />
AND PATIENT CARE<br />
DELIVERY OF<br />
HEALTH SERVICES<br />
GOALS<br />
Improve:<br />
• referral processes<br />
• handoffs<br />
• flow of information<br />
• Increase continuity of care<br />
• Establish clear care protocols<br />
• Improve support for patients<br />
• Incorporate community, regional<br />
and territorial providers<br />
• Increase continuity of care<br />
• Establish clear care protocols<br />
• Improve support for patients<br />
PAST PRACTICE<br />
• Limited communications<br />
• Non-standard referral process<br />
• Missed patients and patient care<br />
• No patient database<br />
• Limited information flow<br />
• Lack of communication<br />
• Missed clients<br />
• No treatment<br />
• Lack of process and<br />
standardization<br />
• Differences in care provision<br />
CHANGES<br />
TO DATE<br />
• Support for CPGs<br />
• Use of standards<br />
• Notable changes in practice<br />
• Better management of patients<br />
in their communities<br />
• Relationship building<br />
• Staff member trained to manage<br />
patient database<br />
• Relationship building<br />
• Identification of patient population<br />
• More consistent care<br />
• Standardization of care<br />
• Identification of patient population<br />
• More consistent care<br />
• Standardization of care<br />
Clarifying issues of consent<br />
Information sharing between members of a care team<br />
is essential for optimal patient outcomes. Yet evidence<br />
from the mental health improvement project indicates<br />
that development of the project pathways highlighted<br />
gaps in understanding and practice related to patient<br />
consent to share medical information.<br />
To address this, obtaining written consent was<br />
highlighted as the first step in the mental health<br />
referral and information sharing pathway once the<br />
client has made contact with the system. 22 In order<br />
to mitigate issues around obtaining consent while<br />
the client is in the crisis, the pathways indicate that<br />
consent should be obtained as soon as possible for<br />
present and future care planning. To further support<br />
increased understanding of consent and information<br />
sharing practices, training sessions on implementing<br />
the pathways discussed issues of consent and emphasized<br />
obtaining consent proactively while the client<br />
is in a non-crisis state. That being said, evaluation of<br />
the pilot project has demonstrated that staff remain<br />
generally confused about when consent should be<br />
obtained and by whom.<br />
17<br />
Making the Case for Change