Full Report
Full Report
Full Report
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
DIABETES<br />
Figure 6<br />
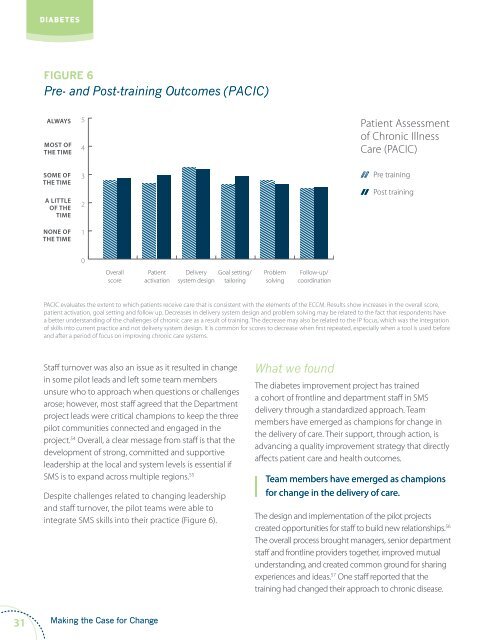
Pre- and Post-training Outcomes (PACIC)<br />
ALWAYS<br />
MOST OF<br />
THE TIME<br />
5<br />
4<br />
Patient Assessment<br />
of Chronic Illness<br />
Care (PACIC)<br />
SOME OF<br />
THE TIME<br />
A LITTLE<br />
OF THE<br />
TIME<br />
NONE OF<br />
THE TIME<br />
3<br />
2<br />
1<br />
Pre training<br />
Post training<br />
0<br />
Overall<br />
score<br />
Patient<br />
activation<br />
Delivery<br />
system design<br />
Goal setting/<br />
tailoring<br />
Problem<br />
solving<br />
Follow-up/<br />
coordination<br />
PACIC evaluates the extent to which patients receive care that is consistent with the elements of the ECCM. Results show increases in the overall score,<br />
patient activation, goal setting and follow up. Decreases in delivery system design and problem solving may be related to the fact that respondents have<br />
a better understanding of the challenges of chronic care as a result of training. The decrease may also be related to the IP focus, which was the integration<br />
of skills into current practice and not delivery system design. It is common for scores to decrease when first repeated, especially when a tool is used before<br />
and after a period of focus on improving chronic care systems.<br />
Staff turnover was also an issue as it resulted in change<br />
in some pilot leads and left some team members<br />
unsure who to approach when questions or challenges<br />
arose; however, most staff agreed that the Department<br />
project leads were critical champions to keep the three<br />
pilot communities connected and engaged in the<br />
project. 54 Overall, a clear message from staff is that the<br />
development of strong, committed and supportive<br />
leadership at the local and system levels is essential if<br />
SMS is to expand across multiple regions. 55<br />
Despite challenges related to changing leadership<br />
and staff turnover, the pilot teams were able to<br />
integrate SMS skills into their practice (Figure 6).<br />
What we found<br />
The diabetes improvement project has trained<br />
a cohort of frontline and department staff in SMS<br />
delivery through a standardized approach. Team<br />
members have emerged as champions for change in<br />
the delivery of care. Their support, through action, is<br />
advancing a quality improvement strategy that directly<br />
affects patient care and health outcomes.<br />
Team members have emerged as champions<br />
for change in the delivery of care.<br />
The design and implementation of the pilot projects<br />
created opportunities for staff to build new relationships. 56<br />
The overall process brought managers, senior department<br />
staff and frontline providers together, improved mutual<br />
understanding, and created common ground for sharing<br />
experiences and ideas. 57 One staff reported that the<br />
training had changed their approach to chronic disease.<br />
31<br />
Making the Case for Change