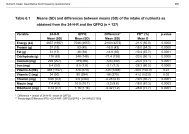
1998b) and comprise only 31.0% <strong>of</strong> the client population at substance abuse treatmentfacilities. In contrast, White South Africans cont<strong>in</strong>ue to be over-represented <strong>in</strong> substanceabuse treatment facilities, relative to the demographic pr<strong>of</strong>ile <strong>of</strong> the general population.These f<strong>in</strong>d<strong>in</strong>gs are <strong>in</strong> keep<strong>in</strong>g with f<strong>in</strong>d<strong>in</strong>gs from previous audits <strong>of</strong> treatment facilities <strong>in</strong>Gauteng and KwaZulu-Natal (Myers & Fakier, 2007), Gauteng (Myers, 2004) and CapeTown (Myers & Parry, 2003).As substance abuse treatment need has not been properly <strong>in</strong>vestigated <strong>in</strong> South Africa, itis unclear whether there are disparities <strong>in</strong> the need for substance abuse treatment servicesamong the racially def<strong>in</strong>ed social groups. Despite this gap, emerg<strong>in</strong>g evidence suggeststhat poor Black/African communities may be especially vulnerable to substance usedisorders, due to the psychological stress associated with rapid urbanisation, poverty,neighbourhood social dysfunction, and a lack <strong>of</strong> basic <strong>in</strong>frastructure (Flisher & Charlton,2001; Kalichman et al., 2006; Latk<strong>in</strong>, Williams, Wang, & Curry, 2005) - factors that<strong>of</strong>ten characterise these communities. Anecdotal reports <strong>of</strong> <strong>in</strong>creas<strong>in</strong>g levels <strong>of</strong> substanceuse among Black/African communities also suggest that this pattern <strong>of</strong> service utilisationreflects the limited extent to which Black/African South Africans have access tosubstance abuse treatment rather than lower levels <strong>of</strong> substance use by these raciallydef<strong>in</strong>ed social groups (Myers et al., 2004; Myers & Parry, 2005).In terms <strong>of</strong> gender, f<strong>in</strong>d<strong>in</strong>gs show that women are also under-represented <strong>in</strong> substanceabuse treatment facilities. Although women comprise at least half <strong>of</strong> the generalpopulation (Statistics South Africa, 2005), on average less than 30.0% <strong>of</strong> the recipients <strong>of</strong>substance abuse treatment services <strong>in</strong> Free State, Limpopo, Mpumalanga, North West andNorthern Cape are women. This f<strong>in</strong>d<strong>in</strong>g is <strong>in</strong> keep<strong>in</strong>g with f<strong>in</strong>d<strong>in</strong>gs from previous audits<strong>of</strong> substance abuse treatment facilities <strong>in</strong> Cape Town; Gauteng as well as KwaZulu-Nataland Gauteng (Myers, 2004; Myers & Parry, 2003; Myers & Fakier, 2007) and<strong>in</strong>ternational research which po<strong>in</strong>ts to the under-representation <strong>of</strong> women <strong>in</strong> treatment(Schober & Annis, 1996; Zule, Lam, & Wechsberg, 2003). However, this pattern <strong>of</strong>treatment service utilisation by women probably reflects the limited extent to whichwomen have access to substance abuse treatment rather than lower levels <strong>of</strong> substanceuse by women; especially given research which suggests that similar proportions <strong>of</strong> menand women dr<strong>in</strong>k at risky levels <strong>in</strong> South Africa (Parry et al., 2005) and that po<strong>in</strong>ts to70
high levels <strong>of</strong> substance use among women <strong>in</strong> Cape Town (Sawyer, Wechsberg, &Myers, 2006).4.3.2. Access to treatment: Target<strong>in</strong>g barriers to treatment entrySeveral studies have identified barriers that h<strong>in</strong>der access to treatment for clients fromunderserved groups. In South Africa, these barriers <strong>in</strong>clude awareness <strong>of</strong> treatmentservices; logistic barriers <strong>in</strong>clud<strong>in</strong>g access to transport; affordability barriers relat<strong>in</strong>g tothe costs <strong>of</strong> services; and l<strong>in</strong>guistic barriers, relat<strong>in</strong>g to the language <strong>in</strong> which services areprovided (Myers, 2007). These barriers, if unaddressed, may negatively impact ontreatment-seek<strong>in</strong>g behaviour (Beardsley et al., 2003; Joe et al., 2002). This studyexam<strong>in</strong>ed the extent to which substance abuse treatment facilities address these keybarriers to treatment entry for clients from historically underserved groups.Awareness-related barriers to treatment entryLimited knowledge and awareness about where to seek help for substance use disordersand how to access help <strong>in</strong>hibits entry <strong>in</strong>to substance abuse treatment (Hser et al., 1998),particularly for poor Black/African substance users (Myers, 2007). Less than half <strong>of</strong>facilities attempt to address this barrier by conduct<strong>in</strong>g rout<strong>in</strong>e awareness campaigns (atleast once a month) that provide <strong>in</strong>formation about substance abuse treatment options.Just over half <strong>of</strong> facilities report rout<strong>in</strong>ely distribut<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong>formation and materialsperta<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g to substance abuse and available treatment options. Over 80.0% <strong>of</strong> facilitiesrout<strong>in</strong>ely conduct outreach among vulnerable groups and conduct outreach <strong>in</strong>disadvantaged areas. In comparison, the <strong>in</strong>ner city areas are relatively neglected, with justover 50.0% <strong>of</strong> facilities rout<strong>in</strong>ely target<strong>in</strong>g these high-risk areas.The important role that outreach can play <strong>in</strong> address<strong>in</strong>g awareness-related barriers amongunderserved Black/African communities (and <strong>in</strong> facilitat<strong>in</strong>g treatment entry) is reflected<strong>in</strong> f<strong>in</strong>d<strong>in</strong>gs that facilities which conduct outreach activities <strong>in</strong> disadvantaged areas treatsignificantly more Black/African clients than facilities without these services.Logistic and affordability barriers to treatment entryAffordability and other logistic barriers (such as access to transport) also hamper entry<strong>in</strong>to treatment for South African substance abus<strong>in</strong>g populations (Myers, 2007). For71
- Page 1 and 2:
Alcohol & Drug Abuse Research UnitM
- Page 3 and 4:
3.1.2 Treatment facility profile by
- Page 5 and 6:
4.3 Targeting barriers to treatment
- Page 7 and 8:
EXECUTIVE SUMMARYA cross-sectional
- Page 9 and 10:
services to historically underserve
- Page 11 and 12:
use, reductions in criminal activit
- Page 13 and 14:
Despite high levels of substance ab
- Page 15 and 16:
Despite the apparent availability o
- Page 17 and 18:
treatment services provided. At pre
- Page 19 and 20: use disorders whose physical and em
- Page 21 and 22: delivery, treatment retention, and
- Page 23 and 24: audit substance abuse treatment fac
- Page 25 and 26: 2.8.3. Further data considerations
- Page 27 and 28: Figure 1. Inpatient intensity of ca
- Page 29 and 30: Since there is a large overlap betw
- Page 31 and 32: the total client population (χ = 4
- Page 33 and 34: Figure 7.Comparison of race profile
- Page 35 and 36: services per month ranges from 13 t
- Page 37 and 38: 3.4.1. Characteristics of staff at
- Page 39 and 40: supervision. In contrast, a much sm
- Page 41 and 42: In terms of client record-keeping,
- Page 43 and 44: Core findings:• Compared to the p
- Page 45 and 46: using 12-step approaches, 75.0% rep
- Page 47 and 48: Figure 16. Proportion of treatment
- Page 49 and 50: 3.7. ADDRESSING BARRIERS TO TREATME
- Page 51 and 52: Table 11. Proportion of facilities
- Page 53 and 54: Table 12. Proportion of facilities
- Page 55 and 56: Figure 20.Proportion of substance a
- Page 57 and 58: Table 14. Proportion of facilities
- Page 59 and 60: Table 15. Proportion of facilities
- Page 61 and 62: 3.9.2. Monitoring of clients’ pro
- Page 63 and 64: Table 16. Proportion of facilities
- Page 65 and 66: PART 4: DISCUSSION OF KEY FINDINGSW
- Page 67 and 68: previous audits of specialist subst
- Page 69: small proportion of South African d
- Page 73 and 74: these barriers appears to significa
- Page 75 and 76: appropriate services for Black/Afri
- Page 77 and 78: clients progress post-treatment, an
- Page 79 and 80: • The number of state facilities
- Page 81 and 82: • Another way of ensuring (indire
- Page 83 and 84: • The age appropriateness of serv
- Page 85 and 86: REFERENCESAllard, S.W., Tolman, R.M
- Page 87 and 88: Myers, B., & Fakier, N. (2007). Rep
- Page 89: Zule, W.A., Lam, W.K., & Wechsberg,