Climate change futures: health, ecological and economic dimensions
Climate change futures: health, ecological and economic dimensions
Climate change futures: health, ecological and economic dimensions
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
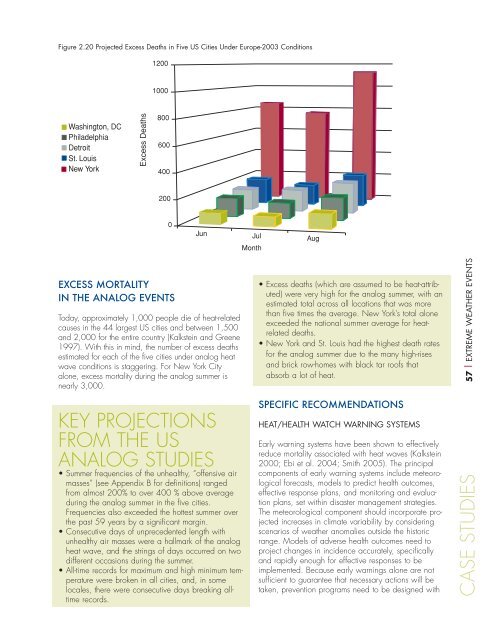
Figure 2.20 Projected Excess Deaths in Five US Cities Under Europe-2003 Conditions12001000Washington, DCPhiladelphiaDetroitSt. LouisNew YorkExcess Deaths8006004002000Jun Jul AugMonthEXCESS MORTALITYIN THE ANALOG EVENTSToday, approximately 1,000 people die of heat-relatedcauses in the 44 largest US cities <strong>and</strong> between 1,500<strong>and</strong> 2,000 for the entire country (Kalkstein <strong>and</strong> Greene1997). With this in mind, the number of excess deathsestimated for each of the five cities under analog heatwave conditions is staggering. For New York Cityalone, excess mortality during the analog summer isnearly 3,000.• Excess deaths (which are assumed to be heat-attributed)were very high for the analog summer, with anestimated total across all locations that was morethan five times the average. New York’s total aloneexceeded the national summer average for heatrelateddeaths.• New York <strong>and</strong> St. Louis had the highest death ratesfor the analog summer due to the many high-rises<strong>and</strong> brick row-homes with black tar roofs thatabsorb a lot of heat.57 | EXTREME WEATHER EVENTSKEY PROJECTIONSFROM THE USANALOG STUDIES• Summer frequencies of the un<strong>health</strong>y, “offensive airmasses” (see Appendix B for definitions) rangedfrom almost 200% to over 400 % above averageduring the analog summer in the five cities.Frequencies also exceeded the hottest summer overthe past 59 years by a significant margin.• Consecutive days of unprecedented length withun<strong>health</strong>y air masses were a hallmark of the analogheat wave, <strong>and</strong> the strings of days occurred on twodifferent occasions during the summer.• All-time records for maximum <strong>and</strong> high minimum temperaturewere broken in all cities, <strong>and</strong>, in somelocales, there were consecutive days breaking alltimerecords.SPECIFIC RECOMMENDATIONSHEAT/HEALTH WATCH WARNING SYSTEMSEarly warning systems have been shown to effectivelyreduce mortality associated with heat waves (Kalkstein2000; Ebi et al. 2004; Smith 2005). The principalcomponents of early warning systems include meteorologicalforecasts, models to predict <strong>health</strong> outcomes,effective response plans, <strong>and</strong> monitoring <strong>and</strong> evaluationplans, set within disaster management strategies.The meteorological component should incorporate projectedincreases in climate variability by consideringscenarios of weather anomalies outside the historicrange. Models of adverse <strong>health</strong> outcomes need toproject <strong>change</strong>s in incidence accurately, specifically<strong>and</strong> rapidly enough for effective responses to beimplemented. Because early warnings alone are notsufficient to guarantee that necessary actions will betaken, prevention programs need to be designed withCASE STUDIES