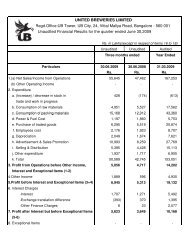
president & cfo - UB Group
president & cfo - UB Group
president & cfo - UB Group
- No tags were found...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Schedules forming part of account for the year ended March 31, 2009 (Contd.)Exchange differences arising on reporting of long term foreign currency monetary items, with the exception ofexchange differences arising on a monetary item that, in substance, forms part of an enterprise’s net investmentin a non-integral foreign operation, at rates different from those at which they were initially recorded during theperiod or reported in previous financial statements, are accounted as below:(a) In so far as they relate to the acquisition of depreciable capital assets, are added to or deducted from the costof the asset and are depreciated over the balance life of the asset; and(b) In other cases, the said exchange differences are accumulated in a ‘Foreign Currency Monetary ItemsTranslation Difference Account’ and amortised over the balance period of such long term asset/liability butnot beyond March 31, 2011.All other monetary assets and liabilities denominated in foreign currency are restated at the rates ruling at theyear end and all exchange gains/ losses arising therefrom are adjusted to the Profit and Loss Account, except thosecovered by forward contracted rates where the premium or discount arising at the inception of such forwardexchange contract is amortised as expense or income over the life of the contract.Exchange differences on forward contracts are recognised in the Profit and Loss Account in the reporting period inwhich the exchange rates change. Any profit or loss arising on cancellation or renewal of such forward contractsis recognised as income or expense for the year.For forward exchange contracts and other derivatives that are not covered by Accounting Standard (AS) -11‘The Effects of Changes in Foreign Exchange Rates’, the Company follows the guidance in the announcementof the Institute of Chartered Accountants of India (ICAI) dated March 29, 2008, whereby for each category ofderivatives, the Company records any net mark-to-market losses. Net mark-to-market gains are not recorded forsuch derivatives.Also refer Schedule 18 Note 12 below.10. Employee Benefitsa) Defined-contribution plansThese are plans in which the Company pays pre-defined amounts to separate funds and does not have anylegal or informal obligation to pay additional sums. These comprise of contributions to the employees’provident fund with the government, superannuation fund and certain state plans like Employees’ StateInsurance and Employees’ Pension Scheme. The Company’s payments to the defined contribution plans arerecognised as expenses during the period in which the employees perform the services that the paymentcovers.b) Defined-benefit plansGratuity:The Company provides for gratuity, a defined benefit plan (the Gratuity Plan), to certain categories ofemployees. Liability with regard to gratuity plan is accrued based on actuarial valuation, based on ProjectedUnit Credit Method at the balance sheet date, carried out by an independent actuary. Actuarial Gains andLosses comprise experience adjustments and the effect of changes in the actuarial assumptions and arerecognised immediately in the Profit and Loss Account as income or expense.Provident Fund:Company’s Provident Funds administered by trusts set up by the Company where the Company’s obligation isto provide the agreed benefit to the employees and the actuarial risk and investment risk fall, in substance,on the Company are treated as a defined benefit plan. Liability with regard to such provident fund plans are43