Advanced CAD System for Electromagnetic MEMS Interactive Analysis
Advanced CAD System for Electromagnetic MEMS Interactive Analysis
Advanced CAD System for Electromagnetic MEMS Interactive Analysis
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
2. Objectives, Approach and Significant Results<br />
2.1 Software Development<br />
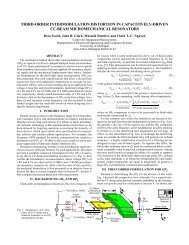
A key objective is to develop and demonstrate fully-integrated, FEM-based prototype solver<br />
capabilities to model behavior and fabrication process-dependency of <strong>MEMS</strong> devices. This<br />
includes capabilities to consider multi-physics and materials dependencies as well as other<br />
process induced factors—<strong>for</strong> example, geometry effects due to deposition/etching. The overall<br />
tool integration strategy was targeted to develop and test key components that overcome limits<br />
currently seen to be "bottlenecks" in <strong>CAD</strong> systems. Application-specific lumped modeling was<br />
pursued early on in the project and used to guide the overall direction of the <strong>CAD</strong> ef<strong>for</strong>ts,<br />
including improved parameter extraction schemes that cross-link device per<strong>for</strong>mance with<br />
physical factors such as layout and process dependencies. The approach used here addresses the<br />
following in<strong>for</strong>mation flow and simulation capabilities:<br />
1. Layered access in <strong>MEMS</strong> specification across levels--layout, process specification,<br />
geometry definition, grid and constitutive models<br />
2. Enhanced element technology <strong>for</strong> discretization of multi-physics systems of equations<br />
3. Unified approach to interface geometry and gridding through use of servers.<br />
4. Demonstration of integrated <strong>MEMS</strong> simulation capability with internet access to<br />
modeling and open interface standards including parameter extraction<br />
5. Prototyping of benchmark canonical RF test structures--both computationally and<br />
experimentally--that demonstrate capabilities of models and tools.<br />
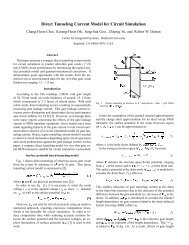
The PhD thesis of Edward Chan [1], completed during the course of this project, describes: the<br />
validation of a canonical benchmark device (RF switch), characterization of the contact electromechanical<br />
phenomena, and the design of an electrostatic actuator with an extended range of<br />
travel. Included in the thesis are analyses (through simulations) of the effects of: changes in<br />
substrate curvature, the influences of stress gradients on fixed-fixed beams, and the importance<br />
of considering film coverage in understanding the behavior of composite materials. Rigid-body<br />
simulations of the electrostatic actuator with series feedback capacitor, used <strong>for</strong> extended travel,<br />
reveal that tilting always occurs at a spacing of ~60% of the initial gap. This tilting occurs due to<br />
asymmetry, but it is unclear why the range does not depend on degree of asymmetry or the size<br />
of the series capacitance. One difficulty related to tilting in the electrostatic actuator with<br />
extended range of travel is the fact that increasing the feedback or reducing asymmetry cannot<br />
mitigate the effect.<br />
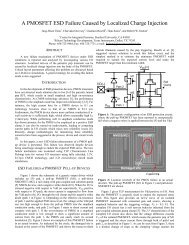
Two aspects of the software and design capabilities developed during this research deserve<br />
special note and discussion--web-based design of <strong>MEMS</strong> and accurate modeling of geometry<br />
and process-flow in<strong>for</strong>mation. In the area of web-based design, demonstrations of the final<br />
prototype are available through the Stan<strong>for</strong>d T<strong>CAD</strong> web site [2]. Subsequent to the ending of<br />
this contract there has been substantial interest expressed by researchers at the Beckmann<br />
Institute at the University of Illinois (Professors Narayan Aluru and Umberto Ravaioli) in<br />
continuing ef<strong>for</strong>ts in this direction with computational support also coming through NCSA<br />
(National Computational Science Alliance) co-located at Illinois. The web-based prototyping<br />
environment now includes a more robust interface, remote process tracking to show the status of<br />
2