enumeration of the number of spanning trees in some ... - Toubkal
enumeration of the number of spanning trees in some ... - Toubkal
enumeration of the number of spanning trees in some ... - Toubkal
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
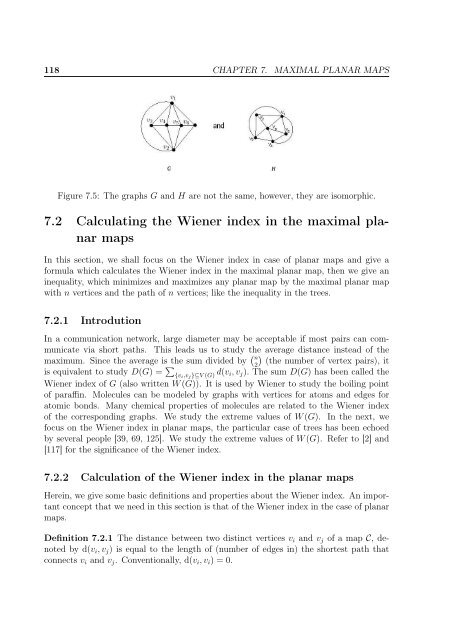
118 CHAPTER 7. MAXIMAL PLANAR MAPSFigure 7.5: The graphs G and H are not <strong>the</strong> same, however, <strong>the</strong>y are isomorphic.7.2 Calculat<strong>in</strong>g <strong>the</strong> Wiener <strong>in</strong>dex <strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong> maximal planarmapsIn this section, we shall focus on <strong>the</strong> Wiener <strong>in</strong>dex <strong>in</strong> case <strong>of</strong> planar maps and give aformula which calculates <strong>the</strong> Wiener <strong>in</strong>dex <strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong> maximal planar map, <strong>the</strong>n we give an<strong>in</strong>equality, which m<strong>in</strong>imizes and maximizes any planar map by <strong>the</strong> maximal planar mapwith n vertices and <strong>the</strong> path <strong>of</strong> n vertices; like <strong>the</strong> <strong>in</strong>equality <strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong> <strong>trees</strong>.7.2.1 IntrodutionIn a communication network, large diameter may be acceptable if most pairs can communicatevia short paths. This leads us to study <strong>the</strong> average distance <strong>in</strong>stead <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong>maximum. S<strong>in</strong>ce <strong>the</strong> average is <strong>the</strong> sum divided by ( n2)(<strong>the</strong> <strong>number</strong> <strong>of</strong> vertex pairs), itis equivalent to study D(G) = ∑ {v i ,v j }⊆V (G) d(v i, v j ). The sum D(G) has been called <strong>the</strong>Wiener <strong>in</strong>dex <strong>of</strong> G (also written W (G)). It is used by Wiener to study <strong>the</strong> boil<strong>in</strong>g po<strong>in</strong>t<strong>of</strong> paraff<strong>in</strong>. Molecules can be modeled by graphs with vertices for atoms and edges foratomic bonds. Many chemical properties <strong>of</strong> molecules are related to <strong>the</strong> Wiener <strong>in</strong>dex<strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> correspond<strong>in</strong>g graphs. We study <strong>the</strong> extreme values <strong>of</strong> W (G). In <strong>the</strong> next, wefocus on <strong>the</strong> Wiener <strong>in</strong>dex <strong>in</strong> planar maps, <strong>the</strong> particular case <strong>of</strong> <strong>trees</strong> has been echoedby several people [39, 69, 125]. We study <strong>the</strong> extreme values <strong>of</strong> W (G). Refer to [2] and[117] for <strong>the</strong> significance <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> Wiener <strong>in</strong>dex.7.2.2 Calculation <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> Wiener <strong>in</strong>dex <strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong> planar mapsHere<strong>in</strong>, we give <strong>some</strong> basic def<strong>in</strong>itions and properties about <strong>the</strong> Wiener <strong>in</strong>dex. An importantconcept that we need <strong>in</strong> this section is that <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> Wiener <strong>in</strong>dex <strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong> case <strong>of</strong> planarmaps.Def<strong>in</strong>ition 7.2.1 The distance between two dist<strong>in</strong>ct vertices v i and v j <strong>of</strong> a map C, denotedby d(v i , v j ) is equal to <strong>the</strong> length <strong>of</strong> (<strong>number</strong> <strong>of</strong> edges <strong>in</strong>) <strong>the</strong> shortest path thatconnects v i and v j . Conventionally, d(v i , v i ) = 0.