120 CHAPTER 7. MAXIMAL PLANAR MAPSRemark 7.2.7 We notice that delet<strong>in</strong>g one edge <strong>of</strong> multiple edges does not affect <strong>the</strong>Wiener <strong>in</strong>dex; through this section, we consider only <strong>the</strong> simple planar maps, i.e., mapswithout loops and multiple edges.Lemma 7.2.8 Let C n be a simple planar map with n vertices and v be a complete vertex<strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong> map C, <strong>the</strong>ndeg(v) = n − 1 and W (v, C n ) = n − 1.Lemma 7.2.9 Let C n be a simple planar map with n vertices (n ≥ 2) and let v be avertex not complete <strong>of</strong> C n , <strong>the</strong>nW (v, C n ) ≥ n.Remark 7.2.101. Let C n be a simple planar map and v be a vertex <strong>of</strong> C n , <strong>the</strong>n W (v, C n ) ≥ n − 1.2. Let C n be a simple planar map with n vertices, e be an edge <strong>of</strong> C n and let C n − e be<strong>the</strong> map obta<strong>in</strong>ed by delet<strong>in</strong>g <strong>the</strong> edge e such that <strong>the</strong> map C n −e rema<strong>in</strong>s connected,<strong>the</strong>n W (C n − e) ≥ W (C n ).Theorem 7.2.11 Let C n be a simple planar map with n vertices, <strong>the</strong>nW (C n ) ≥n(n − 1).2Pro<strong>of</strong>: Let C n be a planar map with n vertices and let v be a vertex <strong>of</strong> C n . By Remark7.2.10, we have: W (v, C n ) ≥ n − 1;W (C n ) = 1 2≥ 1 2≥∑v∈V (C n )∑v∈V (C n )n(n − 1).2W (v, C n )(n − 1) = 1 2 (n − 1) ∑v∈V (C n )Def<strong>in</strong>ition 7.2.12 (A maximal planar map [39]) Let E n be a family <strong>of</strong> planar maps thatconta<strong>in</strong>s:• n vertices, two complete vertices <strong>of</strong> degree n − 1, two vertices <strong>of</strong> degree 3 and n − 4vertices <strong>of</strong> degree 4,• 2(n − 2) faces <strong>of</strong> degree 3 (all faces hav<strong>in</strong>g degree 3),• 3(n − 2) edges,1□
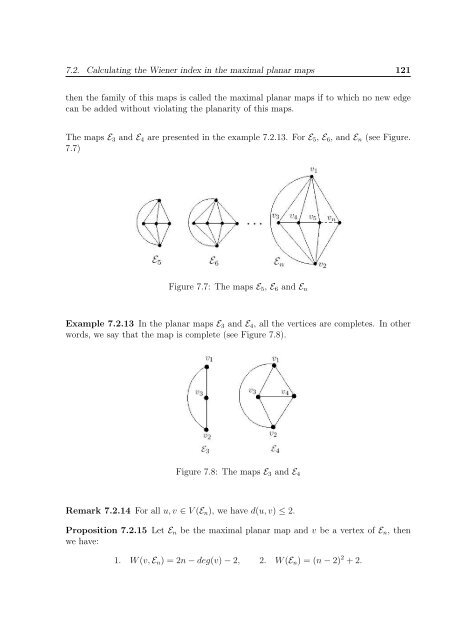
7.2. Calculat<strong>in</strong>g <strong>the</strong> Wiener <strong>in</strong>dex <strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong> maximal planar maps 121<strong>the</strong>n <strong>the</strong> family <strong>of</strong> this maps is called <strong>the</strong> maximal planar maps if to which no new edgecan be added without violat<strong>in</strong>g <strong>the</strong> planarity <strong>of</strong> this maps.The maps E 3 and E 4 are presented <strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong> example 7.2.13. For E 5 , E 6 , and E n (see Figure.7.7)Figure 7.7: The maps E 5 , E 6 and E nExample 7.2.13 In <strong>the</strong> planar maps E 3 and E 4 , all <strong>the</strong> vertices are completes. In o<strong>the</strong>rwords, we say that <strong>the</strong> map is complete (see Figure 7.8).Figure 7.8: The maps E 3 and E 4Remark 7.2.14 For all u, v ∈ V (E n ), we have d(u, v) ≤ 2.Proposition 7.2.15 Let E n be <strong>the</strong> maximal planar map and v be a vertex <strong>of</strong> E n , <strong>the</strong>nwe have:1. W (v, E n ) = 2n − deg(v) − 2, 2. W (E n ) = (n − 2) 2 + 2.