enumeration of the number of spanning trees in some ... - Toubkal
enumeration of the number of spanning trees in some ... - Toubkal
enumeration of the number of spanning trees in some ... - Toubkal
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
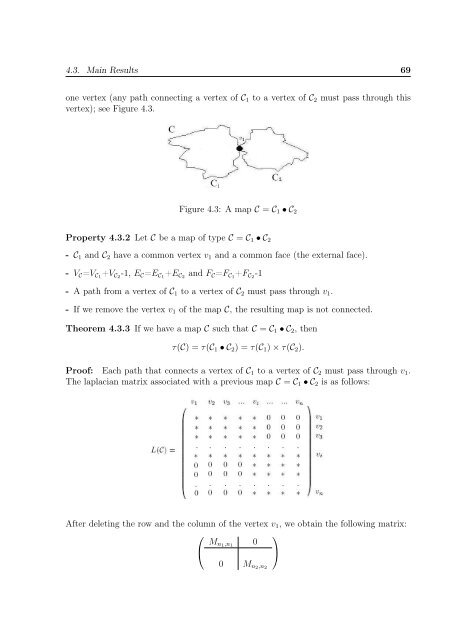
4.3. Ma<strong>in</strong> Results 69one vertex (any path connect<strong>in</strong>g a vertex <strong>of</strong> C 1 to a vertex <strong>of</strong> C 2 must pass through thisvertex); see Figure 4.3.Figure 4.3: A map C = C 1 • C 2Property 4.3.2 Let C be a map <strong>of</strong> type C = C 1 • C 2- C 1 and C 2 have a common vertex v 1 and a common face (<strong>the</strong> external face).- V C =V C1 +V C2 -1, E C =E C1 +E C2 and F C =F C1 +F C2 -1- A path from a vertex <strong>of</strong> C 1 to a vertex <strong>of</strong> C 2 must pass through v 1 .- If we remove <strong>the</strong> vertex v 1 <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> map C, <strong>the</strong> result<strong>in</strong>g map is not connected.Theorem 4.3.3 If we have a map C such that C = C 1 • C 2 , <strong>the</strong>nτ(C) = τ(C 1 • C 2 ) = τ(C 1 ) × τ(C 2 ).Pro<strong>of</strong>: Each path that connects a vertex <strong>of</strong> C 1 to a vertex <strong>of</strong> C 2 must pass through v 1 .The laplacian matrix associated with a previous map C = C 1 • C 2 is as follows:After delet<strong>in</strong>g <strong>the</strong> row and <strong>the</strong> column <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> vertex v 1 , we obta<strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong> follow<strong>in</strong>g matrix:⎛⎞M n1 ,n 10⎝⎠0 M n2 ,n 2