- Page 3:
1To my daughter Hanin.
- Page 6 and 7:
4my wife who has been very supporti
- Page 8 and 9:
6 CONTENTSII Theoretical Part 533 H
- Page 10 and 11:
8 CONTENTS
- Page 14 and 15:
12 LIST OF FIGURES7.11 The maps F n
- Page 16:
14 LIST OF TABLES
- Page 19 and 20:
LIST OF TABLES 17the n-Barrel chain
- Page 21:
Part IPreliminaries19
- Page 24 and 25:
22 CHAPTER 1. DEFINITIONS AND PROPE
- Page 28 and 29:
26 CHAPTER 1. DEFINITIONS AND PROPE
- Page 30 and 31:
28 CHAPTER 1. DEFINITIONS AND PROPE
- Page 32 and 33:
30 CHAPTER 1. DEFINITIONS AND PROPE
- Page 34 and 35:
32 CHAPTER 1. DEFINITIONS AND PROPE
- Page 36 and 37:
34 CHAPTER 1. DEFINITIONS AND PROPE
- Page 38 and 39:
36 CHAPTER 1. DEFINITIONS AND PROPE
- Page 40 and 41:
38 CHAPTER 1. DEFINITIONS AND PROPE
- Page 42 and 43:
40 CHAPTER 1. DEFINITIONS AND PROPE
- Page 44 and 45:
42 CHAPTER 2. SPANNING TREESFigure
- Page 46 and 47:
44 CHAPTER 2. SPANNING TREESThe num
- Page 48 and 49:
46 CHAPTER 2. SPANNING TREESExample
- Page 50 and 51:
48 CHAPTER 2. SPANNING TREESFor exa
- Page 52 and 53:
50 CHAPTER 2. SPANNING TREESIn the
- Page 54 and 55:
52 CHAPTER 2. SPANNING TREES
- Page 57 and 58:
Chapter 3How to count the number of
- Page 59 and 60:
3.3. Counting the number of spannin
- Page 61 and 62:
3.4. Counting the number of spannin
- Page 63 and 64:
3.4. Counting the number of spannin
- Page 65 and 66:
3.4. Counting the number of spannin
- Page 67 and 68:
3.4. Counting the number of spannin
- Page 69 and 70:
Chapter 4New methods to compute the
- Page 71 and 72:
4.3. Main Results 69one vertex (any
- Page 73 and 74:
4.3. Main Results 71Lemma 4.3.8 Let
- Page 75 and 76:
4.3. Main Results 73This recursion
- Page 77 and 78:
4.3. Main Results 75Proof: It is th
- Page 79 and 80: 4.3. Main Results 77Figure 4.12: An
- Page 81 and 82: 4.3. Main Results 79Theorem 4.3.31
- Page 83 and 84: 4.3. Main Results 81Property 4.3.33
- Page 85: Part IIIUse of Derived Theoretical
- Page 88 and 89: CHAPTER 5.86THE NUMBER OF SPANNING
- Page 90 and 91: CHAPTER 5.88THE NUMBER OF SPANNING
- Page 92 and 93: CHAPTER 5.90THE NUMBER OF SPANNING
- Page 94 and 95: CHAPTER 5.92THE NUMBER OF SPANNING
- Page 96 and 97: CHAPTER 5.94THE NUMBER OF SPANNING
- Page 98 and 99: CHAPTER 5.96THE NUMBER OF SPANNING
- Page 100 and 101: CHAPTER 5.98THE NUMBER OF SPANNING
- Page 102 and 103: CHAPTER 5.100THE NUMBER OF SPANNING
- Page 104 and 105: CHAPTER 5.102THE NUMBER OF SPANNING
- Page 106 and 107: CHAPTER 5.104THE NUMBER OF SPANNING
- Page 108 and 109: CHAPTER 5.106THE NUMBER OF SPANNING
- Page 110 and 111: CHAPTER 6.108COUNTING THE NUMBER OF
- Page 112 and 113: CHAPTER 6.110COUNTING THE NUMBER OF
- Page 114 and 115: CHAPTER 6.112COUNTING THE NUMBER OF
- Page 116 and 117: CHAPTER 6.114COUNTING THE NUMBER OF
- Page 118 and 119: 116 CHAPTER 7. MAXIMAL PLANAR MAPSF
- Page 120 and 121: 118 CHAPTER 7. MAXIMAL PLANAR MAPSF
- Page 122 and 123: 120 CHAPTER 7. MAXIMAL PLANAR MAPSR
- Page 124 and 125: 122 CHAPTER 7. MAXIMAL PLANAR MAPSP
- Page 126 and 127: 124 CHAPTER 7. MAXIMAL PLANAR MAPS7
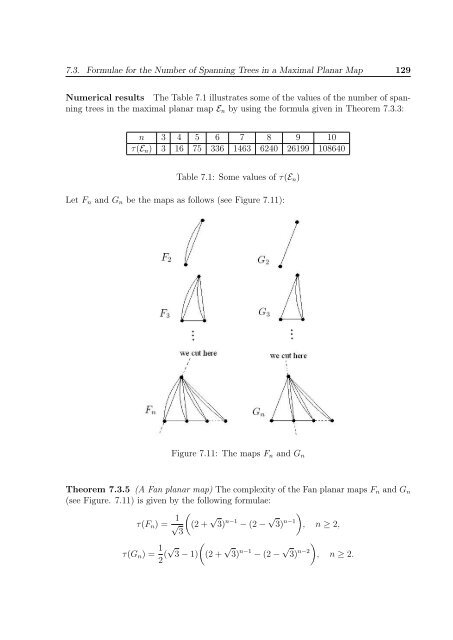
- Page 128 and 129: 126 CHAPTER 7. MAXIMAL PLANAR MAPSa
- Page 132 and 133: 130 CHAPTER 7. MAXIMAL PLANAR MAPSP
- Page 134 and 135: 132 CHAPTER 7. MAXIMAL PLANAR MAPSF
- Page 136 and 137: 134 CHAPTER 7. MAXIMAL PLANAR MAPSI
- Page 138 and 139: 136 BIBLIOGRAPHY[13] N. Biggs, E. L
- Page 140 and 141: 138 BIBLIOGRAPHY[46] P. Erdös, and
- Page 142 and 143: 140 BIBLIOGRAPHY[77] D. Lotfi, M. E
- Page 144 and 145: 142 BIBLIOGRAPHY[107] R. Shrock and
- Page 146 and 147: Auteur :Titre :Directeurs de thèse