enumeration of the number of spanning trees in some ... - Toubkal
enumeration of the number of spanning trees in some ... - Toubkal
enumeration of the number of spanning trees in some ... - Toubkal
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
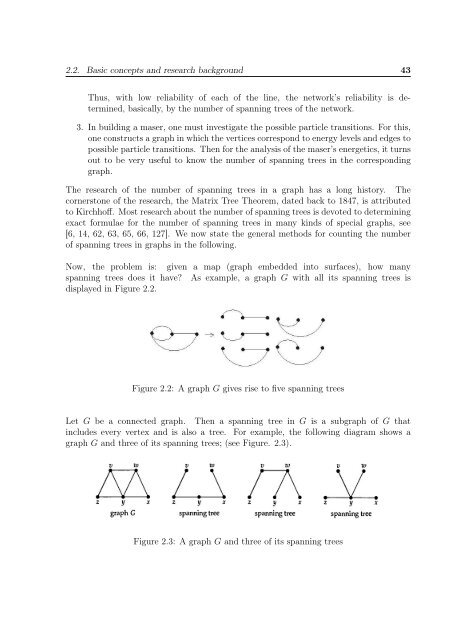
2.2. Basic concepts and research background 43Thus, with low reliability <strong>of</strong> each <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> l<strong>in</strong>e, <strong>the</strong> network’s reliability is determ<strong>in</strong>ed,basically, by <strong>the</strong> <strong>number</strong> <strong>of</strong> <strong>spann<strong>in</strong>g</strong> <strong>trees</strong> <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> network.3. In build<strong>in</strong>g a maser, one must <strong>in</strong>vestigate <strong>the</strong> possible particle transitions. For this,one constructs a graph <strong>in</strong> which <strong>the</strong> vertices correspond to energy levels and edges topossible particle transitions. Then for <strong>the</strong> analysis <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> maser’s energetics, it turnsout to be very useful to know <strong>the</strong> <strong>number</strong> <strong>of</strong> <strong>spann<strong>in</strong>g</strong> <strong>trees</strong> <strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong> correspond<strong>in</strong>ggraph.The research <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> <strong>number</strong> <strong>of</strong> <strong>spann<strong>in</strong>g</strong> <strong>trees</strong> <strong>in</strong> a graph has a long history. Thecornerstone <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> research, <strong>the</strong> Matrix Tree Theorem, dated back to 1847, is attributedto Kirchh<strong>of</strong>f. Most research about <strong>the</strong> <strong>number</strong> <strong>of</strong> <strong>spann<strong>in</strong>g</strong> <strong>trees</strong> is devoted to determ<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>gexact formulae for <strong>the</strong> <strong>number</strong> <strong>of</strong> <strong>spann<strong>in</strong>g</strong> <strong>trees</strong> <strong>in</strong> many k<strong>in</strong>ds <strong>of</strong> special graphs, see[6, 14, 62, 63, 65, 66, 127]. We now state <strong>the</strong> general methods for count<strong>in</strong>g <strong>the</strong> <strong>number</strong><strong>of</strong> <strong>spann<strong>in</strong>g</strong> <strong>trees</strong> <strong>in</strong> graphs <strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong> follow<strong>in</strong>g.Now, <strong>the</strong> problem is: given a map (graph embedded <strong>in</strong>to surfaces), how many<strong>spann<strong>in</strong>g</strong> <strong>trees</strong> does it have? As example, a graph G with all its <strong>spann<strong>in</strong>g</strong> <strong>trees</strong> isdisplayed <strong>in</strong> Figure 2.2.Figure 2.2: A graph G gives rise to five <strong>spann<strong>in</strong>g</strong> <strong>trees</strong>Let G be a connected graph. Then a <strong>spann<strong>in</strong>g</strong> tree <strong>in</strong> G is a subgraph <strong>of</strong> G that<strong>in</strong>cludes every vertex and is also a tree. For example, <strong>the</strong> follow<strong>in</strong>g diagram shows agraph G and three <strong>of</strong> its <strong>spann<strong>in</strong>g</strong> <strong>trees</strong>; (see Figure. 2.3).Figure 2.3: A graph G and three <strong>of</strong> its <strong>spann<strong>in</strong>g</strong> <strong>trees</strong>